Abnormal Gait
What is an Abnormal Gait?
An abnormal gait is a noticeable change in our normal walking pattern. Every person has their natural walking style which is unique in individual. Although, some injuries and medical conditions can cause some changes in our natural walking pattern. Anything which can affect our brain, spinal cord, legs, or feet can change our gait pattern.
Here are some very common examples of an abnormal gait which include:
- Limping.
- Dragging your toes.
- Shuffling your feet.
- Short steps.
- Difficulty in supporting the weight of own body.
- Difficulty with coordination.
Types of abnormal gait
Trendelenburg gait
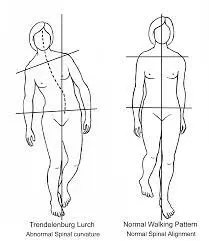
Trendelenburg gait can appear when the way you walk normally is affected by some weakness in your hip muscles. If your glutes are too weak to carry your body weight as you walk then you will walk with a visible side-to-side movement. It may look like you are limping or missing a step during the walk.
What can cause this condition?
- nerve damage or dysfunction
- Osteoarthritis
- Poliomyelitis
- Muscular dystrophy
Treatment
physical therapy is very helpful for restoring some control over your walking and making the side-to-side movement less visible.
The therapist will use his hands to move the patient’s legs in different directions. This can help your joints become more habitual to moving in certain directions and help in increasing your muscle strength and resistance.
Some Other exercises that can help in strengthening your hip abductor muscles include:
- lying on one side and extending the leg straight outward
- lying on the floor and moving one leg upward, over the other, and then backward in the opposite direction.
- stepping sideways and up on an elevated surface, then back down again
- lifting your knee with your lower leg bent, then extending the lower leg outside, and swinging the extended leg back so that your body can lean forward
You should only do these exercises under your physiotherapist’s observation, the physiotherapist can advise you on how to exercise with proper precautions and reduce your risk for additional complications or injuries
Biofeedback
By training so that you can take conscious control of muscle action, biofeedback may help you increase the range of motion in your joints while you’re walking.
Antalgic gait
In an antalgic gait, a person tries to avoid some leg movements to lessen their pain. Typically in that:
the person is not able to bear their full body weight on an affected leg also the normal range of his leg is affected.
During the walk Stance phase period is shortened to reduce pain in the affected leg.
Result in Limping with slow and short steps.
Antalgic gait may result from a number of underlying reasons. Causes typically fit into one of these broad categories:
- traumas
- deformities
- inflammatory conditions
- vascular conditions
- cancers or tumors
Treatment
When the actual reason for pain is being identified and labeled, gait training may help you to normalize you are walking much as possible.
Physiotherapy treatment techniques may include:
Cane, crutches, or a walker. Especially in cases of trauma, these devices are very helpful in taking the weight off the painful area to faster the healing process.
Rest is needed. If any alteration in gait is caused by the ligament sprain or muscle injury, rest is advised often combined with the application of heat or cold which can help the soft tissue healing process.
Low-impact exercises such as Hydrotherapy and biking are advised for strength, endurance, and balance training that can affect gait.
Propulsive gait

This type of gait is commonly seen in people who are suffering from Parkinsonism
Here are some Characteristics of a propulsive gait include a
stooping,
rigid posture
head and neck forward bending
A person’s footsteps usually become short and fast to maintain their center of gravity. which is also described as festinating gait.
Treatment
- Always try to Encourage the person to be as independent as possible.
- Allow enough time for a person’s daily activities, especially during walking. People with this problem are still a risk of falling because they do not have proper balance and are always rushing to catch up.
- make sure the patient walks with walking assistance for safety reasons, specifically on uneven surfaces.
- Consult a physical therapist for exercise therapy and walking retraining.
- To prevent deformation, reposition the body or use a splint to correct the aberrant posture.
- stretching the tight muscles can help to lessen stiffness
- Finding the right balance for each person is crucial since strengthening activities may assist to reduce the effects of disuse weakness, but there is also concern that excessive or inappropriate exercise may speed the advancement of the disease.
Shuffling gait
In Shuffling, a gait person is walking without lifting their feet completely off the ground. So that It results in their feet dragging. The person may shuffle their legs if they feel unbalanced while walking or have an injury that prevents them from lifting their feet off the ground when they walk.
Treatment
Strengthening exercises
Stretching or range of motion exercises
Balance activities
Proprioceptive training which includes orienting your body within the environment
Joint mobilization techniques
Gait training including the use of parallel bars
Prescription of assistive devices like a walker or cane
Spastic gait
A spastic gait pushes the person to walk with only one stiff leg. When a person lifts that leg to walk, they either drag or swing in a semicircular motion (circumduction). This type of gait is commonly seen in people who are diagnosed with cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, or hemiplegia.
Treatment
Exercises are encouraged to do regularly.
Leg braces and in-shoe splints are very helpful with keeping the foot in the right position while standing and walking. A physical therapist can also help you by providing these assistive devices and exercise therapy if needed.
A cane or a walker is necessary for those who have issues with balance.
Waddling gait
A patient with a waddling gait, a type of gait anomaly, strolls around like a duck.
When one walks, they are said to be “walking like a duck,” with the forward-moving leg’s forward-moving pelvis going outward and the backward-moving pelvis of the forward-moving leg moving inward.
Weakness of the gluteus muscles, which results from the weakening of the proximal muscles of the pelvic girdle, is the source of the waddling gait anomaly.
To get over this weakness, the patient drags their lower leg forward while moving their upper body forward.
Injuries to the pelvic musculature, such as falls or car accidents, may be to blame for the weak pelvic muscles that result in a waddling gait.
Treatment
Exercises for training the gait are also recommended to restore it to normal. The pelvic muscles will be strengthened by the exercises.
Yoga poses that target the waddling gait can help to strengthen the pelvic muscles. A. Building programs:- Hip joint active range of motion: the movement includes hip flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and rotation.
Muscle weakness can cause a range of abnormalities and primarily affect the muscles that control gait.
The Gluteus maximus and hamstrings for hip extension, quadriceps for knee extension, soleus and gastrocnemius for ankle plantar flexion, and dorsiflexion to stride forward are the muscles that need to be strong while walking.
What are the complications of gait abnormalities?
The complications of gait abnormalities could include:
- Increasing the chances of falls or injuries.
- Muscle weakness.
- Sudden inability to walk.
- Pain.
- Reduce the inability to maintain independence
Physiotherapy treatment almost always helps patients who have short-term or long-term gait abnormalities. Therapy will help in lowering the risk of falls and some other injuries.
Abnormal Gait Videos:
Summary
One way to return to a normal gait if one is having an abnormal gait is to seek professional assistance from a physiotherapist. Physiotherapy can help you regain mobility, lessen pain, and improve general physical function by determining the root cause of the abnormal gait and creating a customized treatment plan. This will allow you to resume your normal activities and live a higher quality of life.
FAQ
What is an assessment for abnormal gait?
It usually involved observing a person walk came and go from the observer, also observing the length of the stride, hand movement, heel placement, and pelvis angle. some Other factors which are frequently evaluated are the evenness of the stride and balance.



7 Comments