Anconeus Muscle
What is Anconeus?
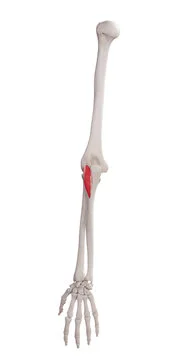
The anconeus is a tiny, triangular arm muscle. It runs from the distal humerus to the proximal ulna and is found on the back of the elbow.
The anconeus muscle, along with the brachioradialis, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, and extensor carpi ulnaris muscles, is part of the superficial flexor compartment.
The anconeus muscle aids in wrist extension and supports the dorsal capsule of the humeroulnar joint as well as the ulna itself.
Origin of Anconeus Muscle
The anconeus muscle is a tiny, triangular muscle that is found at the elbow. It begins on the posterior side of the humerus’s lateral epicondyle.
Insertion
The anconeus enters the olecranon of the ulna and runs along the proximal third of the ulna’s posterior face.
Innervation
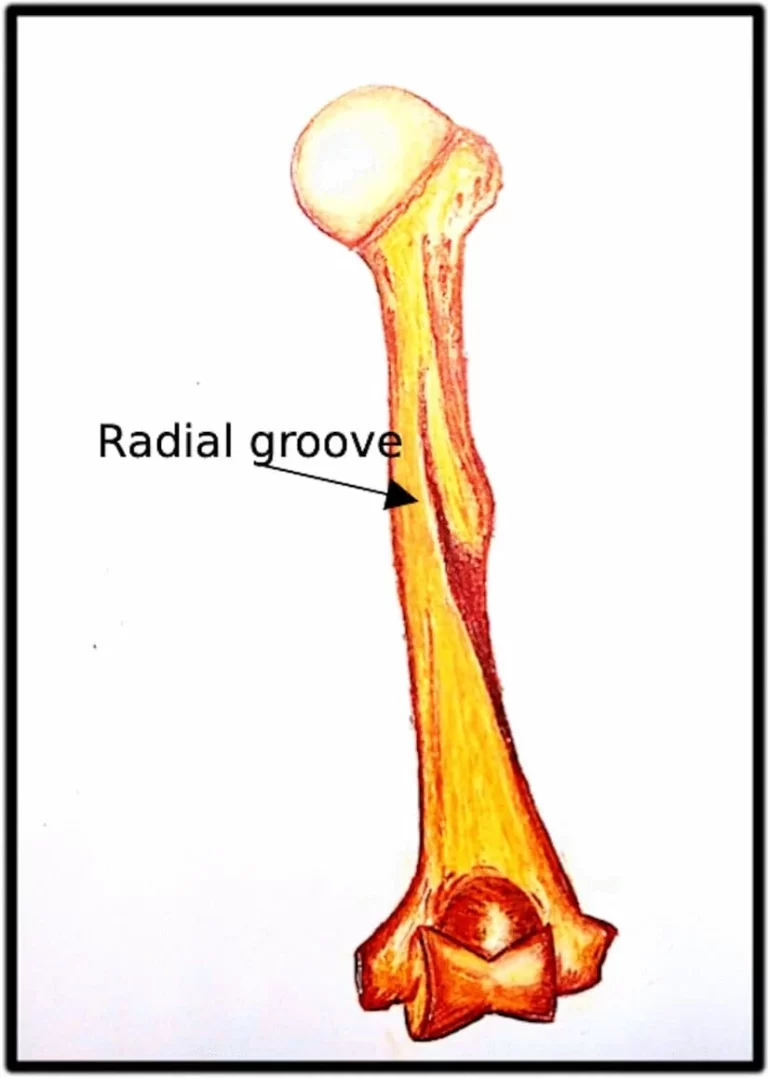
The nerve to the anconeus is a branch of the radial nerve (cervical roots 7 and 8) from the posterior chord of the brachial plexus that innervates the anconeus. The somatomotor branch of the radial nerve that innervates the anconeus splits from the main branch in the radial cleft of the humerus. This innervation pattern is similar to the radial nerve’s innervation of the musculature of the posterior wrist (extensor) compartment.
Function of Anconeus Muscle
The anconeus muscle is a continuation of the triceps brachii muscle, performing the same motion at the elbow. As a result, its contraction causes the wrist to extend.
Because of its long attachment to the ulna, it is thought that the anconeus has the additional role of abducting the ulna, particularly during forearm pronation. This function is highly important for stabilizing the ulna and helps create a rotatory movement of the forearm during activities like screwdriver use.
Furthermore, the anconeus tenses the humeroulnar joint’s dorsal joint capsule, avoiding damage during forearm hyperextension.
Blood supply
The profunda brachii artery supplies the anconeus with blood via the middle collateral artery.
Clinical significance
A shoulder dislocation, fractures of the upper portion of the humerus or around the olecranon, or any injury that damages the radial nerve can all result in anconeus muscle nerve supply damage. The anconeus muscle, as well as other extensors of the elbow and wrist, can be paralyzed if the radial nerve is damaged by these processes. There are no specific acquired injuries that affect the anconeus muscle exclusively; however, any disease that compromises muscular functions, especially arm extension (i.e. muscular dystrophy), will affect this specific accessory muscle.
Heterotopic ossification is an abnormal development of osseous tissue in non-osseous tissue that can be caused by trauma. (eg. muscle tissue). The condition is typically found in the hips, though there have been documented instances of it occurring in the arms and legs. The exact origin of the process is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by surgery or trauma.
Assessment
Assessment of sensory changes in the ulnar nerve distribution (of the fourth digit and the entirety of the fifth), pain, atrophy of the intrinsic muscles of the hand innervated by the ulnar nerve, and a neural provocation test of the ulnar nerve are all components of accurate diagnosis of cubital tunnel syndrome, which may be caused by hypertrophy of anconeus muscle. The tests that establish a connection between ulnar neuropathy and the elbow are used to confirm the diagnosis of cubital tunnel syndrome. To confirm the syndrome, these tests should produce provocative signs, such as symptoms reproducing with elbow flexion, a positive Tinels sign tested at the elbow, or a sign of instability, such as snapping of the ulnar nerve over the medial epicondyle with elbow flexion.
Anconeus stretching
Anconeus stretch drills
Put one arm after your head with the hand of that arm roughly relaxing on your upper trapezius muscle.
Put your further hand on the elbow of the arm that’s after your head.
Drag your elbow downwards until you sense a nice triceps and anconeus stretch. Maintain it for 10-30 seconds (create up to the maximum of 30 seconds) and then recount with the further arm.
Anconeus strengthening
Anconeus Sidekick
Kneel on the floor in front of a bench to perform the Anconeus Sidekick. With the forearm hanging off the opposite side, place the upper arm on top of and above the bench. Extend the arm at the elbow with a dumbbell in your hand so that the wrist is aligned with the elbow and the shoulder. The dumbbell should be slowly lowered back toward the floor. Switch arms after performing this motion three times for 10 to 15 repetitions.
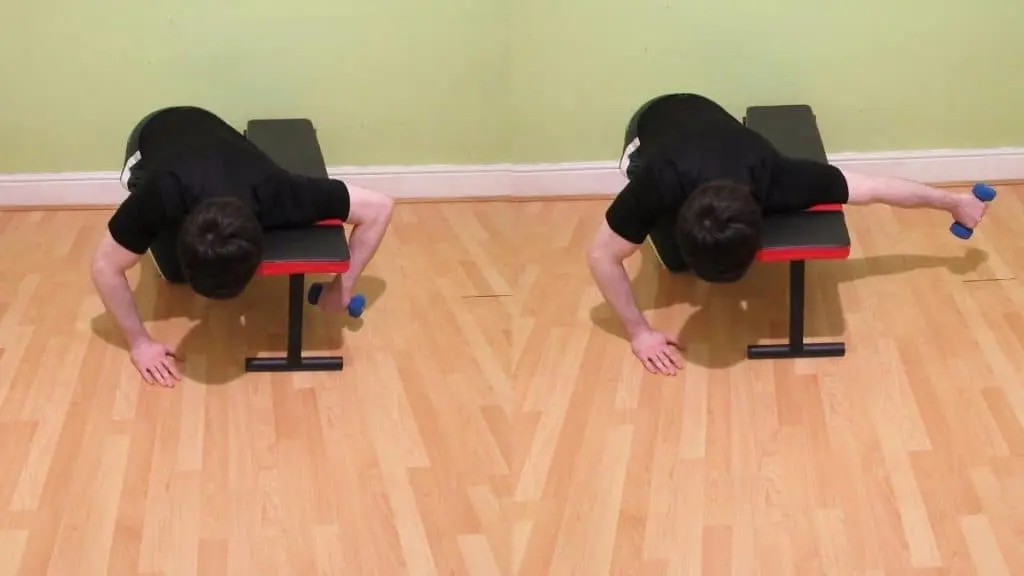

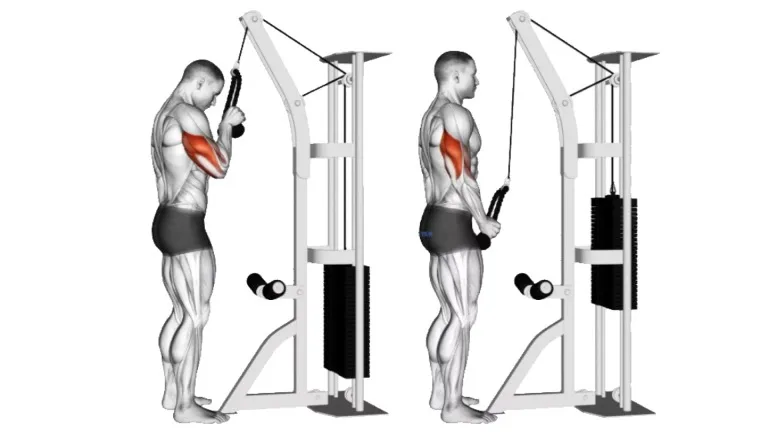
Single-arm triceps pull down
This is a home exercise for strengthening the triceps unilaterally. Anchor a band above your head to a stable object as a starting point. While using the other hand to stabilize your body, grasp the band with one hand. Maintain a stationary elbow close to your body. At a tempo of two seconds, extend the elbows and pull the band down. Lift your hands by bowing your elbows at a 2-second rhythm to finish a reiteration.
Banded triceps pull down
This is a triceps strengthening exercise you can do at home. Anchor a band above your head to a stable object as a starting point. While keeping your elbows stationary next to your body, grasp the band with both hands. At a tempo of two seconds, extend the elbows and pull the band down. To finish a repetition, bend your elbows and raise your hands at a rate of two seconds.

Overhead triceps push down
This is a triceps strengthening exercise that can be done with a cable pulley, pullup assist band, or strength band. Begin by mooring a band above behind you and holding it with two hands. While maintaining a split squat position, raise your elbows so that your humerus, or upper arm, is parallel to the ground. To contract the triceps while keeping your elbows stationary, extend your elbows for two seconds. To finish a repetition, bend your elbow for two seconds without moving your elbows up or down.
Banded overhead triceps extension
The banded overhead triceps extension is a home strengthening exercise that makes use of a pullup assist band or strength band. Holding one end of the band behind your back will get you started. Hold the opposite end your other hand beginning behind your head. To strengthen your triceps, extend your upper arm’s elbow.

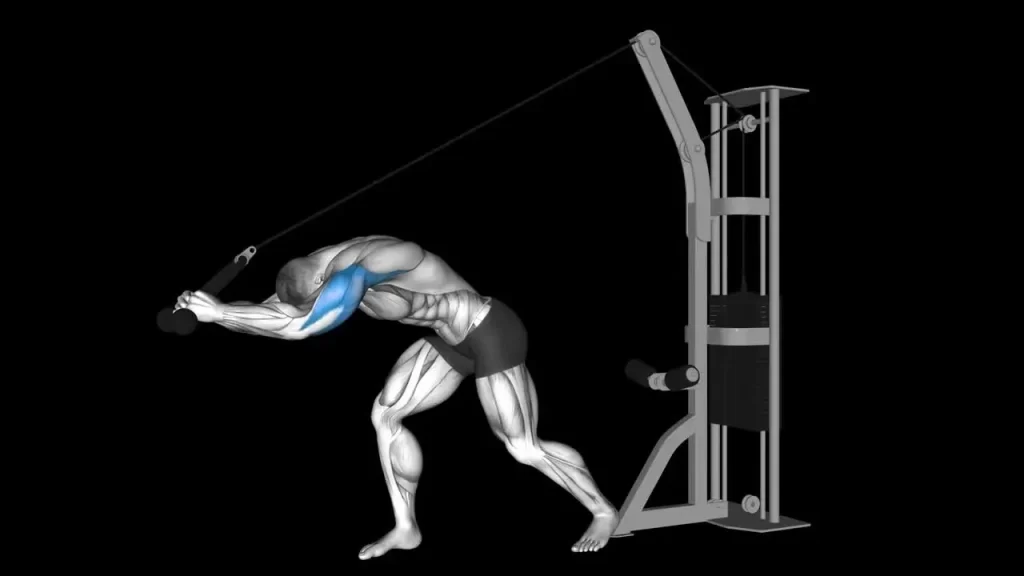
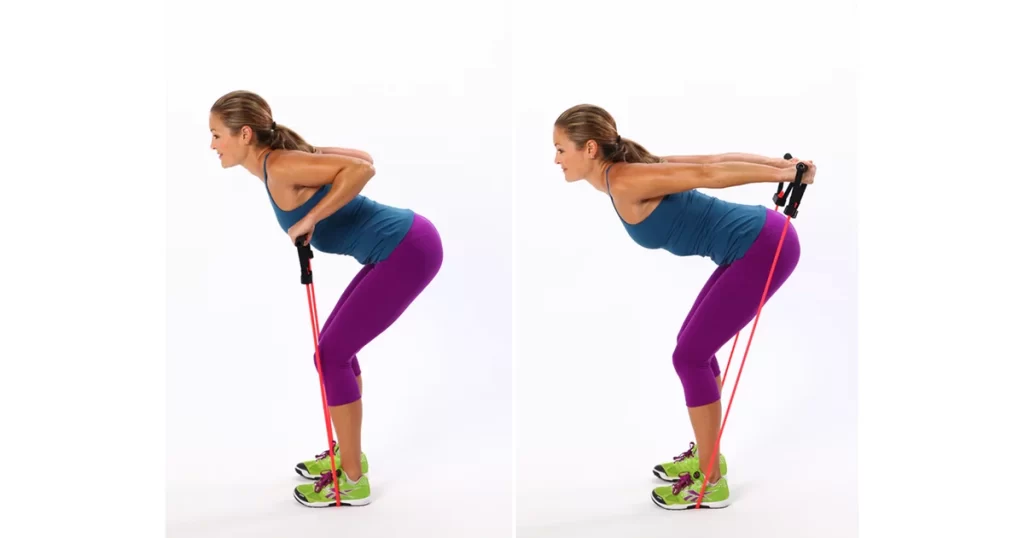
Banded triceps kickback
Triceps strengthening exercises at home include the banded triceps kickback. Anchor a band to a stable object in front of you to get started. While keeping your elbows stationary next to your body, grasp the band with one hand. In a semi-split squat stance, bend forward to lower your torso so that it is parallel to the ground. At a tempo of two seconds, extend the elbow and pull the band. To finish a repetition, revert to your starting position by bending your elbow at a tempo of two seconds.

FAQ
Why is the anconeus muscle important?
The anconeus muscle aids the augmentation of the lower arm and offers help for both the dorsal case of the humeroulnar joint and the actual ulna.
Is anconeus a forearm muscle?
The triangular-shaped anconeus muscle is small in the forearm. It’s occasionally mixed with rear arm muscles brachii or extensor carpi ulnaris.
Why does my anconeus muscle hurt?
The development of anconeus syndrome has been linked to stretch or impact injuries to the anconeus muscle that occur while playing tennis or when the muscle is overused by doing too much digging and shaking hands. Additionally, the anconeus muscle may develop myofascial pain as a result of repeated microtrauma.
How do you massage anconeus?
You only need your hand to release the Anconeus on your own. As shown in the previous video, locate the trigger point on the elbow. Apply pressure to the area by placing your fingers over it. Hold for about 30 seconds before releasing.
What is the antagonist of the anconeus?
The anconeus: Two relationships that are agonistic (brachialis and triceps) and antagonistic (biceps and brachioradialis).


2 Comments