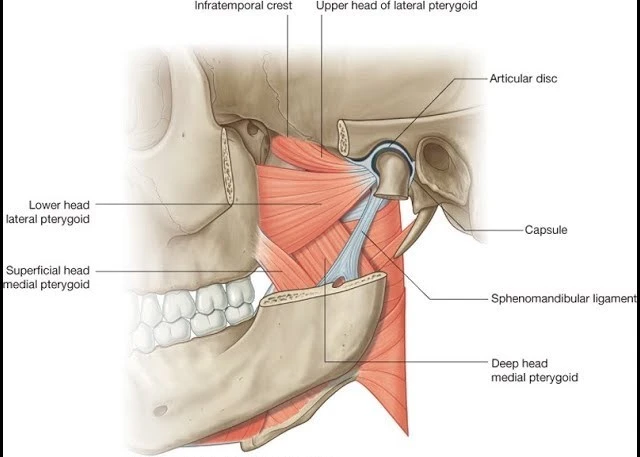
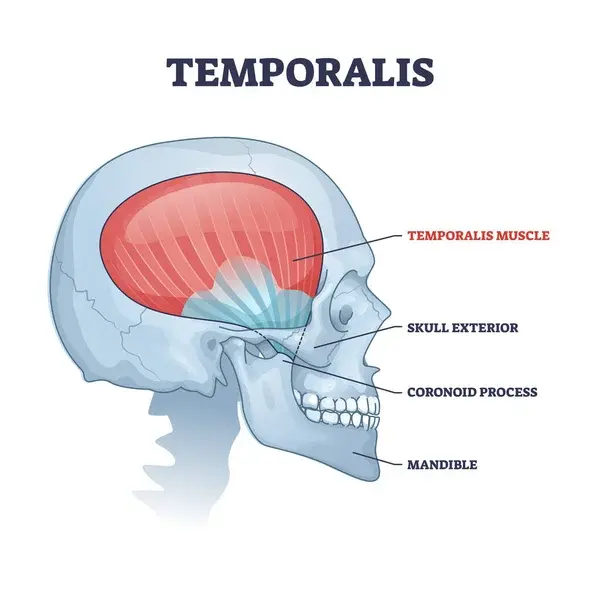
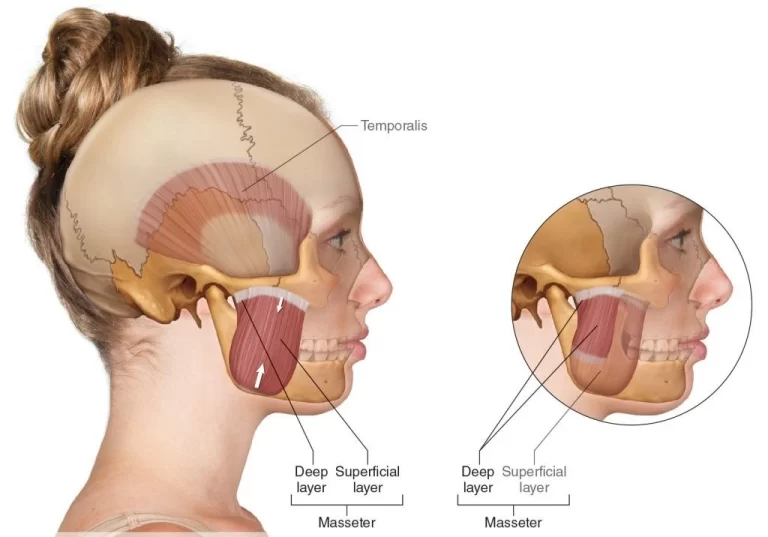
Lateral Pterygoid muscle
Introduction The lateral pterygoid muscle is a craniomandibular muscle that plays an essential role in the inferior temporal region. It is active during mastication and mandibular motions – including protrusion (forward movement of the mandible), abduction (depression of the mandible), and mediotrusion (mandibular condyle movement towards the midline). It functions particularly during speaking, singing, and…