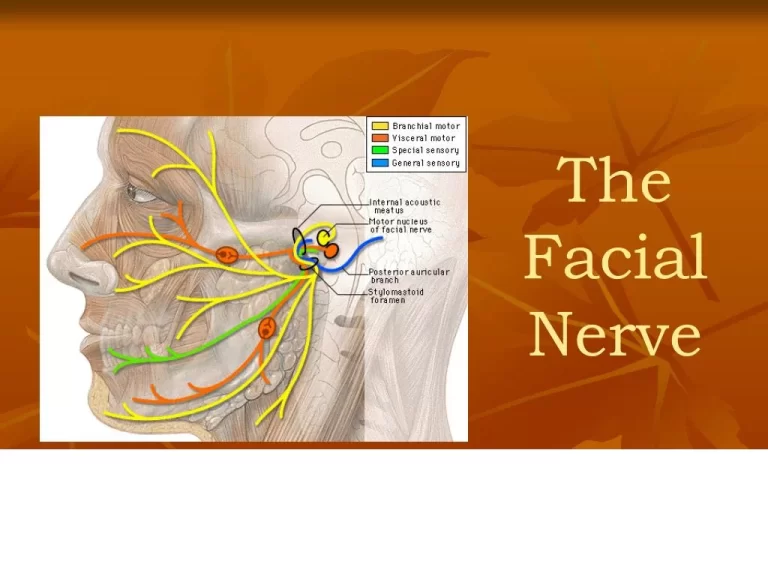
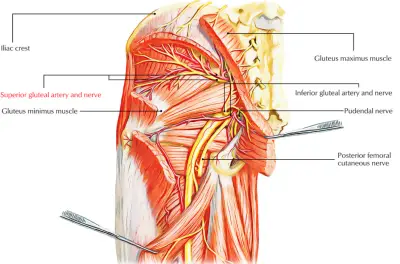
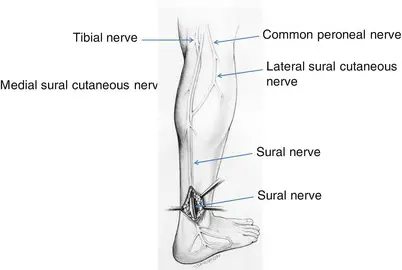
OCULOMOTOR NERVE
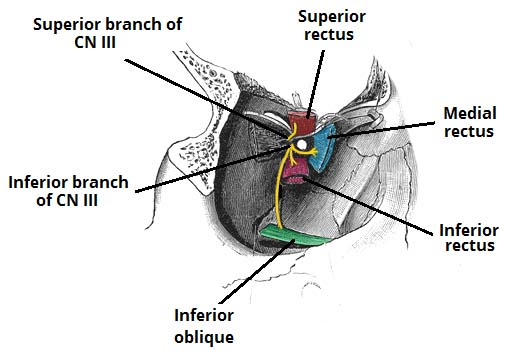
INTRODUCTION : The oculomotor nerve is the third cranial nerve (CN III). It enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure and innervates extrinsic eye muscles that enable most movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation…