Pelvic Floor Muscles
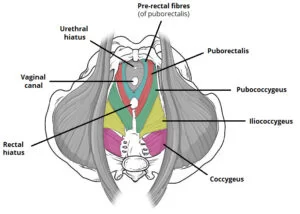
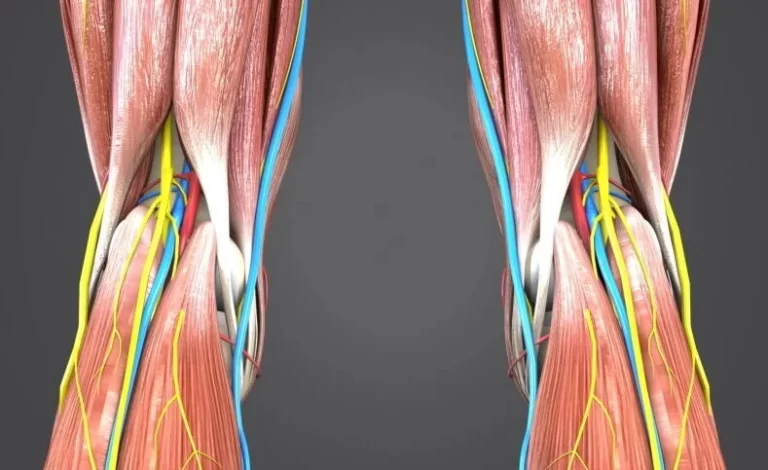
What is a Pelvic Floor Muscles? The pelvic floor muscles are a crucial group of muscles located at the base of the pelvis, forming a supportive hammock-like structure that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. Comprising layers of muscle fibers, ligaments, and connective tissues, the pelvic floor provides essential support for the pelvic…