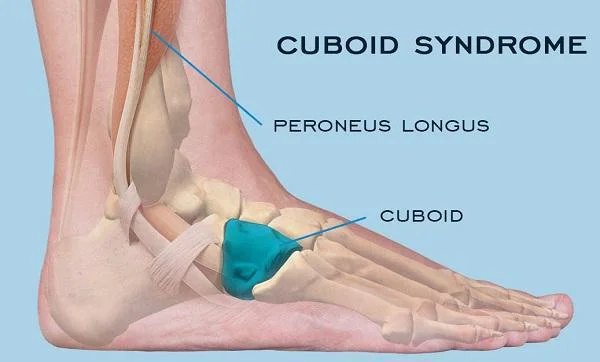
Cuboid syndrome
What is a cuboid syndrome?
Cuboid syndrome is an injury in which the joint and ligaments near the cuboid bone in your foot become injured or torn with cuboid subluxation.
The Cuboid syndrome has misdiagnosed the source of lateral midfoot pain. cuboid syndrome is also called cuboid subluxation. cuboid syndrome is a condition that is an injury to the calcaneocuboid joint and ligaments.
This condition is in the form of little finger-side foot pain and sometimes normal foot weakness. in cuboid syndrome cuboid bone moves down and over alignment with the other bone in the joint the calcaneus joint. cuboid syndrome slightly happens after a sudden injury and overuse of the foot joint.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
The cuboid is a pyramid-shaped, short bone on the lateral side of the foot. It articulates anteriorly with the 4th and 5th metatarsal bases, medially with the lateral cuneiform and navicular, and posteriorly with the calcaneus. The cuboid rotates to 25° during inversion and eversion about an axis that passes from posteroinferior to anterosuperior with respect to the ground. In addition to inversion and eversion, there is some evidence that posterior-anterior distraction of the coracoclavicular joint also occurs during the gait cycle.
The coracoclavicular joint is intrinsically stable due to the congruence of its articular surfaces and reinforcement from ligaments and tendon attachments. The dorsal and plantar cuboid navicular and cuboideometatarsal ligaments and wedge-shaped fibro adipose labra within the coracoclavicular joint and cuboid-metatarsal joints contribute to stability. The peroneus longus tendon, which forms a sling around the lateral and plantar aspects of the cuboid. The cuboid is a pulley for the peroneus longus tendon muscle contraction from midstance through the late propulsive phase exerts an eversion torque on the cuboid. Eversion of the cuboid via the peroneus longus tendon is thought to facilitate load transfer across the forefoot from lateral to medial as the stance progresses.
Symptoms of cuboid syndrome:
The following symptoms of the cuboid syndrome
- Pain on the lateral of the foot
- Pain gets worse with weight bearing
- Dull and aching pain
- Sharp and acute pain
- Difficulty walking
- Hopping is very difficult
- Possible swelling
- Pain can be worse when healing is raised and the heels down
- Reduce the range of motion of the foot
- Reduce the range of motion of the ankle
- sensitivity on the bottom of the foot
- Referred pain to the outside of the ankle
- Redness near the area of injury
- Loss of mobility in your ankle or lateral side of the foot
- Weakness of your fingers or legs on the lateral side of the foot
- Tenderness of the lateral side of your leg
- Edema near the dislocated ligaments or the ankle due to fluid buildup
Mechanism of injury:
There are two mechanisms of injury:
- Planter flexion and inversion injuries
- Overuse syndrome
Planter flexion and inversion injuries:
During plantar flexion and inversion, there is a strong reflex contraction of the peroneus longus muscle.
Overuse syndrome:
Overuse syndrome is uncommonly and rarely seen but it is subluxation of the cuboid occurs secondary to repeated microtome and vigorous activities.
Causes of cuboid syndrom:
causes of a cuboid syndrome may like that
- Overuse
- Sprained ankle
- Pronated feet
- Other activity
Differntial diagnosis:
- Fracture
- Calcaneonavicular coalition
- Extensor digitorum brevis tendinopathy
- Plantar fasciitis
- Sinus tarsi syndrome
- Meniscoid of the ankle
- Gout
- Tarsitis
- Lisfranc injury
- Compression neuropathy of the sural nerve
- Lateral plantar nerve entrapment
- Anterolateral ankle impingement
How do you treat cuboid syndrome?
- Exercises
- Manipulation
- Taping
- Ice therapy
- Rest
- Orthotics
- Cuboid wedge
Physiotherapy treatment of cuboid syndrome:
Physiotherapy treatment is the most common treatment for cuboid syndrome. In cuboid syndrome physiotherapy treatment help to increase the range of motion ad strengthen the muscle.
Physiotherapy treatment sessions require regular attendance for the best and pure result. patient’s physiotherapist can show your exercises to do at home. A physiotherapist can also provide hands-on therapy to improve mobility.
Exercise to relieve foot pain:
- Toe raise, point, and curl
- Big-toe stretch
- Toe splay
- Toe extension
- Toe curls
- Marble pickup
- Tennis ball roll
- Achilles stretch
- Sand walking
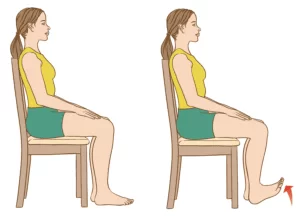
Toe raise, point, and curl:
In the tor raise, point, and curl patient can sit in the straight back chair and foot flat on the floor. keep the dorsi flexion and plantar flexion two times more than the toe curl. Hold 5 seconds. repeat 10 times on the day.
Big toe stretch:
In the big toe stretch patient can sit in a straight back chair with and foot flat on the floor. Bring the left foot to rest on the right thigh. Using the fingers, gently stretch the big toe flexion, extension, and sidewards Keep the big toe in each position for 5 seconds. Repeat this 10 times.
Toe splay
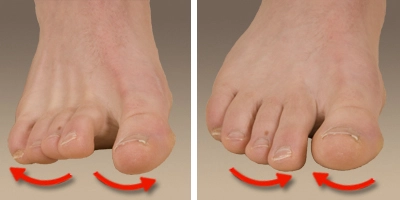
In the toe, the splay patient can sit in a straight back chair with and foot flat on the floor. spread the toes distance as far as possible without straining. hold 5 seconds. repeat 10 times this position.
Toe curls:
In the toe curls patient can sit in a straight back chair and foot on the floor. Lay a small cotton towel on the floor in front of the body, with the short side facing the feet. Place the fingers of the legs of one foot on the short side of the cotton towel. Try to grasp the cotton towel between the toes and pull it toward yourself. Repeat this exercise five times before switching to the other foot.

Marble pickup:
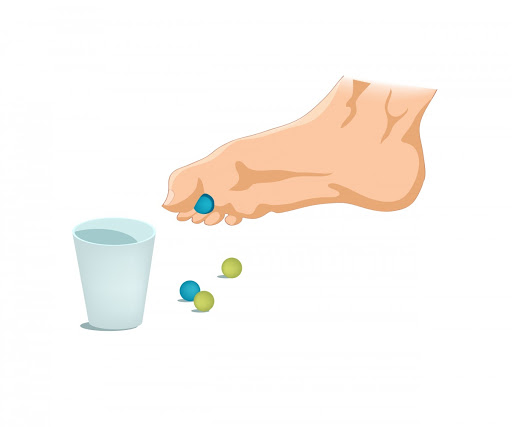
Marble pickup patients can sit in a straight back chair and foot on the floor. Place a bowl and a bowl of 20 marbles on the floor in front of the feet. Using only the fingers of the legs of one foot, pick up each marble and place it in the empty bowl. Repeat this exercise using the other foot.
Sand walking:

Head to a beach, a desert, or any other location with sand. Remove the shoes and socks. Walk for as long as possible. Try increasing the distance slowly over time to avoid overexerting the muscles in the feet.
RICE Method :
Rest your foot.
Ice your foot with cold packs for 20 minutes at a time.
Compress your foot with cold packs for 20 minutes at a time.
Elevate your foot above your heart to reduce swelling.
Cuboid whip:
- Your doctor will ask you to lie flat on your stomach.
- They’ll grip the front, or dorsum, of your foot and put their thumbs on the bottom of your foot near your heel.
- They’ll flex your knee slightly and move your leg upward toward you. Your doctor may ask you to relax your leg at this point.
- They’ll then “whip” your foot downward and push on your foot with their thumbs to “pop” the joint back into place.
Cuboid squeeze:
- Your doctor will put their thumb under your foot near where your cuboid bone is located
- They’ll grip your toes and push them down toward the bottom of your foot
- They’ll then push on the area where your cuboid bone is for about 3 seconds while pushing your toes down.
- Finally, they’ll repeat this process several times until you have full movement back in your foot.
Medication:
- prescribe medication to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Botox is sometimes injected into muscles to reduce tension and spasms.
Surgery:
Surgery may help to lengthen muscles or repair ligaments, tendons, or bones damaged in an accident.
Summary:
Cuboid syndrome is a misdiagnosed source of lateral midfoot pain. cuboid syndrome is also known as cuboid subluxation. cuboid syndrome is a condition that is an injury to the calcaneocuboid joint and ligaments.
This condition is in the form of little toe-side foot pain and sometimes general foot weakness. in cuboid syndrome cuboid bone moves down and out of alignment with the other bone in the joint the calcaneus joint. cuboid syndrome slightly happens after a sudden injury and overuse of the foot joint.
Cuboid syndrome is not a serious condition and cuboid syndrome can easily be treated at home by a doctor and by a physiotherapist.
FAQ:
What does cuboid syndrome feel like?
The cuboid syndrome causes sharp pain on the other side and possibly the underside of the foot. The pain does not usually spread to the rest of the foot or leg.
How do you treat cuboid syndrome at home?
Home remedies involve, resting, icing, and elevating the foot If the pain perseveres, then it may be time to seek help from a medical professional
Does cuboid syndrome cause ankle pain?
Common symptoms of cuboid syndrome are pain outside of the foot which can be felt in the ankle and toes.
Does cuboid syndrome come on suddenly?
Cuboid syndrome is a common cause of outside foot pain. This condition may happen suddenly due to ankle pain.
How long does it take for the cuboid bone to heal?
it takes six weeks for a cuboid fracture to heal a walker boot and another six weeks of rehabilitation with physiotherapy for complete recovery from a cuboid fracture.
Can cuboid cause nerve pain?
Cuboid syndrome occurs when the nerve becomes compressed. the pain that accompanies this condition is felt on the outside of the foot.

3 Comments