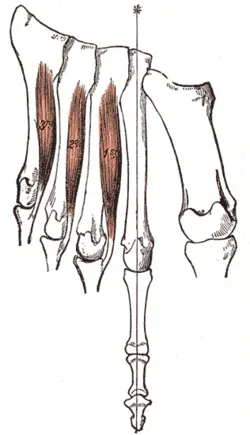
Extensor Digitorum Muscle
What is the Extensor digitorum muscle?
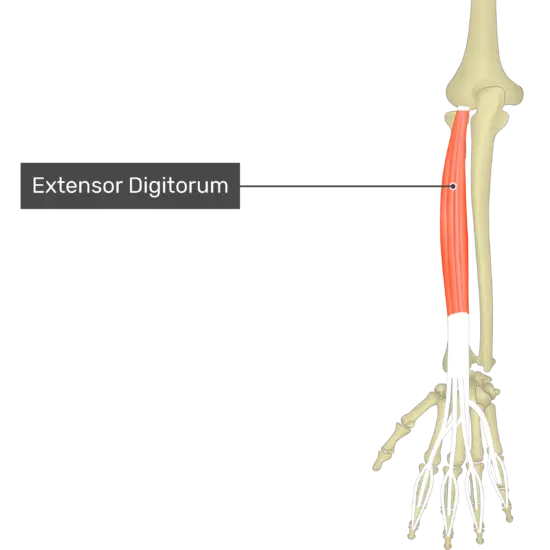
The extensor digitorum is a long muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm. It is one of the lower arm’s shallow extensors, alongside the brachioradialis, extensor carpi radialis longus, brevis, extensor carpi ulnaris, and extensor digiti minimi.
These muscles are easily felt in the lateral aspect of the posterior forearm when they are contracted. Particularly so when the hand is extended.
The extensor digitorum runs from the humeral lateral epicondyle to the medial four phalanges of the hand. As a result, the pull required to flex the four medial fingers at their metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints is produced. Additionally, wrist extension involves the extensor digitorum.
Origin of Extensor Digitorum Muscle
The common extensor tendon is situated in the humeral lateral epicondyle.
Insertion
inserts into the medial four digits extensor expansion.
Relations
The extensor digitorum is the muscle of the posterior forearm that is located closest to the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis longus. The posterior interosseous artery and nerve pass through a tunnel that is enclosed by these three muscles.
The extensor digitorum is located in the forearm, lateral to the extensor digiti minimi and extensor carpi ulnaris muscles, and medially to the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle.
Its tendons are located between the tendons of the extensor pollicis longus on its lateral side and the extensor digiti minimi on its medial side, deep into the extensor retinaculum. Along with the extensor indicis, the tendons of the extensor digitorum reside in the fourth extensor (dorsal) compartment. The extensor digitorum tendons run superficially from the dorsal interossei muscles in the dorsum of the hand.
Innervation
The posterior interosseous nerve, which is a continuation of a deep radial nerve branch (root values C7 and C8), innervates the extensor digitorum.
Blood supply
The branches of three distinct arteries vascularize the extensor digitorum;
- posterior interosseous artery
- radial recurrent artery
- anterior interosseous artery
The common interosseous artery branches from the ulnar artery into the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries. A branch of the radial artery is the radial recurrent artery.
Function of Extensor Digitorum Muscle
The extensor digitorum’s primary function is the extension of four medial fingers in the metacarpophalangeal, proximal, and distal interphalangeal joints, as its name suggests. It is essential to emphasize that this single muscle acts in opposition to the actions of two finger flexors, flexor digitorum profundus, and superficialis digitorum. Because it helps to open the hand and let go of an object, this muscle is part of the grip’s anatomy. The extensor digitorum’s contraction contributes to the augmentation of this joint as it crosses the wrist.
Clinical relevance
Due to its role in middle finger extension, which causes pain when resisted, the extensor digitorum communis has been found to play a role in the pathology of lateral epicondylitis. A positive Maudsley test may be caused by pathology in the extensor digitorum communis, according to some theories.
Extensor digitorum stretching
The Extensor Digitorum can be stretched easily. We will flex the wrist to stretch this muscle because it helps the wrist extend. With the opposite hand, grasp the arm’s palm and gently bend the wrist so that the palm faces you and the fingers are pointing downward. Release after about 30 seconds. Always remember to complete the opposite side. Standing near a wall with your arm outstretched by your side at shoulder level is another way to stretch this muscle. Lean into it as much as you can comfortably by placing the palm’s back against the wall. Release after about 30 seconds. Make sure to also stretch the other hand. Because working at a computer for long periods can cause wrist and related muscle strains, these stretches are extremely beneficial.

Extensor digitorum strengthening exercise
Elastic reverse grip
Your finger extensors will benefit from this exercise. To get started, wrap a band of elastic around your fingers. To stop the band from rising the hand, slowly extend your fingers against the band’s resistance while keeping your middle knuckles flexed.
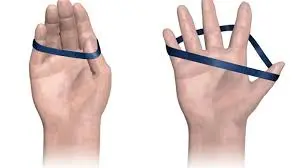
Finger yoga
This is a finger extensor strengthening exercise. To get started, place your palm on a table or desk, or other flat surface. While keeping the other two fingers planted, lift your pinky, middle, and thumb off the surface. While attempting to raise the raised fingers as high as possible, hold this position for up to five seconds. Get back to impartial and substitute situations by lifting the second and fourth fingers as high as conceivable while keeping the others planted. Hold this position once more for up to five seconds. To finish the repetition, return to neutral, and repeat as necessary.

Finger extension with band
This is a finger extensor strengthening exercise. Approximately at the level of your third knuckle, loop a hair or elastic band around the back of your fingers. To stretch the band, extend your fingers out and hold this position for up to five seconds. To finish a repetition, return to neutral.
FAQ
For what reason does my extensor digitorum hurt?
A typical kind of physical issue that can influence the extensor digitorum is the tennis elbow. Overuse of the elbow’s extensor muscles is typically to blame for this injury. Tennis elbow causes pain that is only felt on the outside of the elbow and noticeable weakness in the hand and wrist.
How is the extensor digitorum treated?
Rest: Stay away from the activity that made your tendons itch. While it heals, don’t use your hand or foot too much. Ice: Apply a virus pack to your hand or foot for 15 minutes all at once, four times each day. Compression: To help reduce swelling, wrap an elastic bandage around the painful area.
When the extensor digitorum is damaged, what happens?
A minor cut or finger jamming can injure them, causing the thin tendons to tear from their bone attachment. An injury to the extensor tendon may make it difficult to straighten one or more joints if it is not treated.
How quickly does the extensor recover?
The hand may be bruised and swollen after surgery, and you will probably feel pain as the anesthetic wears off. Recovery can take a long time because the repaired tendons will be very weak until they heal completely. Contingent upon the area recuperation might take somewhere in the range of 1 to 90 days.
Is non-surgical healing possible for the extensor tendon?
The extensor tendons can sometimes be repaired without requiring surgery. A splint, or rigid support that is worn around the hand, can be used to accomplish this.