Fibularis tertius muscle
What is the Fibularis tertius muscle?
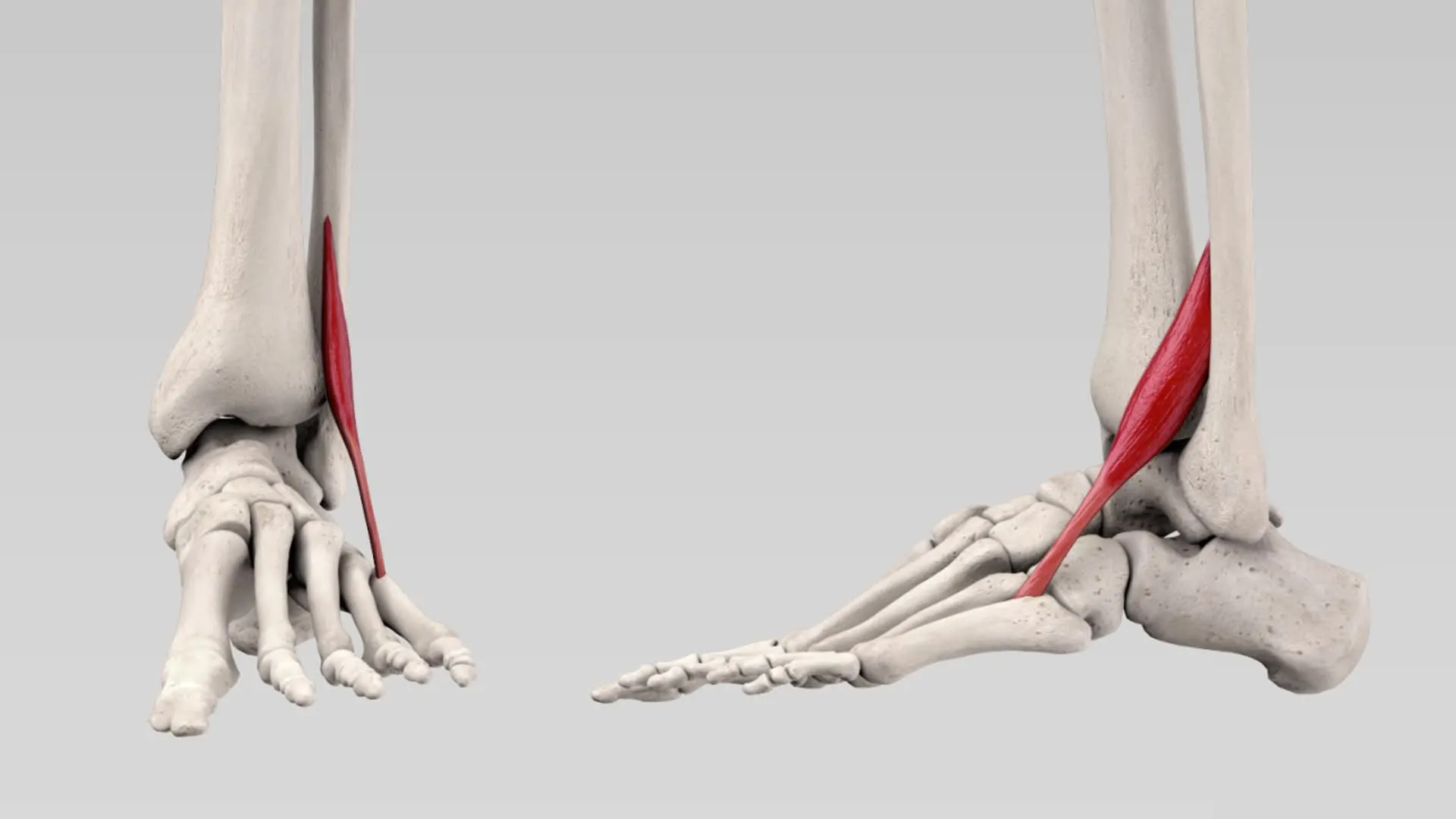
The fibularis tertius muscle, also known as the peroneus tertius muscle, is a small muscle located in the lower leg. It is part of the lateral compartment of the leg and is one of the muscles that make up the group of muscles commonly known as the peroneal muscles. They are collectively known for ankle dorsiflexion.
From the fibula’s distal end to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, the fibularis tertius extends. As a result, it affects and spans two major foot joints; the talocrural (lower leg) and subtalar joints. The fibularis tertius is regarded as a weak dorsiflexor and evertor of the foot due to its moderately small size and weak mechanical leverage. Moreover, the muscle is quite varied; It is known as the fifth tendon of the extensor digitorum longus and can be absent or present in some individuals. In others, it is present.
Origin of Fibularis tertius muscle
Distal half or third of the fibula
Intermuscular septum
Insertion
The fibularis tertius muscle inserts into the dorsal surface of the base of the fifth metatarsal bone in the foot.
Relations
The Fibularis tertius is placed anterior to the fibularis brevis muscle and the anterior lateral malleolar artery. Additionally, it passes laterally to the extensor digitorum longus, where the tendons of both muscles are covered in the same sheath.
The fibularis tertius connects the distal third of the tibia laterally, the talocalcaneonavicular joint posterolaterally, and the tarsometatarsal joint of the foot laterally along its path.
Innervation
The deep fibular nerve, a branch of the Common Peroneal Nerve (a sciatic nerve branch), supplies innervation to the tertiary fibula. It comes from the spinal nerves L5 and S1.
Blood supply
Fibularis tertius obtains arterial blood from several sources:
Anterior tibial artery, through the anterior lateral malleolar artery
Dorsalis pedis arteries and their branches, like the lateral tarsal artery, metatarsal arteries, fourth dorsal metatarsal artery, arcuate artery, and digital arteries
Posterior Tibial artery, via ( through ) the Lateral Plantar artery
Function of Fibularis tertius muscle
The fibularis tertius muscle only can perform two weak movements because it lacks mechanical leverage.
Dorsiflexion of the foot around the talocrural (ankle) joint with the assistance of the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles.
Utilizing the muscles of the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis for foot eversion at the subtalar joint.
Fibularis tertius plays a role in the gait cycle by working with other foot dorsiflexors to lift the foot and toes off the ground during the swing phase. Additionally, it supports the ankle joint, preventing excessive foot inversion during physical activities. However, because its actions can be effectively completed by other stronger muscles, it is difficult to determine the true significance of the fibularis tertius muscle. The femoral tertius muscle is absent in many people who don’t have any particular movement disorder.
Clinical relevance
People who are deficient in the Fibularis Tertius muscle can perform eversion and dorsiflexion with the same level of strength. It appears that the Fibularis Tertius does not give greater protection against ligamentous injury to the ankle.
A condition known as fibularis tertius disorder is characterized by the lower leg’s peroneus tertius catching, locking, popping, or clicking while walking. It is an uncommon state of anterolateral lower leg ache or rear foot ache. This could be optional to impingement and narrowing of the peroneus tertius in the extensor retinaculum.
Anterior compartment syndrome can affect the fibularis tertius muscle.
Surgeons can donate the tendon for tendon transfer or tendoplasty procedures.
Pain in the fibularis tertius muscle can occur due to various reasons, including overuse, muscle strain, or injury.
Fibularis tertius stretching
Lying Shin Stretch
The lying quadriceps stretch is comparable to the lying Shin Stretch.
Lay on your side. Now, place your foot behind your back and bend your upper knee.
Please arrive at the back and handle the forefoot, pulling it towards the back.
Maintain for ten to twenty seconds.
Continue with both feet.

Toe walking exercise
Lean forward. Now lift your heels and toes off the floor with your body weight.
Then walk on the toes which provides your dynamic shin stretch.
Throughout the walk, you can rely on the wall for support.
Walk for one to two minutes.
Fibularis tertius muscle strengthening
Foot eversion
Tie an opposition band to something durable, like the leg of a table. Sit on the ground with the legs straight out before the body, and position the foot into the band at the ball of the foot and with the band put outwardly of the foot. Turning the foot outward after starting with the toes facing up toward the ceiling Return the foot to the starting position while remaining as still as possible with the other leg. Perform 10 to 20 repetitions on both sides.
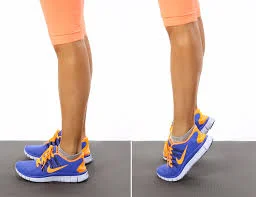
Calf raises
Start by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart and flat on the ground. Keep the rest of your body straight, but don’t lock your knees. Press on the toes gradually, raising the heels off the ground. After maintaining this elevated position for a few seconds, slowly lower your heels to the ground. Perform ten counts for 3 sets. While performing the exercise, you can add additional resistance by holding five-pound weights in each hand and putting the arms down beside your body.
Seated Elastic Band Exercise
The seated Elastic Band Exercise needed the use of an elastic resistance band.
You must sit on the floor with one leg extended in front of you to perform the Sitted Resistance Band Exercise. You can likewise sit in a seat with your foot set up on another seat at this moment.
A resistance band covers one ankle. The other end should be connected to a stable object, like a table leg, around the foot near the toes. So the impact point of the foot doesn’t rub against the floor, resting the lower leg on a little pillow may be useful.
For this exercise, pull the toes and foot up while keeping the knee extended. The ankle may move as you raise the foot. Pull the foot up however much you can and stand firm on the end footing for two seconds.
Slowly ease back into the starting position.
Perform this activity 10 to 20 times or until the anterior tibialis muscle is tired and you can’t flex your lower leg.
Cuff Weight Exercise
A cuff weight is needed for Cuff Weight Exercise.
A cushioned weight that can be folded over the lower leg is known as a cuff weight. For the Cuff Weight Exercise, you must sit in a chair and wrap a cuff weight around your toes. Make sure it’s safe. Let the footrest on the bottom, start this action by sitting with the cuff weight on the foot and afterward flexing the lower leg so the foot and toes move towards the knee.
Maintain the position for two seconds when the foot is flexed up. Return your toes gradually to their starting position.
Ten to twenty times is recommended for the exercise.

FAQ
What causes pain in the peroneus tertius?
With the overuse of the tendons regularly, inflammation of the peroneal tendon can develop over time. Alternatively, it could occur suddenly due to an acute ankle injury like a sprain. The ligaments or the lubricated sheath around the ligaments can grow, making it difficult for them to easily move.
Where is the tertiary fibularis?
leg
The fibularis tertius muscle (FTM) is an interesting anatomic variety. It is believed that patients with an FTM have foot and ankle conditions that are more challenging to manage, and the prevalence of this exclusively human structure, which can be found in the anterior compartment of the leg, is frequently underestimated.
Is the fibularis tertius a tendon or a muscle?
The extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle is frequently thought to include the fibularis tertius (FT) muscle. Hominoid apes lack the muscle, but they do develop a bipedal gait; The muscle only recently appeared in the human foot.
The opponent of the fibularis tertius is what?
The tibialis posterior, along with the fibularis brevis, and the fibularis longus, extend the foot away from the body at the ankle, which is known as plantar flexion. It opposes the tibialis anterior and fibularis tertius, which cause the foot to dorsiflex, or move upward toward the body.
What is the prevalence of fibularis tertius?
The study population has a prevalence of 63% of the fibularis tertius muscle, with males having a higher prevalence than females. The muscle was anyway seen to introduce itself more on the right limb than on the left.