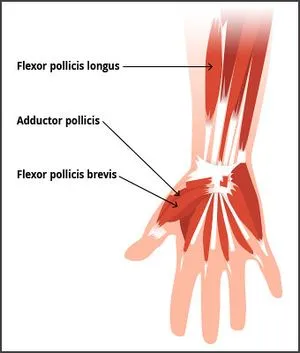
Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
What is Flexor pollicis brevis muscle?
The flexor pollicis brevis is the name of the short and broad intrinsic muscle of the hand. It is a member of the thenar muscles group along with the opponens pollicis, adductor pollicis, and abductor pollicis brevis.
The heads of the flexor pollicis brevis are shallow and deep. The deep head, on the other hand, can be small or even absent at times.
The flexor pollicis brevis flexes the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint, just like the other thenar muscles.
Origin of Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
The trapezium and flexor retinaculum’s crest is the source of the superficial Head.
The trapezoid and capitate bones, in addition to the palmar ligaments of the distal row of carpals bones, are the sources of the deep head.
Insertion
The profound head unit with the shallow head after passing profoundly from the Flexor Pollicis Longus ligament on the spiral sesamoid bone and the foundation of the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Relations
The thenar muscle with the most medial extension is the flexor pollicis brevis. It is lateral to the adductor pollicis muscle and is medial to the abductor pollicis brevis and opposed pollicis muscles.
Along its course, the shallow top of the muscle passes along the outspread side of the ligament of flexor pollicis longus, while the profound head passes profoundly to a similar ligament. Additionally, the opponens pollicis muscle and the superficial head are frequently combined. The motor branch of the median nerve runs across the muscle’s superficial surface.
Innervation
The innervation of the flexor pollicis brevis’s two heads typically differs. The recurrent branch of the median nerve supplies the flexor pollicis muscle’s superficial head, while the deep head receives innervation from the deep branch of the ulnar nerve, which comes from the spinal roots C8 and T1.
Blood supply
Flexor pollicis brevis gets blood vessel supply from parts of the radial artery; branches of the princeps pollicis artery, the superficial palmar artery, and the radialis indicis artery.
Function of Flexor pollicis brevis muscle
The flexor pollicis brevis, which is a part of the thenar muscles, flexes the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal and carpometacarpal joints. This helps the thumb move in the opposite direction, and if it continues, it will cause the thumb to rotate in the medial direction.
When the thumb is flexed against resistance, the flexor pollicis brevis can be tested and palpated on the thenar eminence.
Clinical relevance
The sensory impairments of FPB, which include numbness, paresthesias, and motor deficits in the superficial belly, are the result of the compression of the median nerve that occurs in carpal tunnel syndrome. For circumduction and opposition, all three thumb joints—CMC, MCP, and IP—must be moved simultaneously and coordinatedly. These patterns of movement are disrupted by carpal tunnel syndrome.
Assessment
Manual Muscle Testing of FPB
Position of Patient: The wrist is in a neutral position, with the forearm in a supinated position, the Carpometacarpal (CMC) joint at zero, and the thumb adducted in front of the 2nd Metacarpal.
The position of a therapist: Comfortable position that stabilizes the first metacarpal to prevent wrist and CMC movement by placing one finger on the proximal phalanx in the direction of extension with the other hand.
Test: The patient is instructed to straighten the IP joint while flexing the MP joint of the thumb in native or non-technical language.
Flexor pollicis brevis stretching exercise
Keeping your wrist and hand straight, place a finger from your contrary hand between the knuckle and end joints of your thumb. Make an effort to bend your thumb’s knuckle without bending the tip by resisting the movement with your opposite hand. Try to remain in this position at all times.
Flexor pollicis brevis muscle strengthening exercise
Lean forward and spread your legs slightly as you sit. Then, with your hand and wrist in front of your knee, place your affected forearm on your thigh.
Step on the opposite end of an exercise band by grasping one end with your palm up.
Roll your palm inward toward your thigh for two counts while keeping your wrist straight. Gradually move your wrist back to the beginning position for five counts.
Eight to twelve times.

FAQ
What causes pain in the flexor pollicis brevis?
Overuse, infectious myositis, strain, tears, atrophy, and other injuries can all affect the flexor pollicis brevis. When hand or thumb pain is present or the thumb’s flexion is reduced, an injury should be suspected.
How can pain in the flexor pollicis brevis be treated?
Treatment. To activate the Flexor Pollicis Brevis Muscle, position the wrist in a neutral position with the palm facing upward. Press as hard as you can with the thumb until it reaches the base of the little finger. After holding the pressure for a few seconds, let go.
Which nerve is connected to the flexor pollicis brevis?
Our research on the flexor pollicis brevis muscle shows that the median nerve innervates the superficial head and the ulnar and median nerves innervate the deep head (double innervation).
What are the pollicis brevis abductor and flexor muscles?
The thumb is flexed and rotated by the flexor pollicis brevis. One of the muscles that make up the thenar eminence is known as the abductor pollicis brevis.
What does the flexor pollicis brevis do?
Action. At the metacarpophalangeal joint, the flexor pollicis brevis flexes the thumb and flexes and medial rotates the first metacarpal bone at the carpometacarpal joint.

2 Comments