Flexor pollicis longus muscle
What is Flexor pollicis longus muscle?
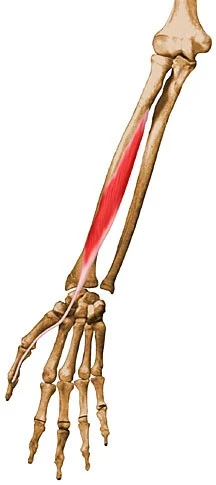
The forearm’s flexor pollicis longus is a long muscle, as its name suggests. Along with the pronator quadratus and flexor digitorum profundus, it is a member of the deep flexors of the forearm. The flexor pollicis longus, which is located in the forearm but is inserted into the hand, is also considered an extrinsic hand muscle.
The flexor pollicis longus inserts into the distal phalanx of the thumb after originating from a large area on the radius and adjacent structures. It then crosses three joints. The flexion of the thumb at the interphalangeal joint, which is a movement that is necessary for gripping, is the primary function of the flexor pollicis longus.
Origin of Flexor pollicis longus muscle
It comes from the adjacent half of the interosseous membrane and the middle of the anterior surface of the radius. FPL has likewise been found to take its starting point from the average epicondyle of the humerus, the coronoid cycle of the Ulna, and the flexor digitorium shallow.
Ballesteros et al.’s study, the embellishment head (Gantzer’s muscle) of FPL has 47.1% beginning from the flexor digitorium shallow, 29.4% from the epicondyle of the humerus, and 23.5% is from a coronoid cycle of the Ulna in the lower arm. According to Hemmady et al.[6], the medial epicondyle of the humerus contains 55.5% of the accessory head of FPL, while the coronoid process of the ulna contains 16.6%.
Insertion
The muscle forms a large, flattened tendon that runs through the carpal tunnel and crosses three hand joints before joining the distal phalanx at its base.
Relations
The flexor pollicis longus is adjacent to the flexor digitorum profundus in the forearm. The anterior interosseous nerve, artery, and vein traverse the interosseous membrane’s anterior surface through a groove created by these two muscles. Between the opponent’s pollicis and the oblique head of the adductor pollicis muscle in the wrist, the flexor pollicis longus tendinous sheath passes underneath the flexor retinaculum.
Depending on the circumstance, the flexor pollicis longus can be combined with the flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, or pronator teres. The flexor pollicis longus may even be absent in some individuals.
Innervation
The anterior interosseous branch of the median nerve, which is derived from the spinal roots C7 and C8, supplies the flexor pollicis longus with nerve supply.
Blood supply
The blood supply to the flexor pollicis longus is split in two. Its average part is provided by the front interosseous course, an aberrant part of the ulnar vein; The radial artery supplies blood to the lateral portion. If the muscle is well developed, the median artery might also help the flexor pollicis longus.
Function of Flexor pollicis longus muscle
The flexion of the thumb at the interphalangeal joint is the flexor pollicis longus’s primary function. The flexor pollicis longus is the only muscle that flexes the interphalangeal joint of the thumb, making it necessary for activities that require hand gripping.
The flexor pollicis longus also contributes to the flexion of the wrist and flexes the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint. When you flex your thumb, this muscle can be felt easily in the lower third of the forearm.
Clinical relevance
Trigger thumb is a powerlessness of the FPL ligament to easily float through the pulley framework because of pulley stenosis coming about because of tenosynovitis, and most normally includes the A1 pulley
The presence of the extra head of FPL has a few clinical ramifications. It can pack the middle nerve and front interosseus nerve; the last option might bring about paresis or loss of motion of the FDP, FPL, and pronator quadratus, and the previous lead to loss of motion of certain muscles in the thenar compartment as well as tactile deficiencies.
A tendinous interconnection FPL and FDP of the subsequent digit known as the Linburg-Comstock peculiarity might prompt the powerlessness to exclusively flex the distal IP of the thumb and the pointer.
Volkmann’s contracture is an optional complexity compartment disorder. that causes muscle and nerve ischemia or potentially possible rot; as the necrotic tissue recuperates, scar tissue withdrawal brings about a shortening of the impacted tissue. Flexor digitorum profundus and FPL muscles are normally impacted; their observable shortening through fibrosis makes sense of the exemplary flexion distortion of Volkmann’s Ischaemic contracture.
Assessment
The flexor pollicis longus is tried holding fixed the proximal phalanx of the thumb is held while flexing the distal phalanx against an obstruction.
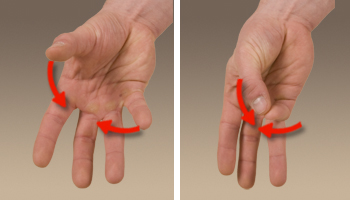
Flexor pollicis longus stretching
With your fingers pointing upward and your thumb extended to one side, pull your thumb down with the other hand at first.
There are numerous small muscles, tendons, and ligaments in the palm and thumb. Applying too much force too quickly should not cause this area to stretch too much.
Flexor pollicis longus exercise
Thumb isometrics
The thumb muscles can be strengthened in multiple directions with this exercise. Start by making a fist with your thumb and applying pressure in both directions with your other hand. Maintain an upright thumb to resist the pressure, and hold for 5 to 7 seconds.
Finger opposition
This is an exercise in finger dexterity. To make a pinch grip, alternately touch your thumb with each finger and keep it for up to two seconds at a time.
FAQ
Is the longus flexor pollicis a tendon?
It is likewise critical to take note that the flexor pollicis longus is one of nine ligaments that move through the carpal passage. The four tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis and the four tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus make up the remaining eight tendons.
What causes an injury to the flexor pollicis longus?
The rupture of the flexor pollicis longus (FPL) tendon during volar locking plate fixation for distal radius fractures is a significant side effect. The ligament burst is generally brought about by erosion between the distal edge of the plate and the FPL ligament and has been all around identified as of late with ultrasonography.
How long does the healing process for the flexor pollicis longus take?
Your FPL connects to a muscle in your forearm after beginning at the tip of your thumb. It then moves through the wrist. Tendons that have been repaired lack blood supply and take a long time to heal.
Are flexor tendons capable of self-healing?
Injuries to the flexor tendon do not heal on their own and frequently necessitate surgery to restore the tendon to its normal position. A splint and hand therapy after surgery may be used to protect you and help you recover from surgery.
Might a flexor ligament at any point mend without a medical procedure?
You won’t be able to bend one or more fingers if your flexor tendons are damaged. Ligament harm can likewise cause agony and expansion (irritation) in your grasp. Using a rigid support called a splint that is worn around the hand, damage to the extensor tendons can sometimes be treated without having to have surgery.


2 Comments