Great auricular nerve
Introduction
The great auricular nerve is a superficial nerve of the neck that get arises from the cervical plexus. It gets arises from the anterior rami of spinal nerves C2 and C3 and is the longest ascending branch of the cervical plexus.
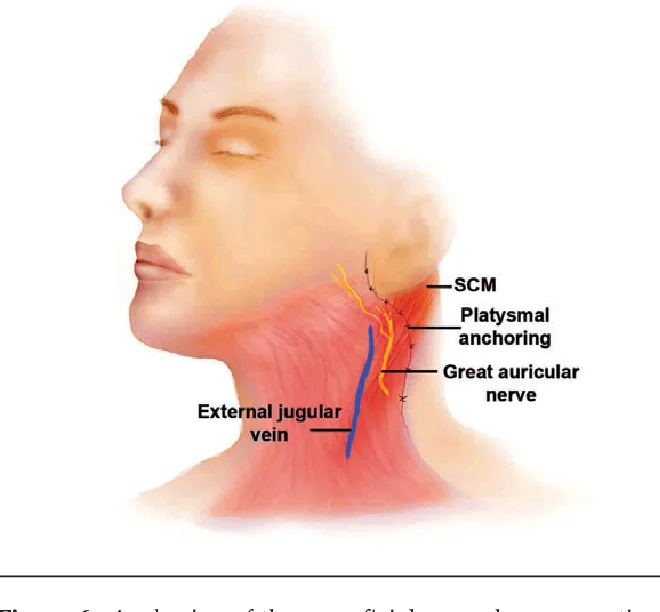
Along its course, the great auricular nerve pierces on the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle at the Erb’s point, which is the commonest site where all cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus intersect and become superficial. The great auricular nerve supplies the skin of the auricle, as well as the area enveloping the parotid gland and mastoid process.
Origin and course of Great auricular nerve
The great auricular nerve is the longest ascending branch of the cervical plexus, gets arising from the anterior rami of spinal nerves C2 and C3. The nerve gets arises just behind the middle region of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and shortly thereafter curves around its posterior border and pierces on the muscle’s anterior surface. Here, the great auricular nerve penetrates the deep cervical fascia and takes an ascending course, passing under the platysma muscle along the external jugular vein. As it reaches the parotid gland, the great auricular nerve divides into its end branches.
The Erb’s point, or punctum nervosum, is the region where all the cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus connect, pierce the deep cervical fascia and become superficial. Aside from the great auricular nerve, these branches also contain lesser occipital, transverse cervical, and supraclavicular.
Branches and nerve supply of the great auricular nerve
The great auricular nerve gives off two end branches:
The anterior branch also called the facial branch supplies the skin over the parotid gland. This branch is submerged into the substance of the parotid gland, where it establishes a connection with the facial nerve.
The posterior branch, also called the mastoid branch, supplies the skin over the mastoid process and the posterior surface of the auricle. This branch gives off a tiny lateral filament, which provides the lobule and concha. Along its course, the posterior branch communicates with the lesser occipital nerve, the auricular branch of the vagus nerve (CN X), and the auricular branch of the posterior auricular nerve.
What are the clinical relations?
What is Frey’s syndrome?
Frey’s syndrome is a rare neurological disorder characterized by the incident of sweating and flushing on the cheek area near the ear in response to eating and salivation. The disorder can occur due to several causes, frequently as complications of surgeries that include the parotid gland. It is believed that the connection found between the facial nerve (parasympathetic innervation) and the great auricular nerve (sensory innervation) through its anterior branch might be part of the anatomical basis of this disorder.
FAQ
Is the greater auricular nerve a cranial nerve?
The large auricular nerve is a cutaneous nerve of the head. It gets originates from the cervical plexus, with branches of spinal nerves C2 and C3. It gives sensory supply to the skin over the parotid gland and the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and surfaces of the outer ear.
What happens if the great auricular nerve is damaged?
any Injuries to the greater auricular nerve can definitely cause numbness of the earlobe and upper neck area. This injury is normally always noted immediately following surgery. The onset of numbness seven months following surgery makes greater auricular nerve injury unexpected
What does the greater auricular nerve affect?
The great auricular nerve is a superficial branch of the cervical plexus that gives sensory supply to the skin enveloped by the parotid gland, external ear, and posterior auricular region
Why does the great auricular nerve hurt?
The great auricular nerve can be damaged or injured by neck surgery, tumor, and long-time pressure on the neck. But, great auricular neuralgia is a very infrequent condition. It was treated by several medications and landmark-based great auricular nerve block with a poor prognosis
Where does the great auricular nerve come from?
The great auricular nerve runs from the cervical plexus as a superficial branch, gets originating from the second and third cervical vertebral levels (C2–C3). The great auricular nerve leaves the cervical plexus at the posterior aspect of the sternocleidomastoid muscle at a point called Erb’s point.
How do you harvest the greater auricular nerve?
The greater auricular nerve can be found between the angle of the mandible and the tip of the mastoid process on the lateral aspect of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, posterosuperior to the external jugular vein The nerve can be harvested through an oblique skin incision placed in a skin crease.
What is an auricular defect?
Based on the involved tissue, auricular defects are categorized into cutaneous and cutaneous-cartilaginous defects Primary closure is normally applicable in cases of medial auricular cutaneous defects due to the malleable nature of the tissues involved