Medial Pectoral Nerve
The medial pectoral nerve is a branch of the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that originates from the spinal cord in the neck and innervates the upper limb.
Along with the lateral pectoral nerve, it is one of the pectoral nerves that supply the muscles in the chest area. Particular muscles in the chest and shoulder region receive motor innervation from the medial pectoral nerve.
Medial Pectoral Nerve Anatomy:
The medial pectoral nerve is also known as the medial anterior thoracic nerve.
Branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus and derived from spinal nerve roots C8-T1.
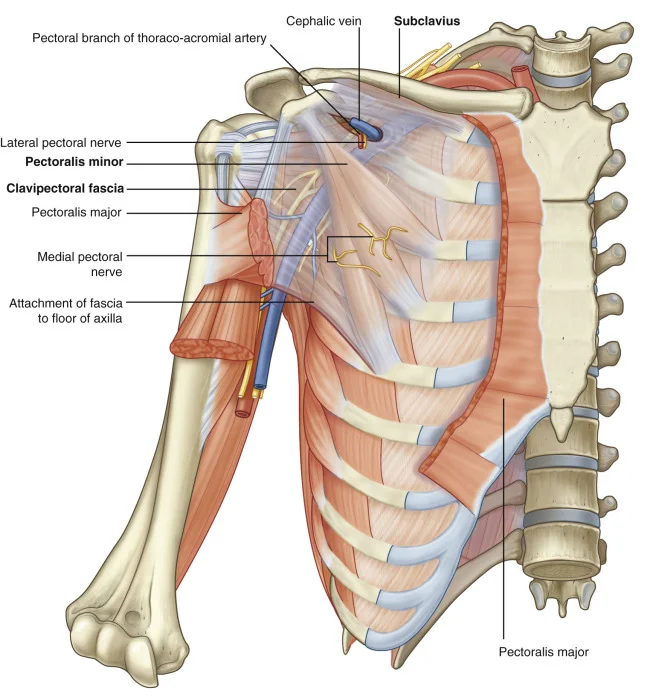
It provides motor innervation to the pectoralis minor muscle and pectoralis major muscle.
It runs down the inferior border of the pectoralis minor muscle.
Origin
The medial pectoral nerve arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus it can however occasionally arise directly from the anterior division of the inferior trunk of the brachial plexus.
It’s awake from the eighth cervical (C8) and first thoracic (T1) spinal nerve roots.
Course and relations
the medial pectoral nerve encompassing behind the first part of the axillary artery turned forward in the middle of the axillary artery and vein, and connect in front of the artery with a filament from the lateral nerve. then enters the deep surface of the pectoralis minor muscle, it’s divided into several branches.
Function:
The pectoralis major muscle consists of the clavicular part and the sternal part. The sternal portion receives innervation from the medial pectoral nerve, which functions to extend the arm at the shoulder from the bent position.
Clinical Significance
Medial Pectoral Nerve Injury
Direct trauma to the axillary region frequently results in injury to the medial pectoral nerve. Furthermore, it is prone to iatrogenic injury during surgeries in this area (such as axillary node dissection and breast surgery). The degree of nerve damage affects the clinical presentation.
The most common complaints from patients are pain in the chest wall or difficulty elevating the shoulder. Electrodiagnostic testing procedures and imaging techniques like MRI are the best ways to make a diagnosis. The usual forms of treatment are conservative or surgical.
When repairing a damaged brachial plexus or axillary nerve, the medial pectoral nerve may be used as a donor nerve.
Summary
Overall, the pectoralis major and minor muscles receive motor innervation from the medial pectoral nerve, a key upper limb nerve that supports movement and stability in the chest and shoulder region.
FAQs
What happens if the medial pectoral nerve should damage?
Cause of the insertion of the pectoralis minor muscle to the coracoid apophysis, this muscle assist produce a medial rotation of the scapula opposite resistance, with the scapula and the upper limb fixed. As a result, an injury to the medial pectoral nerve should lead to an inability to raise the shoulder.
How long do damaged nerves take time to heal?
If the medial pectoral nerve should be injured or traumatized but is not cut, it should recover over 6-12 weeks. A cut nerve will grow at 1mm/ day, after 4 weeks of rest following the injury. Some people observe continued enhancement beyond many months.
How do you treat nerve damage?
For mild nerve injuries, nonsurgical treatment options include medication, Physical Therapy And massage therapy. Peripheral nerve surgery should reconstruct or repair damaged nerves. You might require surgery to repair severely compressed nerves, cut nerves, or nerves that are not healing on their own.
Should nerve damage affect the chest?
Brachial neuritis might happen via peripheral neuropathy that impacts the chest, shoulder, arm, and hand. Peripheral neuropathy should a disease characterized at the side of pain or loss of function in the nerves that carry signals to and from the brain and spinal cord CNS to other parts of the body.
Is the medial pectoral nerve motor or sensory?
The medial pectoral nerve is a motor branch by one and the other the lateral and medial pectoral nerves, nerves that are divisions of the brachial plexus, give motor supply to the Pectoralis major muscle.
What are the medial pectoral branches?
Medial pectoral branches, arising from the medial cord, are located by dissecting the axillary artery. the medial pectoral branches are normally found close to and somewhat beneath the largest pectoral arterial branches. The medial pectoral nerve branches reach the pectoral muscles.