Scapular Assistance Test = SAT
The scapular assistance test is a physical examination maneuver used by healthcare professionals, typically in the field of orthopedics or sports medicine, to assess scapular muscle function.
The test is designed to evaluate the contribution of the scapular stabilizing muscles to shoulder function and stability. It can help diagnose conditions related to scapular dyskinesis or muscle weakness.
- This test is first described by Kibler.
- Coordinated movement of the scapula which is needed for the normal function of the shoulder joint means GH joint.
- When the humerus is elevated; the scapula moves into upward rotation, external rotation, or lateral rotation & posterior tilt.
- Abnormal scapular movement or Scapula dyskinesis which is associated with too many shoulder pathologies.
Purpose of A scapular assistance test
- This test is used to assess the scapular motion which may be linked to shoulder pain.
- This test is a symptom-related alteration test in which the examiner assists the scapula into posterior tilt & upward rotation as the patient elevates the arm which is simulating to force a couple of the serratus anterior & lower trapezius muscles.
- Then perform the scapula posterior tilt & upward rotation influence to the subacromial space, relieving the pressure on the tendon and bursa of subacromial space, thus helping in identifying patients whose pain is related to subacromial impingement.
The technique of A scapular assistance test
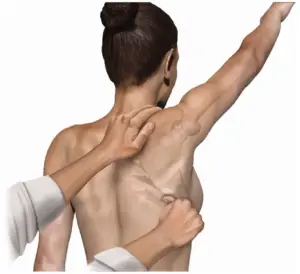
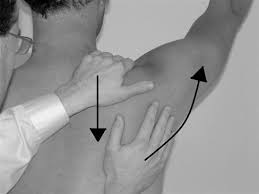
- This test involves scapula upward rotation only, then it is modified to include posterior tipping of the scapula, as posterior tipping movement is also lacking in individuals with subacromial impingement.
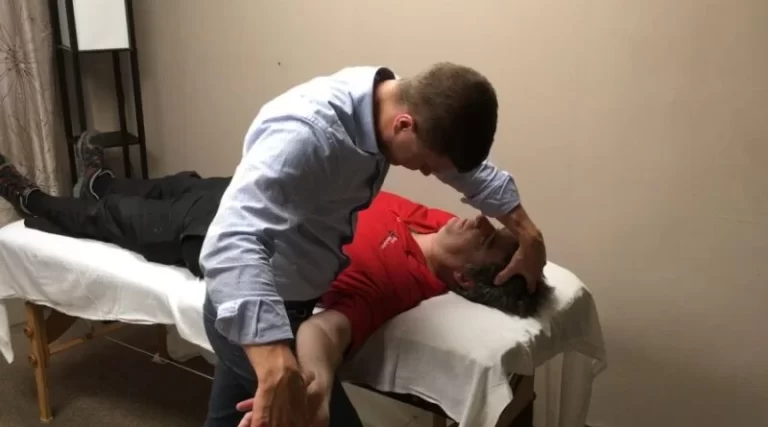
- The starting position of the patient is standing.
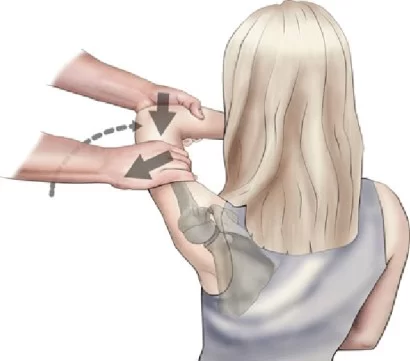
- Then put one hand on the superior border of to scapula which involves to shoulder with the fingers over to the clavicle & put the other hand on the inferior angle of the scapula with the fingers wrapped laterally around to thorax.
- Then examiner assisted in the scapula’s upward rotation by pushing the inferior angle of the scapula upwards & laterally means externally.
- It assists in posterior tipping of the scapula by pulling the superior angle of the scapula posteriorly, while the patient actively elevates the arm.
Result of A scapular assistance test:
- Decreased pain would be a positive test & would indicate that the scapular control muscles are weak as the assistance by the examiner stimulates the activity of the serratus anterior & lower trapezius during elevation. During this treatment, the test is used as a method to increase the subacromial space.
Evidence of A scapular assistance test:
- Alon Rabin et al
- It was found that when the modified scapula assistance test
- Which is performed in scapular
- Plane kappa coefficient = 0.53
- Percent agreement = 77%,
- When this test is performed in the sagittal plane
- Kappa coefficient =0.62
- Percent agreement = 91%
- The conclusion of the modified scapula assistance test is moderate interrater reliability, which makes it acceptable for clinical use.
It’s important to note that the scapular assistance test is just one component of a comprehensive shoulder examination, and it should be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical findings and diagnostic tests for a more accurate assessment and diagnosis.

One Comment