Tachycardia
What is tachycardia?
Tachycardia is a medical term used to describe a condition in which the heart beats at a faster rate than normal. The normal resting heart rate for adults is typically between 60 and 100 beats per minute. Tachycardia is generally defined as a heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute at rest.
There are different types of tachycardia, and they can be broadly classified into two categories: supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and ventricular tachycardia (VT).
Because the heart beats too constantly, it does not have the time it requires to fill with blood between beats. This can be harmful if the heart can not provide all the cells with the blood and oxygen they require.
The heart usually reacts to electrical signals from a sinoatrial (SA) node of the heart. These signals regulate how usually a heart beats. When you have had a shock or are extremely passionate or worried, or are exercising, the heart may send signals more repeatedly for a brief time. This is named sinus tachycardia and goes out when an individual calms down/rests.
The atria, ventricles, and the electrical circuitry of the heart:
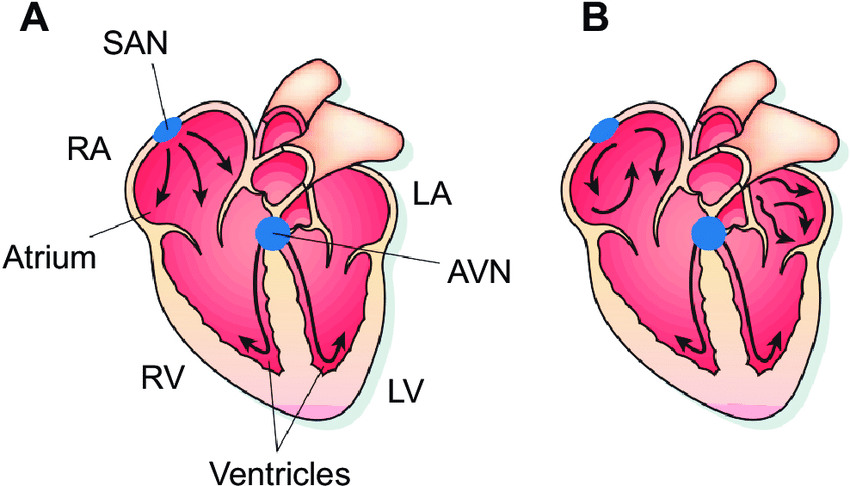
The human heart has four chambers:
- The atria: The two upper chambers
- The ventricles: The two lower chambers.
- The heart has right and left atria and ventricles.
The heart has a biological pacemaker named the sinoatrial (SA) node in the right atrium. This constructs electrical stimulants. Separately one initiates an individual heartbeat.
As the electrical stimulants leave the sinoatrial (SA) node, they travel to the atria causing atrial muscle contraction. This contraction moves blood into the ventricles.
The electrical stimulants persist to the atrioventricular (AV) node which is a group of cells. The atrioventricular (AV) node delays down the electrical signs and then transmits them onto the ventricles.
Accomplishing it permits time for the ventricles to load with blood. When the ventricular muscles acquire the electrical signs they contract, the right ventricle pumping blood either to the lungs or the left ventricle to the whole body parts.
An issue with the electrical signs can outcome in a quicker than usual heartbeat. It’s called tachycardia.
Whom does tachycardia impact?
Atrial/supraventricular tachycardia can impact:
- Females and individuals designated women at birth better than men and individuals designated men at birth.
- Children particularly those who have stress.
- Anyone who is extremely exhausted and drinks an excess of alcohol/caffeine.
- Individuals who smoke a lot.
Ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation can impact:
- Individuals with heart attack, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis (inflamed heart muscle), heart failure, and heart illness.
- Individuals who smoke and have hypertension/diabetes.
What are the types of Tachycardia?
The following paragraphs will summarize some ordinary types of tachycardia.
Sinus tachycardia
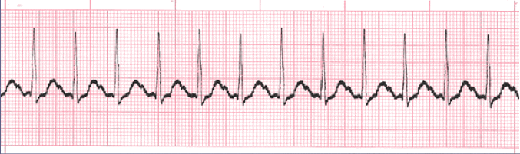
In sinus tachycardia, the heart beats quicker than regular but the beat is normal, and the stimulant arrives from the sinoatrial (SA) node.
Causes contain:
- cognitive and physical stress
- fever
- the usage of specific medications
- some health illnesses
- infection, thyroid, and blood count problems
Inappropriate sinus tachycardia
Doctors don’t understand completely what generates improper sinus tachycardia, but neurological characteristics seem to play a role.
It appears more conceivable to impact:
- super athletes
- individuals experiencing psychological anxiety
- women
- individuals underlying a COVID-19 infection
- individuals with postural orthostasis tachycardia syndrome (POTS)
Investigators say therapy is demanding because physicians comprehend so slightly near the reason. A physician may regale improper sinus tachycardia with beta-blockers.
Atrial or supraventricular tachycardia
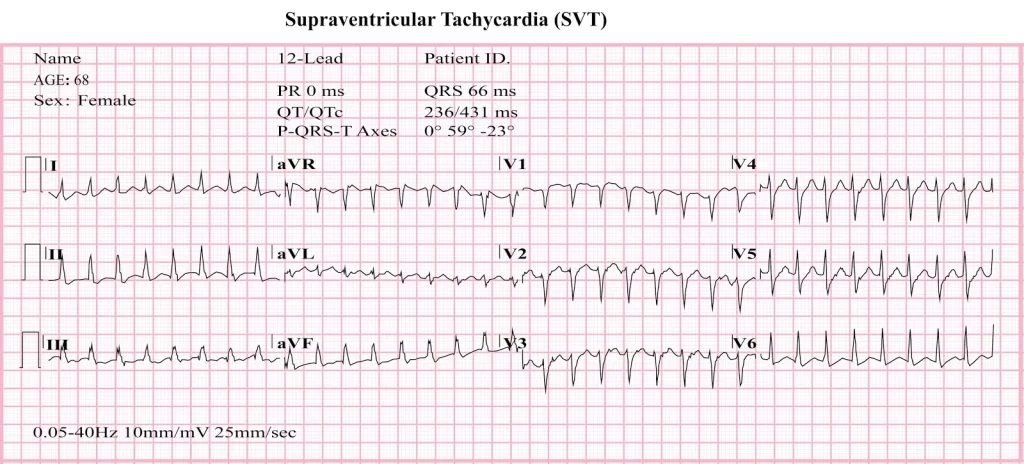
Supraventricular tachycardia is an accelerated heartbeat that begins in the right and left atria of the heart.
It is a considerably typical heartbeat issue in children and youthful individuals. Many individuals foremost undergo it between the ages of 25 to 40 years.
An attack may stay from a few minutes to several hours. It isn’t generally severe, but in intense circumstances, it can cause unconsciousness and cardiac arrest.
Atrial fibrillation
Periodically electrical movement in the atria can override the biological pacemaker of the heart. This forced to the chambers contract rapidly and irregularly. This is understood as atrial fibrillation (A-fib).
Most individuals with atrial fibrillation (A-fib) even have another heart disease. It’s more possible to impact those beyond the age of 65 years. Drinking alcohol and smoking tobacco may contribute, as might hypertension and sleep apnea.
Atrial fibrillation (A-fib) can boost the chance of a stroke.
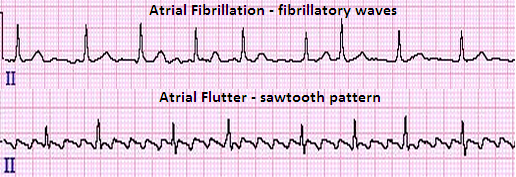
Atrial flutter
This is identical to atrial fibrillation (A-fib), but the beats are more methodical. Many individuals have both atrial fibrillation (A-fib) and atrial flutter.
Ventricular tachycardia
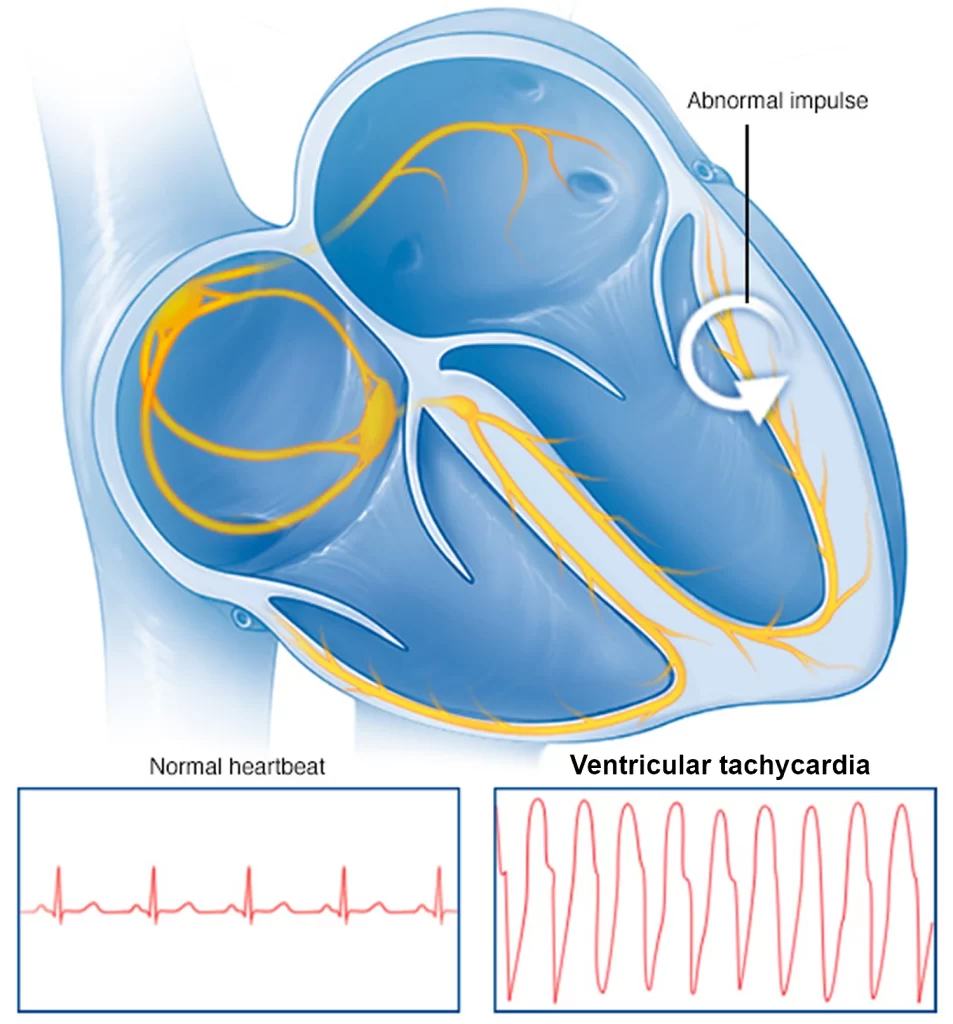
Abnormal electrical signs in the lower chambers affect a fast heart speed. This can outcome from cardiovascular difficulties, for example, an earlier heart attack, the usage of particular medications, and a hereditary situation guiding to lengthy QT.
The rate of the heartbeat doesn’t permit the ventricles to load and tighten correctly, thereby decreasing blood supply to the body.
The reason and severity of the signs resolve how severe it is. Long attacks can be very severe and require a quick medical alert. They can force the heart to eliminate.
Ventricular fibrillation
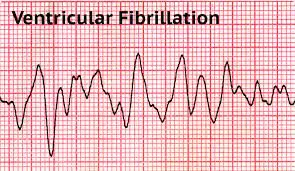
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) is a severe cardiac irritation. The ventricles flutter rather than beat, resulting in inadequate blood supply to the body.
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) is medical trouble. If a regular heartbeat doesn’t return fast, blood circulation can end, which can cause death.
What are the Symptoms of Tachycardia?
Relying on the type and causes of tachycardia, the underlying sign and symptoms may appear:
- A fast pulse
- Chest pain
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Low blood pressure
- Lightheadedness
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Sudden weakness
- Fainting or a loss of consciousness
- Cardiac arrest, in some cases
Regardless, many individuals have no signs and just discover that they have tachycardia while a regular investigation.
What are the Causes of Tachycardia?
A disturbance in the typical electrical stimulants that contain the pumping movement of the heart and the beat at which the heart pumps leads to tachycardia.
Relying on the type of tachycardia, the below factors may trigger it:
- A reaction to certain medications
- Congenital irregularities of the heart
- Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol or caffeine
- Using cocaine or other illegal drugs
- Electrolyte imbalance
- A vitamin B1 deficiency is understood as beriberi
- Inadequate blood supply and damage to heart tissues due to heart disease, coronary artery disease, heart valve disease, heart failure, heart muscle disease, tumors, or infections
- Hypertension, or high blood pressure
- Smoking
- Absolute lung illnesses, thyroid disease, anemia (less Hb in the blood), and other health problems
- Fatigue
- Severe bleeding
- Physical & mental stress, containing disease and anxiety
- Previous heart surgery
Regardless, sometimes the precise reason may not be apparent.
Risk factors of Tachycardia
The underlying elements can raise the risk of tachycardia:
- Age as some types involve various age groups
- Genetic elements
- An individual/family history of heart illness
- Anxiety
- Increased consumption of caffeine and alcohol
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Cognitive stress
- Smoking
- The usage of illegal medicines
- Thyroid disease
Possible complications of Tachycardia
The chance of complications relies on several elements, containing:
- The severity and period of the tachycardia
- The type of tachycardia
- The general fitness of the individual
- Any other heart illnesses they may have
- The design and part of the heart muscle
The most typical complications contain:
- Blood clots: Blood clots can especially raise the chance of heart attack/stroke.
- Heart failure: Without therapy the heart can evolve weaker, raising the chance of heart defeat.
- Fainting: A individual with a quick heartbeat may lose consciousness, raising their chance of a fall/other accidents.
- Sudden death: This generally only happens with ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation.
An individual may even undergo:
- Palpitations
- Fainting and dizziness
- Tiredness and fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain and tightness, or angina
- Low blood pressure and shock
- Heart failure
How to Diagnose the Tachycardia?
If an individual needs medical guidance for a supposed heartbeat issue, the physician will:
- Questions about their signs and symptoms
- Bring out a physical examination
- Demand tests
These tests may contain:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Electrodes connected to the skin can estimate electrical stimulants that the heart assembles.
- Echocardiogram: This is a kind of ultrasound (US) that constructs a moving picture of the heart.
- Wearable devices: The individual can hold a Holter monitor/event recorder. These instruments can observe heartbeats and electrical stimulants for days/weeks.
- Blood tests: This assistance resolves whether thyroid and other issues are taking part in tachycardia.
- Graded exercise test: This can assist determine how physical exercise affects heartbeats.
- Implantable loop recorder: A loop recorder is an instrument that a physician can put beneath the skin. They can do this in the office. It records continuously the activity of the heart and can remain in for several years. It can assist analyze and observe heart arrhythmias that appear more intermittently.
- Electrophysiology study: These are intrusive tests that assist physicians comprehend why an arrhythmia happens and where it initiates from.
How to Treat Tachycardia?
Tachycardia treatment relies on different elements, containing:
- The reason
- The age of the individual
- Their general fitness
- Heart function and structure
The treatment goal is to manage the reason, but a physician may even attempt to:
- Delay the heart speed
- Control additional attacks
- Decrease the chance of complications
If there is no exact following reason, it may bring some time to discover an appropriate treatment alternative.
Ways to slow a fast heartbeat
There are several manners to delay a fast heartbeat while an attack. The underlying areas will look at these in more elements.
Vagal maneuvers
The vagus nerve enables to control the heartbeat.
Some strategies and maneuvers can impact this nerve and assist to delay the heartbeat. Such methods contain:
- Using abdominal pressure
- Using cold water on the face of individuals
- Using soft force on the region of the neck where the carotid artery is located
- Maintaining the nostrils locked during the individual impacts out via the nose
- Blowing on your thumb
- Enduring down like you are having a bowel movement
- Coughing
These may be useful in an emergency situation.
Medication
A physician can assist with antiarrhythmic medicines either orally or intravenously. This medicine’s goal is to reform a regular heartbeat and maintain heart speed.
Some instances of antiarrhythmic medicines contain:
- Adenosine (Adenocard)
- Diltiazem (Cardizem CD)
- Metropolol (Lopressor)
- Amiodarone (Cordarone)
- Sotalol (Betapace)
- Mexiletine (Mexitil)
Cardioversion and defibrillators
A doctor can connect electrodes to the individual’s body and have an apparatus provide an electric impulse to the heart. This resets the electrical stimulants in the heart and may reform a regular heartbeat.
There are various methods of functioning cardioversion and defibrillation.
These are as below:
- In an emergency setting: During deferring for medical service to reach a first responder/bystander may utilize an involuntary superficial defibrillator if the individual’s heart moves into a beat that contains it from hammering appropriately.
- In the hospital: A cardiologist may utilize cardioversion as a component of organized therapy.
- Ongoing treatment: An implantable cardioverter defibrillator can constantly observe the individual’s heart rhythm. A cardiologist can inject the little instrument into the chest, where it notices irregular heart rhythm and produces a shock to reform a regular beat when required.
Cardioversion’s goal is to regale the irregular heartbeat and change it to a regular beat. A physician may utilize medicines/electrical power to do this. The electrical therapy delivers fast, synchronized low-power shocks to reform the beat.
Defibrillation is an electrical therapy that delivers more effective shocks to the heart to habilitate a perfusing beat, which permits blood to initiate circulating too. Automated external defibrillators (AED) are available in many public places for emergency use. An implantable defibrillator is a device a doctor implants under the skin to provide a shock when needed.
Prevention of Tachycardia
Some actions can assist prevent and handle tachycardia. The underlying sections will discuss these actions in more detail.
Lifestyle factors:
Some manners to control tachycardia and other heart problems at home contain:
- Avoiding the usage of tobacco and illegal medicines
- Use of alcohol & caffeine, Adderall, cocaine, power drinks, methamphetamine, and cardiac impulses
- Decreasing anxiety, if conceivable
- Acquiring adequately sleep
- Following a nutritional diet and acquiring normal exercise
Medications:
Drugs that can assist individuals handle tachycardia contain:
- Antiarrhythmic medicines
- Calcium channel blockers, for example, diltiazem (Cardizem) and verapamil (Calan)
- Beta-blockers, for example, propranolol (Inderal) and metoprolol (Lopressor)
- Blood thinners, for example, warfarin (Coumadin) and apixaban (Eliquis)
Blood thinners can help control the complications of atrial fibrillation. Instances contain warfarin (Coumadin) and apixaban (Eliquis).
Radiofrequency catheter ablation:
An electrophysiologist can put catheters into the heart via the blood vessels.
Electrodes at the ends of the catheter can ablate, or harm little chambers of the heart that are accountable for the irregular heartbeat.
Surgery:
Sometimes a physician will suggest surgery to construct restorations or modifications that can assist decrease the chance of tachycardia. A pacemaker/defibrillator can help handle some kinds of tachycardia.
A physician will suggest surgery if other treatments haven’t functioned and if the individual has another heart disease.
FAQ
When is tachycardia serious?
When the heart beats more than 100 times/minute at rest that is tachycardia. Because the heart beats too frequently it does not have the time it requires to load with blood in between the beats. This can be harmful if the heart can not provide all of the cells of the body with the blood and oxygen they require.
What foods decrease tachycardia?
Find potassium in foods for example:
Apricots.
Bananas.
Cantaloupes and honeydew melons.
Lima beans.
Oranges.
Peas.
Skim and low-fat milk.
Spinach.
Can tachycardia go away?
Tachycardia is usually benign and goes out on its own. Regardless, if the heartbeat will not return to normal, individuals requirement to consult a doctor. Overworking the heart for excessively prolonged can conduct to a heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular difficulties.
Can walking cure tachycardia?
Obtaining in shape with average aerobic exercise manages to reset a resting heart rate at a more inferior level. Exercise even enables a person to get his aggression getaway in a healthy ritual. But consult with the doctor before initiating a new exercise schedule.
Can tachycardia weaken the heart?
A period of untreated and frequent attacks of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) may debilitate the heart and conduct to heart defeat, especially if there are other medical illnesses present.



5 Comments