List of the nerves in the human body
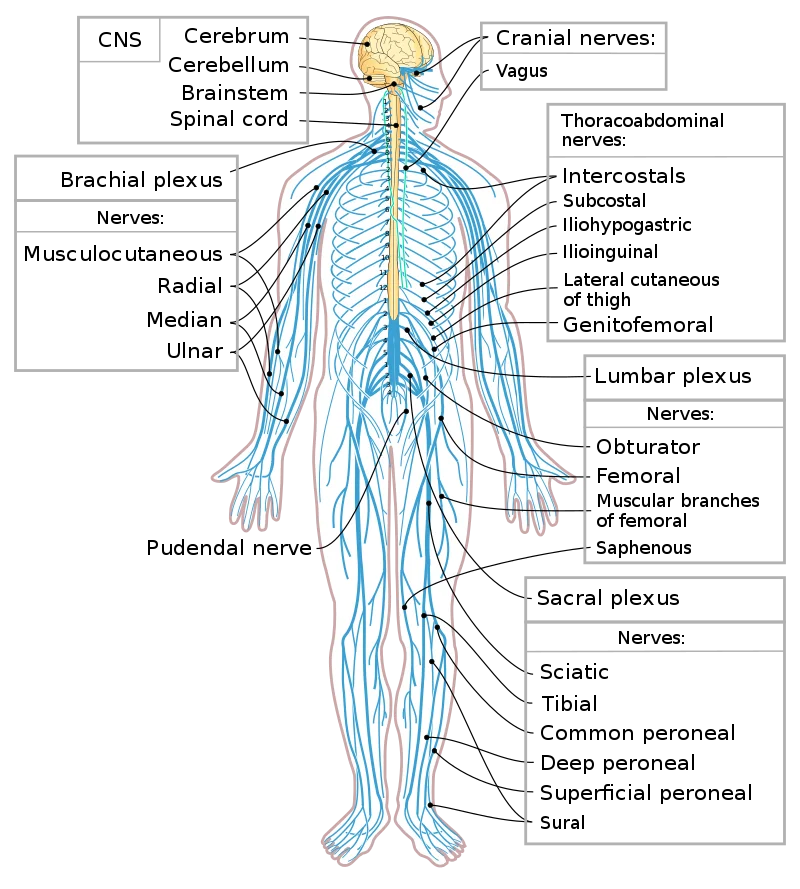
List of nerves – There are 12 cranial nerves, and this list is further classified into a list of spinal nerves, a list of nerves that travels into the upper limb, lower limb, trunk, and organs.
What are nerves?
Nerves are like cables that conduct electrical impulses between the brain & the rest of the body. These impulses help you feel sensations & move the muscles. They also maintain certain autonomic functions like breathing, sweating & digesting food.
Nerve cells are also called neurons. Neurons are present all over the body, especially in the brain & spinal cord. Nerves, together with the brain & spinal cord, are the foundation of the nervous system. Most of the time when doctors use the term “nerve,” they’re referring to the part of the nervous system outside of the brain & spinal cord. This is called the peripheral nervous system.
What is the purpose of nerves?
Nerves send electrical signals from one part of the body to another. These signals control the;
- Voluntary movement.
- Senses (touch, pain, feeling hot & cold, vibration, hearing, sense of balance, taste, smell & sight).
- Blood pressure.
- Breathing.
- Digestion.
- Heart rate.
- Stress response.
So how many nerves are in the Human Body?
There are so many peripheral nerves in the Human body. There are sensory nerves that take sensation from the skin and internal organs unite together to form the sensory branches of the cranial and spinal nerves.
The motor part of the cranial nerves and spinal nerves branches into smaller nerves that divide into even smaller nerves. So one spinal or cranial nerve may further divide into too many branches from 2 to 30 peripheral nerves.
What is the structure of the nerves?
the nerves are made up of:
- Axons are cord-like groups of fibers in the center of the nerve.
- Dendrites are branches that conduct electrical impulses.
- Endoneurium is a layer of connective tissue surrounding axons.
- The perineurium is a layer of connective tissue that surrounds groups of axons called fascicles.
- Epineurium is a layer of connective tissue that covers the outer surface of the nerve.
What conditions & disorders affect the nerves?
Some conditions affect how well the nerves send signals. If damage or any kind of injury interferes with nerve signals, you may develop a neurological condition.
Common conditions that affect the nerves include:
Peripheral neuropathy: Damage to the peripheral nerves (nerves outside of the brain & spinal cord).
Sciatica: Pain that affects the nerve roots in the lower back, or the sciatic nerve, the nerve that runs from the lower back down the backs of both legs.
Location
- classification of the Areas of the Sensory Roots upon the Surface of the Body
- anatomy of the nervous system
- Development of the nervous system
- The spinal cord & medulla spinalis
- The brain & encephalon
- The hindbrain or rhombencephalon
- The midbrain or mesencephalon
- The forebrain or prosencephalon
- Composition & central connections of the spinal nerves
- the passageway from the brain to the spinal cord
- The meninges or outer covering of the brain & medulla spinalis
- The cerebrospinal fluid
List of Cranial nerves
The cranial nerves-there are a total of 12 pairs of cranial nerve
- The olfactory nerve
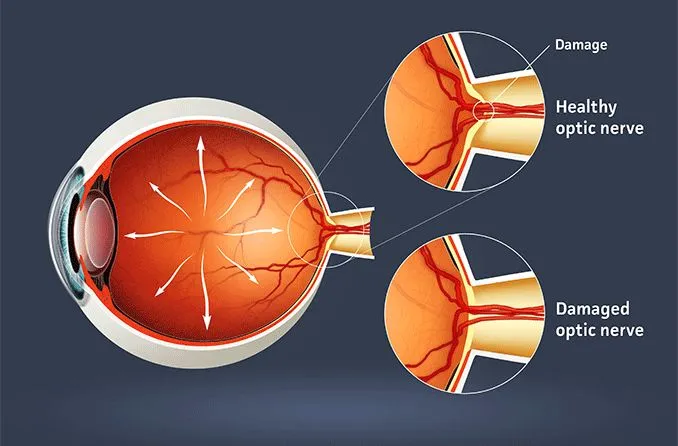
- The optic nerve
- The oculomotor nerve
- The trochlear nerve
- The trigeminal nerve
- The abducens nerve
- The facial nerve
- The vestibulocochlear nerve
- The glossopharyngeal nerve
- The vagus nerve
- The accessory nerve
- The hypoglossal nerve
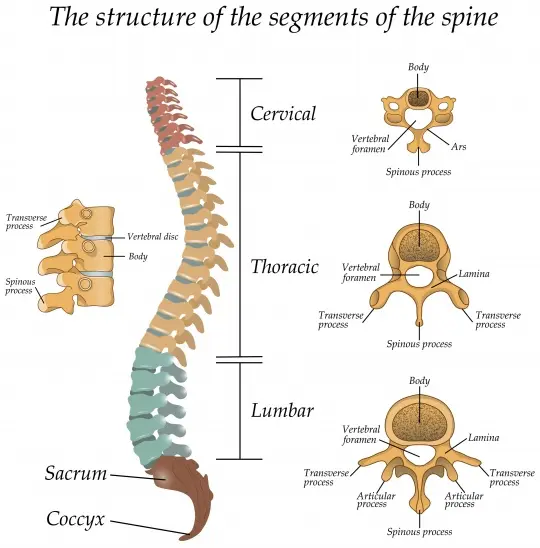
List of The spinal nerves
spinal nerves are mixed nerves that interact directly with the spinal cord to modulate motor & sensory from the body periphery.
- The posterior divisions
- The anterior divisions
- The thoracic nerves
- The lumbosacral plexus
- The sacral and coccygeal nerves
- The sympathetic nerves
- The cephalic portion of the sympathetic system
- The cervical portion of the sympathetic system
- The thoracic portion of the sympathetic system
- The abdominal portion of the sympathetic system
- The pelvic portion of the sympathetic system
- The great plexuses of the sympathetic system
List of Nerves of the upper limb
- brachial plexus
- Axillary nerve
- Dorsal scapular nerve
- Dorsal branch of the ulnar nerve
- Musculocutaneous nerve
- Radial nerve
- dorsal scapular nerve
- thoracic nerve
- suprascapular nerve
- nerve to subclavius
- lateral pectoral nerve
- medial pectoral nerve
- the medial cutaneous nerve of the arm
- the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm
List of the Nerves in the lower limb
- branches of lumbar plexus (L1-S4)
- iliohypogastric
- ilioinguinal
- genitofemoral
- lateral femoral cutaneous
- obturator nerve
- femoral nerves.
- branches of sacral plexus (L5-S2);
- superior gluteal
- inferior gluteal
- sciatic nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous,
- pudendal nerves
- nerve to piriformis
- nerve to obturator internus
- nerve to quadratus femoris.
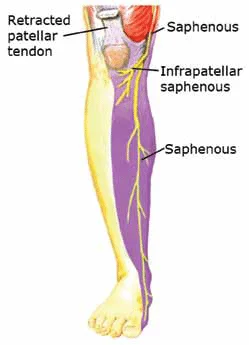
- saphenous nerve
- femoral cutaneous nerves
- obturator nerve
- gluteal nerve
- cluneal nerve
- superior genicular (medial &lateral)
- inferior genicular (medial &lateral)
- middle genicular
- tibial nerve
- deep fibular nerve
- dorsal digital nerves
- proper plantar digital nerves
- lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve
- plantar nerves
Parasympathetic nerve -a network of the nerves that relaxes the body after periods of stress or danger.
sympathetic nerve-The sympathetic system controls “fight-or-flight” responses.
Nerve supply to the heart
- cardiac plexus
- vagus nerves
- vagal cardiac nerves
Nerve supply to the thoracic region
- intercostal nerve
Nerve supply to the lung
- pulmonary plexus
- vagus nerve [parasympathetic innervation-]
nerve supply to the liver
- hepatic plexus
- coeliac plexus [sympathetic supply]
- vagus nerve [parasympathetic innervation-]
nerve supply to the small intestine
- splanchnicvagus nerve [parasympathetic innervation]
- nerve supply to the large intestine
- vagus nerve [parasympathetic innervation-]
- pelvic splanchnic nerves.
- The superior & inferior mesenteric
- inferior hypogastric plexus
FAQ
What is the most important nerve in the body?
The vagus nerve is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system & is one of the most important nerves in the body. The vagus nerve helps to regulate or maintain many severe aspects of human physiology, including the heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, digestion & even speaking
Where is the strongest nerve in the human body?
the sciatic nerve, the largest & thickest nerve of the human body is the principal continuation of all the roots of the sacral plexus.
How do I know if I have any type of problems with my nerves?
The major signs of nerve damage include the following:
Numbness & tingling sensations in the hands & feet.
Feeling like you are wearing tight gloves or socks.
weakness of the muscle, especially in the arms & legs.
Regularly dropping objects that you’re holding.
Sharp shooting pains in the hands, arms, legs, or feet.
What do nerves do?
Nerves are like cables that carry electrical impulses between the brain & the rest of the body. These impulses help you feel sensations & move the muscles. They also maintain certain autonomic functions like breathing, sweating, & digesting food. Nerve cells are also called neurons.
What nerves control what?
Most of the time, cranial nerves are divided as being either sensory or motor. Sensory refers to the five senses touch, smell, taste, hearing, & sight & motor nerves are responsible for controlling and maintaining the movement & function of glands & muscles.
mention what are the four major functions of the nervous system.?
The four main functions of the nervous system include:
Control of the body’s internal environment to maintain or preserve ‘homeostasis’ As an example of this is the regulation of body temperature.
Programming of spinal cord reflexes. An example of the spinal cord reflex is the stretch reflex.
Memory & learning.
Voluntary control of movement.
What are the common nervous system disorders?
Headache. Headaches are one of the most common neurological disorders & there are a variety of different kinds of headaches, such as migraines, cluster headaches, & tension headaches.
Stroke
Seizures
Parkinson’s Disease
Dementia.
How can I keep my nerves healthy?
You can keep your nerves and entire nervous system healthier by adopting healthy habits, like:
Avoid tobacco or quit smoking.
Eat a nutritious diet full of whole grains, healthy fats, lean protein, fruits & vegetables.
Limit alcohol intake.
Manage health conditions that can affect the nerves, such as diabetes.
decrease stress with healthy coping techniques such as meditation or exercise.
Sleep at least seven to eight hours each night.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water & other fluids.
What are the 12 cranial nerves?
Olfactory nerve.
optic nerve.
oculomotor nerve.
trochlear nerve.
trigeminal nerve.
abducens nerve.
facial nerve.
vestibulocochlear nerve.
glossopharyngeal nerve.
vagus nerve.
accessory nerve.
hypoglossal nerve.