Tachypnea
What is Tachypnea?
Tachypnea or tachypneic breathing is fast and shallow breathing. If your breath speed gets quick but then returns to normal speed it is understood as transient tachypnea. Various medical diseases induce tachypnea.
Tachypnea can impact newborns and adults. It is considered ordinary among newborns who were born prematurely (preterm) and among adults with respiratory illnesses such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
A person usually feels fast breathing when exerting and participating in a strenuous activity, for example, running. Tachypnea can even occur when the individual is at rest. Some individuals with tachypnea may experience extremely short breath, during others may not have any prominent signs at all. Tachypnea isn’t usual, also while exercising.
This type of breathing can be because of different inequalities in the body, specific drugs, and health illnesses varying from anemia and asthma to heart defeat and lung cancer.
This article contains the possible reasons for tachypnea and the medical situations in which it may happen.
What are the Causes of Tachypnea?
Physiological Causes
A physiological reason leads to the person’s usual capability to restore an uncommon disease. Tachypnea isn’t in itself an irregular physical reaction. Instead, it’s a regular reaction to something unnatural occurring in the body.
Tachypnea can be induced by 3 primary physiological procedures:
- An imbalance between respiratory gases: A inferior oxygen level in the blood is understood as hypoxemia. A raised level of carbon dioxide in the blood is understood as hypercapnia. Both of these can generate tachypnea.
- An acid-base imbalance: When the body feels that the blood is over-acidic, it bobbles carbon dioxide out of the lungs in an try to alleviate the body of acid. This can again induce tachypnea.
- A fever: When a person has a fever, their breathing evolves more quickly as their body attempts to discharge heat.
In these examples, tachypnea isn’t strange. Rather, it’s how the body balances for an irregularity.
Physical causes
Tachypnea is not always the effect of chronic medical/health circumstances.
- Choking: When a person chokes an object partially/totally obstructs her airway. If she/he can respire at all your breathing will not be in-depth and casual. In circumstances of choking quick medical attention is essential.
- Anxiety attacks: During anxiety is usually considered a moral cognitive disorder, anxiety can have bodily signs on the body. Anxiety attacks are bodily reactions to fear/anxiety. In an anxiety attack, an individual may feel quick breathing/shortness of breath.
- Strenuous physical activity: While boosted physical exercises such as severe exercise and vigorous sex, the body utilizes up more oxygen and notices a gain in carbon dioxide. Analyses indicate that person may breathe 3 or 4 times more repeatedly as an outcome. Exercise is a definitive example of hyperpnea. Hyperpnea is the proper breathing reaction to boost carbon dioxide exhibition in the body. During individuals taking part in these movements, tachypnea and hyperpnea are useful and reasonable instead of a signal of any health difficulties. It is your body’s way of satisfying these raised oxygen needs and obtaining rid of carbon dioxide.
Pathological causes
Some following situations could indicate that quick, shallow breathing issues are a severe health danger.
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN)
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) is an illness exclusive to newborn infants. For a few days after birth infants with Transient tachypnea of the newborn may take more than 60 breaths/minute. Other signs contain:
- snorting
- nasal flaring
- skin and muscles that seem to be surrendering during breathing
Regardless, this quick breathing generally brings sufficient without cure after 48 hours.
If a birthing parent provides a baby before their expected date, it creates TTN more possible. Yet, juveniles of any gestational period might have TTN straight after birth. TTN happens because the developing lungs feel a hesitation in removing liquid, even though it is indefinite precisely how this evolves.
Potential risk characteristics contain:
- delivery before 39 weeks of the gestation period
- cesarean delivery without struggle
- gestational diabetes in the parent
- asthma in the birthing parent
- existing small/large for their gestational period
- perinatal asphyxia, and decrease blood and gas transfer to and from the fetus near the moment of birth
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) is normally a mild illness seen at birth. Signs normally settle after 12-24 hours but may endure as prolonged as 72 hours in extreme circumstances. Thus, if signs obtain more harmful and do not determine shortly after delivery, a therapist may guide the child to a newborn intensive care unit (NICU) for oxygen supplementation, monitoring, and cure.
Allergic reactions
An allergic reaction to an individual stimulus may guide to a physical response that contains tachypnea.
Other conditions that may result in tachypnea
Infections
Infections that involve the lungs, for example, pneumonia and bronchitis, can lead to breathing problems. This can translate to quicker and additionally rapid breaths.
For example, juveniles 1 year and older with bronchiolitis may take more than 40 breaths/minute, as per the World Health Organization (WHO).
If these conditions acquire more harmful, the lungs could load with liquid. This causes it hard to take deep breaths. Some irregular illnesses can be incurable without therapy.
Respiratory issues
If constructional impairment, inflammation, and illness are involving how your lungs perform, your breathing is possible to evolve less effectively as an impact. These can be acute/chronic and may contain:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD): COPD is an ordinary lung illness. COPD contains chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Bronchitis is a rash of the airways, and emphysema is the descent of air sacs in the lungs.
- Pleural effusion: Pleural effusion happens when excessively large liquid constructs up between the slim membranes that streak the lung, also understood as the visceral pleura.
- Pulmonary embolism: Pulmonary embolism is a blood clot in the lung cavity. This can cause tachypnea, along with chest pain, coughing, and inconsistent breathing.
- Asthma: Tachypnea can be a sign of an asthma seizure. It is a chronic inflammatory illness of the lungs. It is often the reason for quick and superficial breathing in kids, which can be more destructive at night, after exercise, and while in touch with stimuli for example allergens and cold air.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning: If you respire in overly largely of the odorless, colorless gas carbon monoxide (CO), it could cause tachypnea, as well as a headache, nausea, dizziness, and potential unconsciousness.
Sepsis
Sepsis is a body-comprehensive illness that is potentially incurable. It is a medical emergency that generally evolves as an excessive reaction to an illness.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), lung illnesses are typical stimuli of sepsis, and tachypnea is one of its signs.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a severe illness that happens when your body does not create sufficient insulin. As an effect, acids named ketones assemble in your body.
Diabetic ketoacidosis frequently causes quick breathing, which contains hyperpnea & hyperventilation, to recompense for the buildup of ketoacids in the body. If your body can’t tolerate this raised breathing way, you may drain out, causing respiratory pain.
Epidemiology of Tachypnea
Tachypnea in infants is a difficulty with the respiratory system that can evolve obviously briefly after delivery. It can result from inadequate clearance of fetal lung liquid, which causes respiratory pain. Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) has a more elevated majority in preterm infants. It happens in around 1 in 100 preterm infants, whereas, in term infants, it presents in approximately 4-6 per 1000 infants.
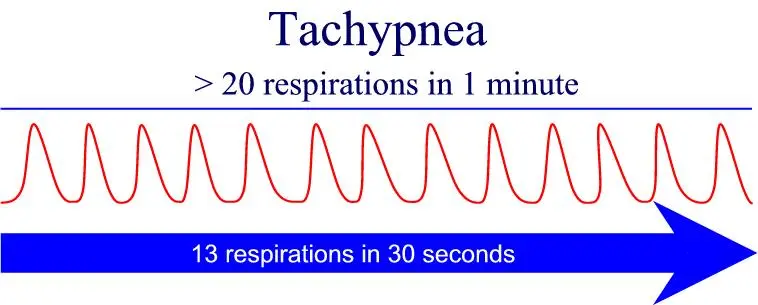
Tachypnea in adults is respiring additionally than 20 breaths/minute. 12-20 breaths/minute is a standard range.
Pathophysiology of Tachypnea
Tachypnea is a word utilized to describe quick and superficial breathing, which shouldn’t be complicated with hyperventilation, which is when a people’s breathing is quick but in-depth. Both are equal in that each result from a buildup of carbon dioxide in the lungs, causing raised carbon dioxide in the blood.
This buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood creates the blood more sarcastic than ordinary which warns the brain. In reaction, the brain signals the respiratory movement to grow in speed in an try to fix the inequality. In accomplishing so, the blood pH can replace within the standard range in acerbity.
What are the symptoms of Tachypnea?
When you have tachypnea, your breathing can sense quickly and superficially. You may even have other symptoms, For example:
- Dyspnea: shortness of breath and the feeling that you can not acquire sufficient oxygen
- Cyanosis: blue-colored fingers and lips
- Retracting: stinking in the chest muscles while breathing
Tachypnea may even happen without any noticeable signs. This is ordinary when it is affiliated with illnesses such as:
- Metabolic imbalances
- Central nervous system conditions
How to Diagnose Tachypnea?
History and Physical Examination:
Patients may present with objections to experiencing shortness of breath. They even may say that they don’t sense as if they can obtain in sufficient air. On physical exam, patients may have blue-colour fingers/lips and utilize supplement muscles/chest muscles to breathe. On the further hand, patients can present without any noticeable signs.
In infants, tachypnea can be because of fluid retention in the lungs within the first 24 hours of birth. Newborns can present with a blue color in the perioral region, grunting, and symptoms of breathing problems, retraction of the chest while breathing, shortening of the head, and spread of nostrils.
Evaluation:
The evaluation and reason for tachypnea are conditional on the general disposition of the patient. Therapists can estimate based on oximetry, arterial blood gases (ABG), chest x-ray, chest CT, pulmonary function tests (PFT), glucose, electrolytes, hemoglobin, EKG, VQ scan, brain MRI and a toxicology screen.
The diagnosis of tachypnea will contrast relying on age, other medical difficulties, existing drugs, and other signs. Some diagnostic implements may contain:
- Oximetry: A clip may be put on a finger to evaluate the amount of oxygen in the blood.
- Arterial blood gases (ABGs): These count oxygen level, carbon dioxide range, and the pH of your blood. The pH can aid examine for difficulties with metabolic processes of the body. If the pH is lower, examinations may be done to examine for reasons for example elevated levels of acid in the blood and liver difficulties.
- Chest X-ray: An X-ray can fast discover some reasons for tachypnea, like a crumpled lung.
- Chest computerized tomography (CT): This may be done to examine for lung illnesses/tumors.
- Pulmonary function tests (PFT): These are especially useful when examining illnesses such as COPD and asthma.
- Glucose: A blood sugar test is usually accomplished to supervise and establish diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) when the body constructs too many blood acids named ketones.
- Electrolytes: Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) levels can assist estimate some of the reasons for tachypnea.
- Hemoglobin: A entire blood count and hemoglobin test may be accomplished to examine for proof of anemia and illnesses.
- Electrocardiogram (EKG): An electrocardiogram can examine for proof of a heart attack/abnormal heart rhythms.
- VQ scan: This test estimates how air moves in and out of the lungs. It even estimates blood circulation in the lungs. It’s generally done if there is a chance that a blood clot is stopping one of the arteries that carry blood to the lung.
- Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): If no apparent reason for tachypnea is seen, a brain MRI may be useful. This can assist lead to brain irregularities like tumors.
- Toxicology screen: Many medications can induce tachypnea, involving medicine, over-the-counter, and prohibited medicines. In trouble scenes, a toxicology screen is usually done if the reason for tachypnea is anonymous.
Differential Diagnosis:
During tachypnea guides to quick, shallow breathing, other illnesses can even be misinterpreted for tachypnea as they may present likewise. Hyperpnea guides both rapid and deep breathing, and dyspnea demonstrates the sense of shortness of breath.
How Tachypnea Is Treated?
Treatment for tachypnea relies on the following reason.
For instance, if tachypnea is because of asthma/COPD, the doctor may define an inhaled drug, for example, a bronchodilator and epinephrine. The drug rapidly enlarges the alveoli in the lungs so that more additional oxygen can acquire in the lungs.
If tachypnea is because of pneumonia and another respiratory illness, determining the illness should set a termination to the tachypnea. This may entail antibiotics if the illness is bacterial, & supporting maintenance if the illness is viral.
If tachypnea is initiated by stress, encountering methods to control stress may control tachypnea in the future. Counseling, breathing training, and relaxation methods are all useful options to regard.
A therapist may help with oxygen via a mask/a tube put in the nostrils to regale tachypnea. This therapy is typical among younger children and newborns.
Treatment for tachypnea for elder children and adults generally implicates bringing slow deep breaths to control hyperventilation. To do this, you can breathe by operating the diaphragm during gradually breathing in via the nose and exhaling via the mouth/nose. This breathing method can assist you to relax by promoting the lungs to load up with air and raise fully.
If tachypnea induces extreme respiratory pain, seek emergency medical therapy. This might contain:
- Pressurized oxygen through a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) apparatus.
- Air from a ventilator device that forces air in and out of the lungs.
Relying on the reason for tachypnea, a cure for the following reason determines the sign and controls it from recurring. This kind of therapy could contain:
- Taking pills such as antibiotics, anticoagulants, and antihistamines.
- Utilizing an inhaler (bronchodilator).
- Experiencing mental behavioral treatment for stress.
Breathing Technique to Treat Tachypnea:
Diaphragmatic Breathing or Belly Breathing
The diaphragm is thought to accomplish the mainly of work during breathing. Diaphragmatic breathing exercise otherwise understood as belly breathing training encounters the diaphragm muscles and helps reinforce them to control stress on any other region of the body.
Obey these actions for the diaphragmatic breathing technique:
- Calm your body then sit/lie down, whichever you are considerably relaxed with.
- Put one of your palms on your abdomen and one on your chest.
- Gradually inspire via your nose for 2 seconds. Notice your breath driving from your chest and loading your abdomen.
- Breathe out for 2 seconds via pursed lips while pushing on your abdominal region.
- Do repeat these actions for 1 minute.
Diaphragmatic breathing is especially useful for people with COPD and also who are healing from COVID-19. These activities can be specifically useful in reconstructing your lung function. Confer with a professional doctor about designing a personalized training program.
Pursed-lip Breathing
Pursed lip breathing is usually utilized to calm your body, mind, and soul. This exercise functions by calming the muscles and maintaining your airway open for a longer duration of time, letting you be more physically engaged. This takes the stress off of your lungs and enables enhanced oxygen and carbon dioxide transfer. This method can be rehearsed at any time.
How to practice pursed-lip breathing:
- inspire via your nose gradually for a calculation of 4.
- Purse your lips concurrently.
- Kindly breathe out gradually via your pursed lips. Your exhale should take double as elongate as you inhale about 8 seconds.
- Do repeat this for 1 minute.
More Tips for Healthy Lungs
- Stop smoking and avoid areas where you could be disclosed to secondary smoke/other irritants.
- Be sure to maintain your air filters sanitary and decrease air impurities, for example, dust, mold, and dander to enhance your indoor air quality.
- Design a healthy and balanced diet and contain meals rich in antioxidants.
- Exercise frequently. Start physical activity at your convenience level and increase your workout performance as you build up your strength and endurance, for example, Do aerobic exercise.
- Keep up to date with your vaccinations. You should acquire vaccinated against the flu & pneumonia each year to encourage superior lung health and sidestep lung illnesses.
Prognosis of Tachypnea
Tachypnea may be involved in patients, but it isn’t consistently expressive of a necessary condition. Though patients usually need the guidance of a medical expert, there are a variety of reasons, and some may require quick medical consideration.
Complications of Tachypnea
Tachypnea can result from physiological reasons for example exercise, there are pathologic reasons that may be of consideration. The difficulties that occur from these pathologic reasons are ones that therapists should be acquainted with as they can guide to declining physical exams and patient supervision products.
Tachypnea can be a sign of sepsis and acidosis, like diabetic ketoacidosis and metabolic acidosis. Patients with lung difficulties for example pneumonia, pleural effusion, pulmonary embolism, COPD, asthma, and an allergic response even present with tachypnea. Congestive heart defeat can even be a reason for tachypnea and, if not controlled, can progress to declining heart defeat.
Anxiety states and hyperventilation while panic seizures would cause tachypnea and can cause hypocapnia and decreased carbon dioxide levels, decreasing respiratory movement.
How can tachypnea be prevented?
Not all reasons for tachypnea can be controlled. You can take actions to decrease the chance of tachypnea by:
- Avoiding allergens.
- Exercising regularly to assemble persistence.
- Avoiding places with smoke and high pollution.
- Putting a carbon monoxide sensor in your home and transforming the batteries every six months.
- Consult with a cognitive health specialist to regale anxiety.
- Regaling or handling any following requirements.
Conclusion
Tachypnea defines as abnormally quick breathing. It isn’t identical to dyspnea, where you sense as if you aren’t accumulating sufficient air.
You may sense tachypnea because your body is endeavoring to restore something weird that is happening in your body. It could even be induced by something superficial, like fear/anxiety.
FAQ
How long does tachypnea last?
Newborns generally rescue from transient tachypnea within 2-3 days. After a cure for the reason for tachypnea, elder children and adults recover fast. Tachypnea can arrive back if the cause is not regaled.
Which is the difference between Tachypnea and dyspnea?
The words tachypnea and dyspnea represent different things:
Tachypnea: This is a medical definition of quick, shallow breathing, with no emphasis on how the sensory experience for the individual undergoing it.
Dyspnea: This is a word that represents the sense of breathlessness. Some individuals with tachypnea will undergo breathlessness, but others may not.
What are tachypnea and bradypnea?
Bradypnea is a respiratory speed that is inferior to normal for a period. Tachypnea is a respiratory speed that is greater than usual for age. Hyperpnea in expanded volume with/without an improved rate of breathing.
What is tachypnea vs tachycardia?
Quick breathing (tachypnea) and heartbeat (tachycardia): Fit adults carry 12-20 breaths/minute. More than 20 breaths demonstrate abnormally quick breathing known as tachypnea. A resting heart speed more elevated than the usual 60-100 beats/minute is named tachycardia.
What drugs cause tachypnea?
Aspirin, stimulants, and marijuana use of this drugs can induce a rapid, shallow breathing speed. Though not an immediate reason, chemotherapy can induce anemia, which can exacerbate tachypnea.