Grip Muscles – Anatomy and Exercise
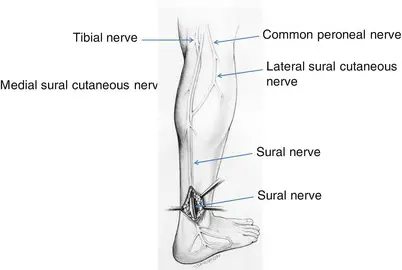
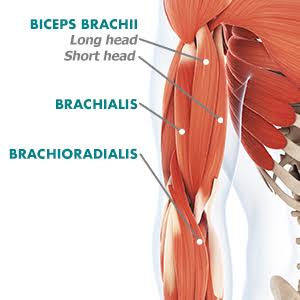
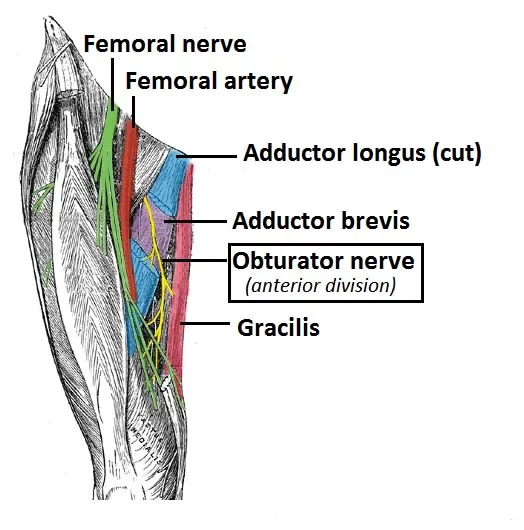
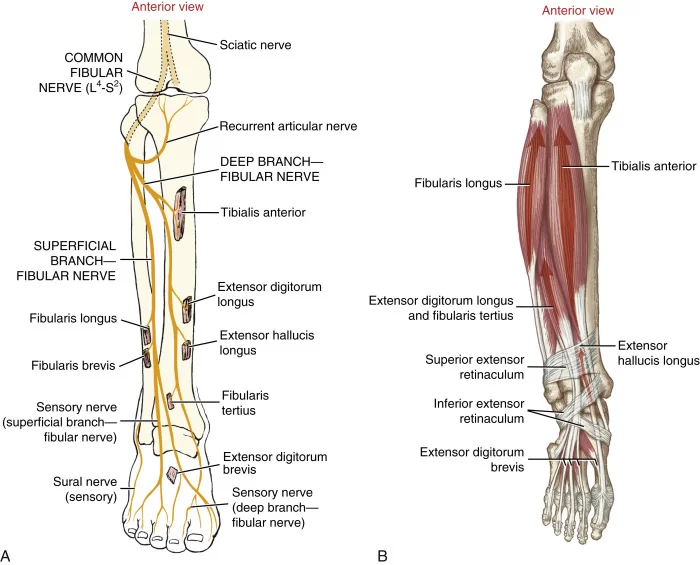
Introduction The muscles that are involved in the act of gripping are known as Grip Muscles, the Grip Muscles are flexor digitorum profundus, flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digiti minimi brevis, flexor pollicis longus, extensor digitorum, lumbricals, interossei, adductor pollicis. Anatomy of Grip Muscles 1. Flexor Digitorum Profundus Origin It originates from the upper 3/4 of…