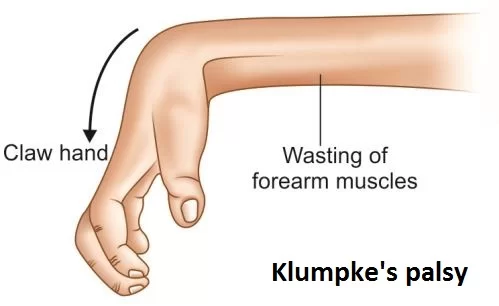
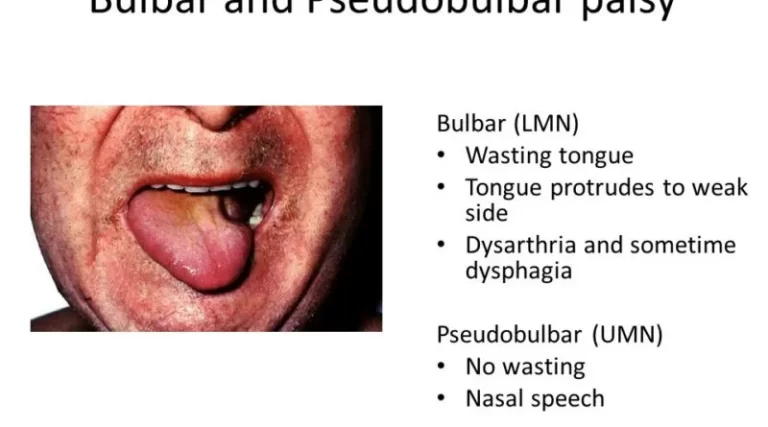
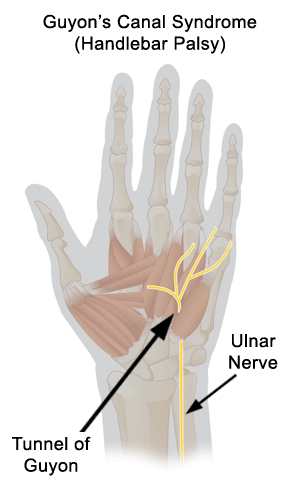
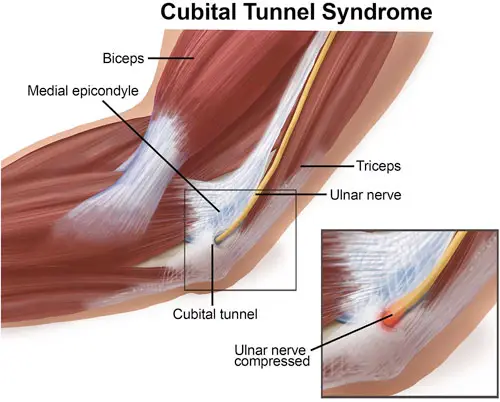
Post-herpetic neuralgia
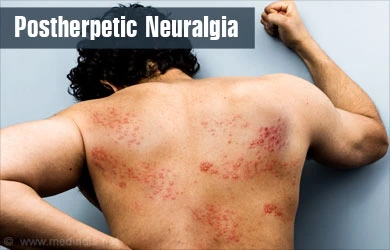
What is Post-herpetic neuralgia? Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a complication of shingles infection (also known as herpes zoster). Shingles are caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, which is the exact virus that induces chickenpox. Shingles cause an aching, blistering rash and further symptoms. The rash most generally happens in a band pattern on…