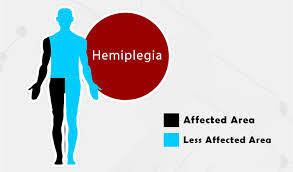
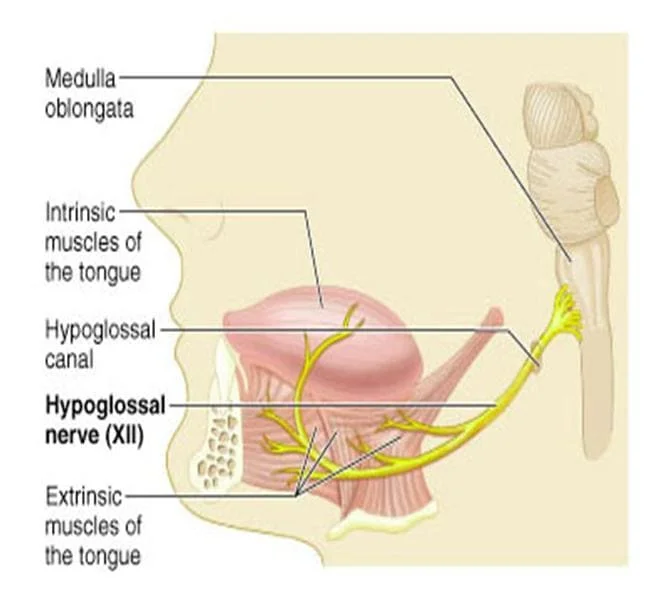
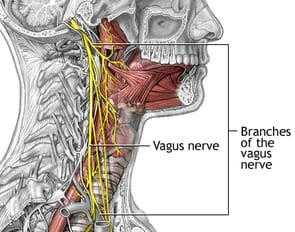
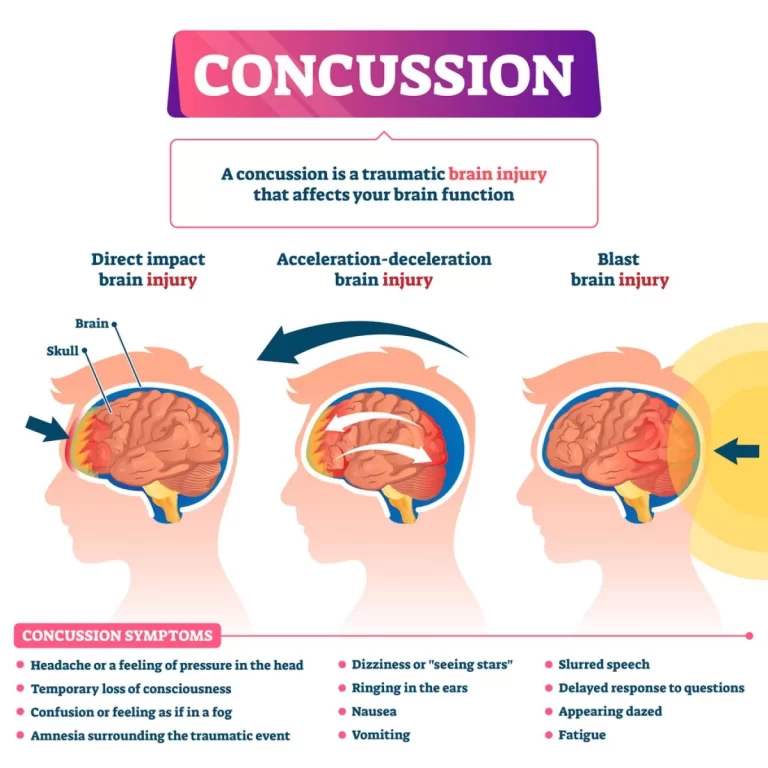
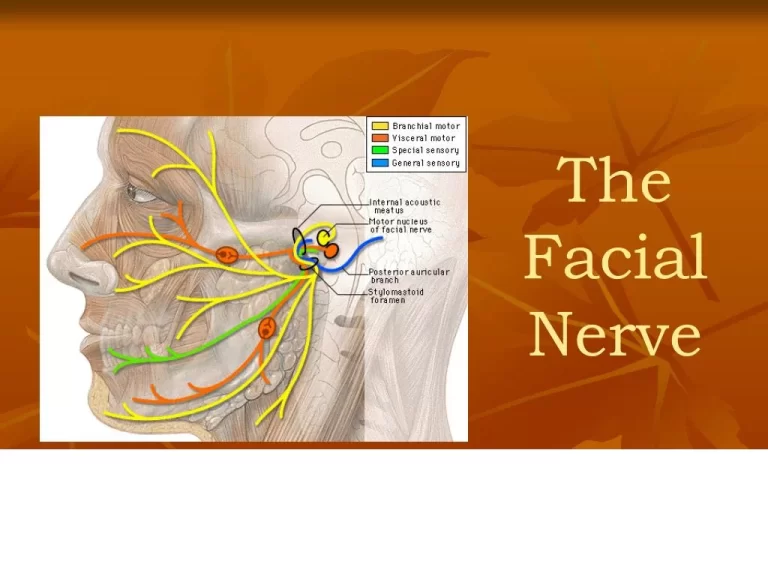
HEMIPLEGIA
WHAT IS HEMIPLEGIA ? Right Hemiplegia vs Left Hemiplegia WHAT ARE THE CAUSE OF HEMIPLEGIA? Stroke Brain and Nervous System Infections Brain Trauma Genetic Disorders/Congenital Diseases Brain Tumors Brain Lesions Brain Diseases Psychological Conditions Cardiovascular Problems Loss of Oxygen to the Brain Causes of Right-Sided Hemiplegia? The causes of hemiplegia include neurological conditions such as:…