Depressor supercilii muscle
Introduction
Latin musculus depressor supercilii
Anatomical terms of muscle :
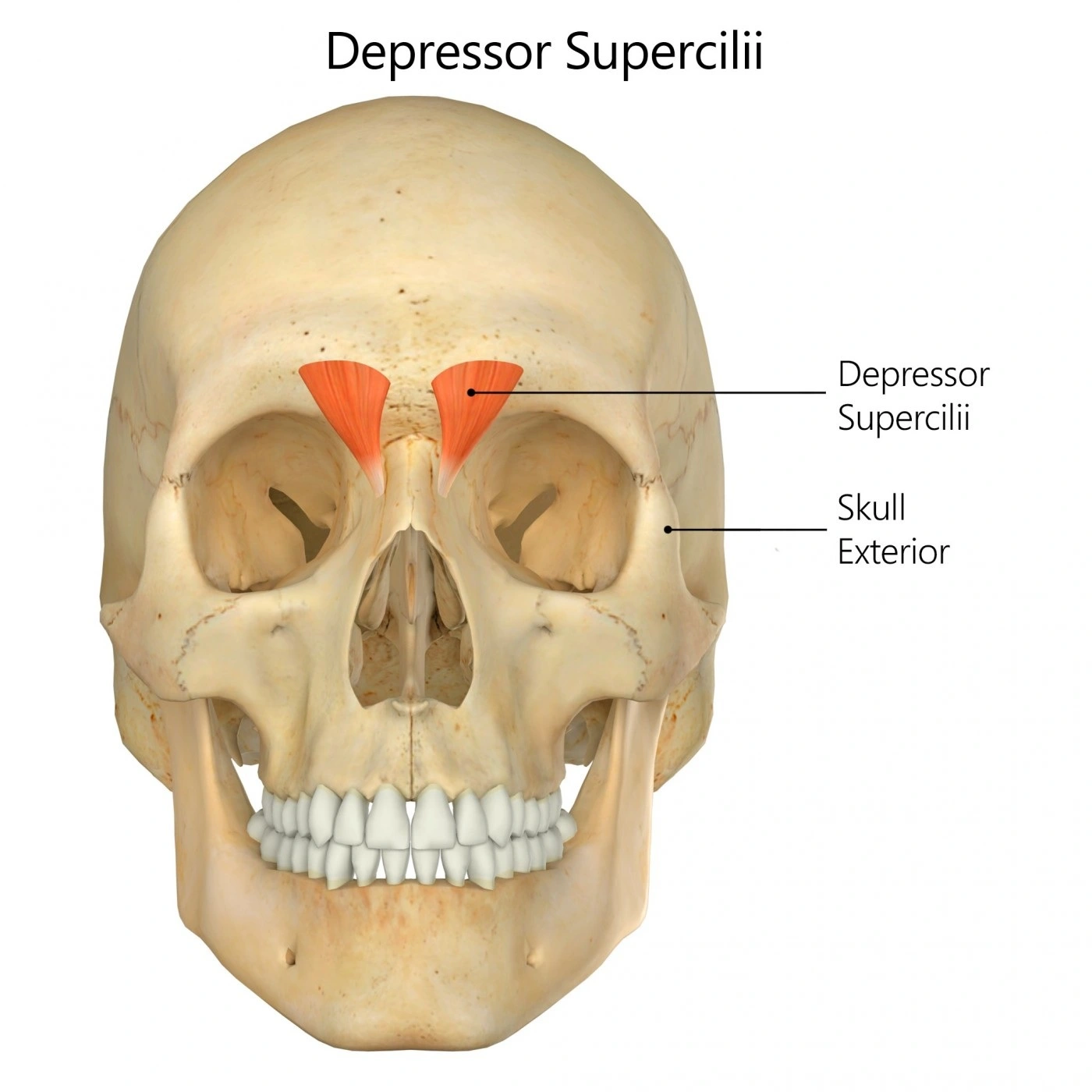
The depressor supercilii muscle is found near the eye, and it’s thought to assist in moving and lowering the eyebrow. Also, it’s thought to assist in moving the glabella, which is the skin above the nose and between the eyebrows.
The depressor supercilii is an eye-fixed muscle of the human body. The character of this muscle is in some dispute. Few printed anatomies include it and lots of authorities consider it to be part of the orbicularis oculi muscle.
On the opposite hand, many dermatologists, ophthalmologists, and plastic surgeons hold that the depressor supercilii may be a distinct muscle and has a definite, individual effect on the movement of the eyebrow and skin of the glabella.
Origin and insertion :
The depressor supercilii originates on the medial orbital rim, close to the lacrimal bone, and inserts on the medial aspect of the bony orbit, inferior to the corrugator supercilii. In a few specimens it exhibits two heads and in others, only one.
Nerve supply :
The facial nerve supplies the depressor supercilii muscle.
Action :
The main activity done by the depressor supercilii muscle is the depression of the eyebrow.
Depressor supercilii exercises :
Frown (assisted):
Using your fingers to help, pull your forehead muscles downwards and inwards, creating a frown. Hold this position, then relax.
The depressor supercilii muscle is different from the corrugator supercilii muscle and therefore the medial head of the orbital portion of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The depressor supercilii muscle was noted to be superior in orientation and dark redder in colour than the orbicularis oculi muscle. The depressor supercilii muscle arises from the frontal process of the maxilla approximately 1 cm above the medial canthal tendon and seemed to originate from two distinct heads in most specimens, a unique finding. In specimens containing two heads of the depressor supercilii muscle, the angular vessels pass between both muscle heads. In the specimen containing one muscle head, the angular vessels were found anterior to the muscle. The insertion of the depressor supercilii muscle within the dermis lay approximately 13 to 14 mm superior to the medial canthal tendon.
In comparison to other muscles of the face, it’s relatively small. However, among physicians and researchers, there’s still debate over whether the depressor supercilii is part of the orbicularis oculi. Some plastic surgeons believe the muscle to be independent of its specific function, while other physicians argue that this muscle is a segment of the orbicularis oculi muscle.
Depressor supercilii muscle Video
Researches
The DS was connected to the LLSAN or the OOc INF by the muscle fibres or aponeuroses in 33 of the 44 (75.0%) specimens. The DS was connected to both, the LLSAN and OOc INF by muscle fibres or aponeuroses and has no connection to each in 5 (11.4%) and 11 (25.0%) specimens, respectively.
The DS is connected to the LLSAN by muscle fibres and thin aponeuroses in 6 (13.6%) and 4 (9.1%) of the 44 specimens, respectively. The muscle fibres or aponeuroses connecting to the DS and LLSAN are often attached to the originating fibres of the LLSAN and sometimes to the centre portion of the LLSAN. The connecting muscle fibres or aponeurosis between the DS and LLSAN attended to be thicker than those between the DS and OOc INF. The DS is connected to the OOc INF by muscle fibres and thin aponeuroses in 5 (11.4%) and 23 (52.3%) of the 44 specimens, respectively. within the cases where the DS was connected to the OOc INF by thin aponeuroses, the muscle fibres of the OOc INF replaced the skinny aponeurosis, coursing on the medial palpebral ligament, and therefore the thin aponeurosis of the OOc INF was then connected to the DS. One specimen had both thin aponeuroses between the DS and OOc INF.
Among the five specimens where the DS is connected to both the LLSAN and OOc INF, the DS of one specimen had muscle fibres connecting to the LLSAN and OOc INF. The DS in one specimen has aponeuroses connected to the LLSAN and OOc INF. The DS in three specimens has muscle fibres and aponeurosis connected to the LLSAN and OOc INF, respectively. Within the specimen that had muscle fibres of the DS connected to both the LLSAN and OOc INF, two muscle fibres were connected before combining with the DS.
The muscle fibres or a skinny aponeurosis connected to the DS and LLSAN were often situated slightly medial to the angular vein, and sometimes slightly lateral or superficial to the angular vein, whereas the muscle fibres or a skinny aponeurosis connected to the DS and OOc INF were often situated slightly lateral to and sometimes superficial to the angular vein. Both aponeuroses were found between the DS and OOc INF in one specimen, with each aponeurosis situated just medial and lateral to the angular vein.
Sex-related differences in the majority of the muscle fibres or the aponeurosis connecting the DS and LLSAN or between the DS and OOc INF were studied. Muscle fibres or aponeurosis were connected to the DS and LLSAN and the DS and OOc in 5 males and 5 females, and in 15 males and 13 females, respectively. Regardless, our study indicates a significant difference between males and females in the prevalence of muscle fibres connecting to the DS and LLSAN or the DS and OOc INF: all five specimens with muscle fibres connected to the DS and OOc INF are male, while males are formed by four of the six specimens with muscle fibres connected to the DS and LLSAN. The existence of muscle fibres or aponeurosis connecting to the DS and LLSAN and the DS and OOc was found to be symmetrical in one male and two females, and six males and four females, respectively.
FAQ
Is the depressor supercilii a depressor of the eyebrow?
The insertion of the depressor supercilii muscle in the dermis lie approx 13 to 14 mm superior to the medial canthal tendon. The origin, insertion, and anatomy of the depressor supercilii muscle help it to act as a depressor of the eyebrow.
What cranial nerve innervates the depressor supercilii?
The depressor supercilii muscle is innervated by the temporal divisions of the 7th cranial nerve ( facial nerve ). The depressor supercilii muscle leads the eyebrow downwards.
What is the literal meaning of the depressor supercilli muscle?
The literal meaning of this depressor supercilli muscle is that it presses the partition down.
What are some interesting information about depressor supercilli muscle?
The nature of this muscle is controversy. Some researches consider it to be part of the orbicularis oculi muscle, while others maintain that the depressor supercilii is a muscle and has a definite, individual effect on the motion of the eyebrow and skin of the glabella
Is depressor supercilli muscle can be considered in facial muscle?
Yes, the depressor supercilli is considered in the facial muscle which is situated between both the eyebrows and orbits.