Flexor digitorum brevis muscle
What is the Flexor digitorum brevis muscle?
Flexor digitorum brevis (FDB) is a broad muscle located deep in the sole. Because the plantar foot muscles can be broken down into groups (medial to lateral) or layers (superficial to deep), there are two ways to specify the exact location of the flexor digitorum brevis:
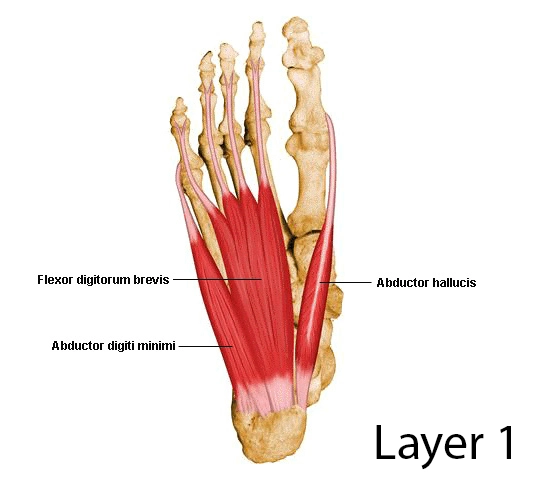
Along with the abductor hallucis and abductor digiti minimi muscles, it is a member of the first layer of plantar muscles.
It is categorized as the central plantar muscles of the foot, together with quadratus plantae, lumbricals, plantar interossei, and dorsal interossei muscles.
Toe flexion at the metatarsophalangeal joints of the lateral four digits is controlled by the flexor digitorum brevis. It also helps the longitudinal arch of the foot while moving the body forward during gait.
Origin
The central portion of the plantar aponeurosis and the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity which places the Flexor Digitorum Brevis muscle arrives.
Insertion
A tendon attaches each toe to the middle phalanges of the four lateral toes, where the muscle inserts.
Relations
The muscles of the abductor hallucis and abductor digiti minimi are both lateral to the flexor digitorum brevis. This muscle passes deep to the dense layer of the plantar aponeurosis. Flexor digitorum brevis muscle tendons arrive medially to the common plantar digital nerves and vessels. Deep to flexor digitorum brevis you can see quadratus plantae and lumbrical muscles together with the tendons of the flexor digitorum longus muscle.
Innervation
The medial plantar nerve (S1-S3), which is the larger of the two terminal parts of the tibial nerve, is where the flexor digitorum brevis muscle gets its innervation.
Blood supply
The posterior tibial artery’s components vascularize the flexor digitorum brevis muscle; arteries of the medial and lateral plantar regions. The further blood supply reaches from the parts of the anastomotic network of anterior tibial and posterior tibial arteries; common plantar digital arteries and plantar metatarsal arteries
The majority of the blood that comes from the flexor digitorum brevis muscle goes into the anterior and posterior tibial veins through the medial plantar vein. Further drainage is conducted by a deep plantar venous arch.
Function of Flexor digitorum brevis muscle
The primary action of the flexor digitorum brevis is the flexion of the second to fifth digits at the metatarsophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints. This order of movements is various from flexor digitorum longus muscle which also works as a flexor of phalanges, but begins with flexion in distal interphalangeal joins.
Because they work together to keep the toes firmly planted on the ground, these two muscles must be coordinated for the gait cycle. This muscle also helps the longitudinal arch of the foot and stabilizes the foot while walking or running.
Clinical relevance
The Flexor Digitorum Brevis is a foot muscle that plays a crucial role in stabilizing the longitudinal arch of the foot.
Flexor digitorum brevis muscle stretching
Toes 2 to 5 at the metatarsophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints stretch the flexor digitorum brevis, the foot’s internal muscle.

Flexor digitorum brevis muscle strengthening
Toe flexion on both sides
Whether you’re sitting or standing, flex the toes toward the floor. Hold, relax, and afterward do it again.
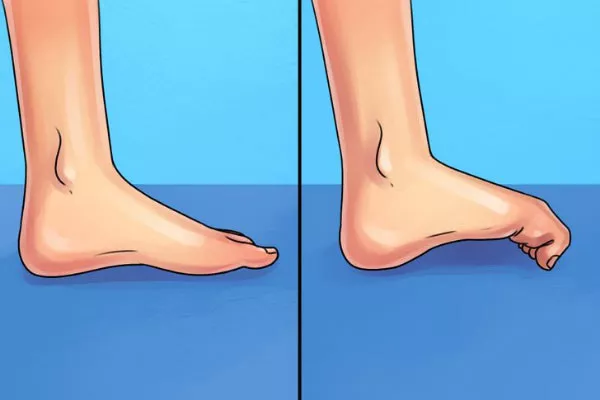
Arch lifts
The arch lift activity is a muscle activation activity to teach you how to keep or maintain the intrinsic foot muscles liable for stabilizing the medial longitudinal arch. To do this activity perfectly it’ll be essential to note that the toes and calf muscles should be relaxed during this activity. In this respect, it is an activity to assist you dissociate the intrinsic foot muscle role from toe and ankle function.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of a flexor digitorum brevis injury?
Dysfunction of the flexor hallucis brevis will generally present as an ache in the ball of the foot when extending the great toe, a problem and ache during gait, and toe deformities. This might be because of muscle injury of the flexor digitorum brevis or sesamoiditis.
How do you strengthen flexor digitorum brevis?
Toe flexion on both sides
Standing or sitting, flex the toes downwards, towards the bottom. Maintain, relax, and then repeat.
Where is flexor digitorum brevis?
The Flexor digitorum brevis is situated in the sole, straight over the central area of the plantar aponeurosis, which it is strongly connected to.
Why is foot strength important?
These muscles are essential in both balance and ‘posture’ of the lower body. Poor “posture” in the foot, like bad posture in the back, can cause pain and possibly injury further up the kinetic chain. Having strong feet is essential to stabilize the posterior chain at the lowest level.
What is the function of the digitorum brevis?
When the foot is fully dorsiflexed, the extensor digitorum brevis extends or straightens the middle three toes.



One Comment