Pectoral Nerves
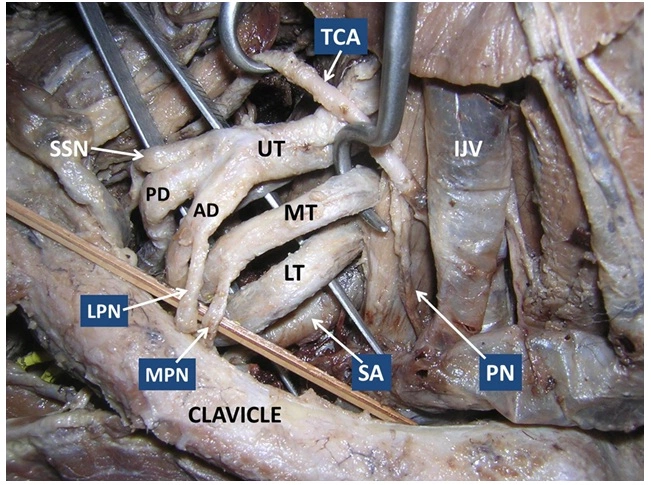
Medial pectoral nerve
The medial pectoral nerve, this is also known as the medial anterior thoracic nerve, is a branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus. alongside originating, the nerve travels together with the axillary artery & vein, being located between them.
The medial pectoral nerve is lonely a motor nerve. Its main function is to give motor supply for the pectoralis major & pectoralis minor muscles.
Anatomy & function of the medial pectoral nerve
Origin and course
Medial pectoral nerve
- The medial pectoral nerve (C8, T1) rises as the lateral branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus. It originates posterior to the axillary artery. Upon originating, the nerve travels anteriorly towards the pectoral muscles alongside the axillary vein and axillary artery. Before reaching the lower margin of the pectoralis minor muscle,
- The nerve partly terminates by penetrating or piercing the pectoralis minor muscle. Some fibers appear from the lateral aspect of the muscle and continue towards the pectoralis major muscle to supply it.
Branches and innervation
- Pectoralis major muscle
- Pectoralis minor muscle
- the medial pectoral nerve gives off two sets of muscular branches; one for supplying the pectoralis minor, and the another for supplying a portion of the pectoralis major.
- This specific part of the pectoralis’s major function is to extend the arm at the shoulder from a flexed position. Therefore, the injury of the medial pectoral nerve commonly leads to the inability to elevate the shoulder.
Clinical relations
Medial pectoral nerve injury
The medial pectoral nerve is normally injured the direct trauma to the axillary region. in Addition, it can be injured iatrogenically, during surgical procedures in this region (e.g. breast surgery, axillary node dissection). The clinical presentation of the injury depends on the level of nerve injury. normally the patients complain about pain in the chest wall or the inability to elevate the shoulder. The diagnosis is best confirmed by imaging procedures such as MRI and electrodiagnostic testing procedures. Treatment is usually conservative or surgical.
Lateral pectoral nerve
The lateral pectoral nerve, also known as the lateral anterior thoracic nerve, is a branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus. sometimes it might also arise from the anterior divisions of the upper and middle trunks of the brachial plexus. The lateral pectoral nerve carries fibers from C5, C6 & C7 spinal nerves. After emerging, the nerve travels anteriorly, piercing the clavipectoral fascia to reach the deep surface of the pectoral muscles.
The lateral pectoral nerve mostly carries motor fibers. Its main function is to give motor supply primarily to the pectoralis major muscle, but also gives minor contributions to the pectoralis minor muscle.
Origin, course, and innervation
Lateral pectoral nerve
- The lateral pectoral nerve (C5, C6, C7) typically rises as the most proximal branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, immediately above or deep to the clavicle. From its origin, the nerve travels anteriorly across the axillary artery and vein toward the pectoral muscles. Together with the thoracoacromial artery, the lateral pectoral nerve pierces or penetrates the costocoracoid membrane, which is the upper deep portion of the clavipectoral fascia that extends from the first ribcage to the coracoid process of the scapula. The nerve then discontinues at the deep surface of the pectoralis major muscle, supplying it.
- directly after appearing from the lateral cord, the lateral pectoral nerve gives a communicating branch to the medial pectoral nerve. This communicating branch forms a loop called ansa pectoralis, which travels anterior to the first part of the axillary vessels, giving nerve fibers that supply the pectoralis minor muscle
- The medial pectoral nerve gives rise to muscular branches that supply the pectoralis major muscle. This muscle is involved in adduction, internal rotation, flexion, and extension of the arm at the shoulder joint, as well as drawing of the scapula anteroinferior at the scapulothoracic joint. In addition, the lateral pectoral nerve sends a communicating branch to the medial pectoral nerve to supply the pectoralis minor muscle. The lateral pectoral nerve also supplies the anterosuperior part of the glenohumeral joint capsule.
Clinical relations
Lateral pectoral nerve injury
Injuries of the brachial plexus frequently result in the dysfunction of the lateral pectoral nerve. However, isolated lesions of the nerve are uncommon and rare. The few reported cases of such lesions have been related to traction injuries from sports, seat belts in car accidents, and compression injuries from repeated contractions of the pectoralis major muscle in targeted training administration.
The nerve can also be injured iatrogenically, during surgical procedures in the pectoral region or surface such as breast surgery. Clinically, patients present with weakness and atrophy of the pectoral muscles or some parts of the pectoral muscles. Treatment is either conservative or surgical, based on the level of injury or severity of functional deficiency.
FAQ
What happens if the pectoral nerve is damaged?
Due to the insertion of the pectoralis minor muscle to the coracoid apophysis, this muscle helps produce a medial rotation of the scapula against resistance, with the scapula & the upper limb fixed. Therefore, an injury to the medial pectoral nerve can cause an inability to elevate the shoulder.
Where do pectoral nerves originate?
The pectoral nerves rise from the brachial plexus supplying pectoral muscles. The lateral pectoral nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus and contains fibers from cervical spinal nerves C5, C6, and C7.
What are the pectoral nerves called?
The lateral pectoral nerve also called the lateral anterior thoracic nerve, which is the branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus. sometimes, it may also arise from the anterior divisions of the upper & middle trunks of the brachial plexus.
How long does a pectoral nerve block last?
The nerve block can last up to 24 hrs. During this time: It is important to protect your chest wall and breast from injury.
What muscles does the pectoral nerve innervate?
It innervates the pectoralis major muscle and gives fascicles to the ansa pectoralis, an anastomosis with the medial pectoral nerve
How serious is a pectoralis tear?
Pectoralis major tears are more commonest among young, physically active men between the age of 20 and 40, especially athletes. This injury can cause serious disability