Posterior auricular nerve
Introduction
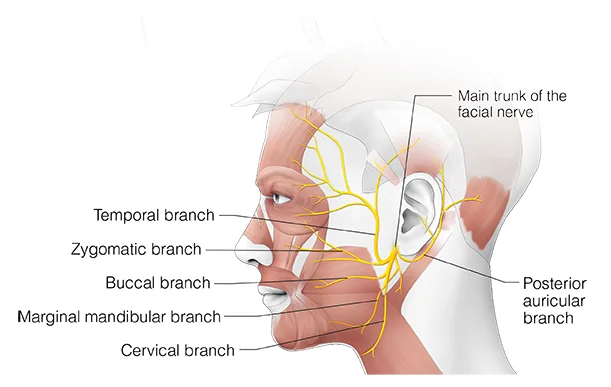
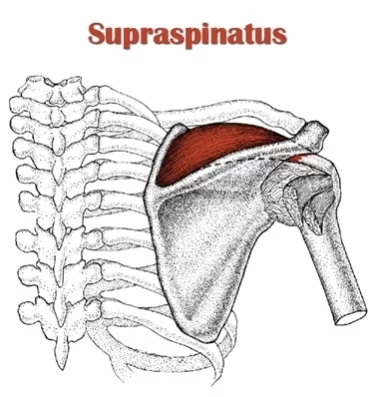
The posterior auricular nerve
The posterior auricular nerve is the first extracranial branch of the facial nerve trunk. It supplies the posterior belly of the occipitofrontalis and the auricular muscles and provides cutaneous sensation from the skin envelope of the mastoid process and parts of the auricle.
Extracranial branches
The facial nerve leaves the skull through the stylomastoid foramen, after which it gives off the following branches:
The posterior auricular nerve is the first extracranial branch to appear which continues to give motor supply to the occipital belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle (occipital branch) and intrinsic auricular muscles (auricular branch). It uniformly supplies the skin and all around the external acoustic meatus and the retroauricular region.
in addition, the digastric and stylohyoid branches of the facial nerve are given off which carry motor fibers to the particular muscles.
Finally, the facial nerve penetrates the parotid gland (but does not supply it) and bifurcates into superior (temporofacial) and inferior (cervicofacial) trunks, which again give rise to its five terminal branches:
- Temporal branches: they supply the frontalis muscle, orbicularis oculi muscle, and corrugator supercilii muscles.
- Zygomatic branches: supply the orbicularis oculi muscle.
- Buccal branches: it supplies the orbicularis oris muscle, buccinator muscle, and zygomaticus muscles.
- Marginal mandibular branch: it supplies the depressor labii inferioris, depressor anguli oris, and mentalis muscles.
- Cervical branch: it supplies the platysma muscle in the neck.
FAQ
What does the posterior auricular nerve affect?
The posterior auricular nerve innervates the occipitalis muscle, part of the occipitofrontalis muscle, as well as the auricularis posterior (a vestigial muscle in humans), interscutularis, and intrinsic ear muscles.
Why is my posterior auricular hurting?
Many things can cause pain behind the ear, which include infections, impacted earwax, dental problems, Temporomandibular joint disorder, and nerve irritation. A healthcare professional can get to the bottom of the pain after taking a medical history and examination. The treatment will rely on the source of the pain.
What happens if the great auricular nerve is get damaged?
Injuries to the great auricular nerve can certainly cause numbness of the earlobe and upper neck surface. This injury is normally always observed immediately following surgery. The onset of numbness seven months following surgery makes great auricular nerve injury unexpected.
Which nerve separates the auricular posterior nerve?
the facial nerve
The posterior auricular nerve is a branch of the facial nerve (CN VII). It conveys branches from the vagus nerve, the great auricular nerve, and the lesser occipital nerve.
Is the posterior auricular nerve motor or sensory?
The first extracranial branch to get arise is the posterior auricular nerve, giving motor innervation to some of the extraarticular muscles. instantly distal to this, motor branches are sent to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and to the stylohyoid muscle.
Is pain behind the ear serious?
Seeking a healthcare provider is crucial because there are many possible conditions for pain or a headache behind the ear, and you need a proper diagnosis to be able to treat it and ease the pain.
What helps nerve pain behind the ear?
Non-surgical Treatments
Heat: patients frequently feel relief when heating pads or devices are placed in the location of the pain.
Physical therapy or massage therapy.
Oral Medication:
Percutaneous nerve blocks: these injections can be used for both diagnosis and treatment purposes in occipital neuralgia.
Can stress cause pain behind the ear?
These joints can become inflamed or swollen and painful. While most people with Temporomandibular joint inflammation feel the pain in the jaw and behind the ear, others may just experience a headache behind the ear. TMJ can be caused by: stress.
What type of headache is behind the ear?
Occipital neuralgia: Inflamed or injured nerves that supply the scalp cause occipital neuralgia. Pain from this source can be piercing, throbbing, or severe in the upper neck, back of the head, or behind the ears. The pain is relieved by anti-inflammatory medicines and pain medications
How to know if nerve damage is healing?
As the nerve recovers, the area the nerve supplies may feel a little unpleasant and tingly. This may be accompanied by an electric shock sensation at the level of the growing nerve fibers; the region of this sensation should move as the nerve heals and grows