Procerus Muscle
Introduction
The procerus muscle is a small facial muscle located between the eyebrows and the bridge of the nose. It is responsible for causing the skin to wrinkle vertically, which results in the formation of horizontal lines on the forehead.
The procerus muscle is a pyramidal-shaped muscle of facial expression part of the glabellar complex.
The procerus muscle is derived from the second pharyngeal arch, innervated by branches of the facial nerve, and supplied by the facial artery via the external carotid artery.
The structure and functionality of the procerus muscle and the associated glabellar complex are of clinical importance in cosmetic and surgical procedures, including botulinum toxin injection, injectable fillers, and blepharoplasty.
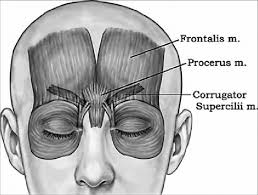
Procerus Muscle Anatomy
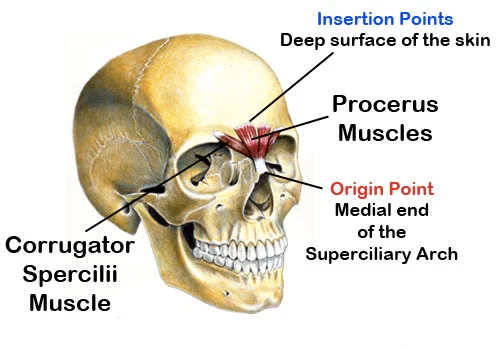
Procerus is one of the muscles of the forehead and nose.
It arises from the fascia overlying the superior surface of the nasal bones and the superior parts of the upper lateral nasal cartilages.
It passes superiorly to insert into the skin of the inferomedial forehead. It is in continuity with the occipitofrontalis muscle.
It is innervated by the temporal branch of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Procerus acts to produce transverse wrinkles in the skin overlying the nasal radix. Also, it acts to depress the brow and by fixing the upper part of the nose, may indirectly assist with nasal flaring.
It is targeted in the anti-wrinkle treatment of injected botulinum toxin for cosmetic purposes.
Origin
- The procerus originates from the midline of the nasal bone and from the nasal cartilage.
Insertion
- The procerus inserts into skin of the lower part of the forehead between the eyebrows and into the frontal belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle.
Action
- The procerus depresses the medial eyebrow angle.
- When contracting, the procerus muscle depresses the medial parts of the eyebrows and wrinkles the skin between them.
- This action enables frowning, making procerus an important contributor to the expansive array of human facial expressions.
- Contractions of procerus are responsible for producing a transverse fold across the root of the nose.
Nerve Supply
- The nerve supply to the procerus is provided by the buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Blood Supply and Lymphatics
- The procerus muscle receives its blood supply via branches of the facial artery.
- The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies the superficial face.
- Lymphatics from the face, scalp, and neck drain into the superficial ring of lymph nodes, these lymph nodes are known as the pericervical collar.
- This ring of lymph nodes includes the submental, submandibular, parotid, mastoid, and occipital lymph nodes.
Structure and Function:
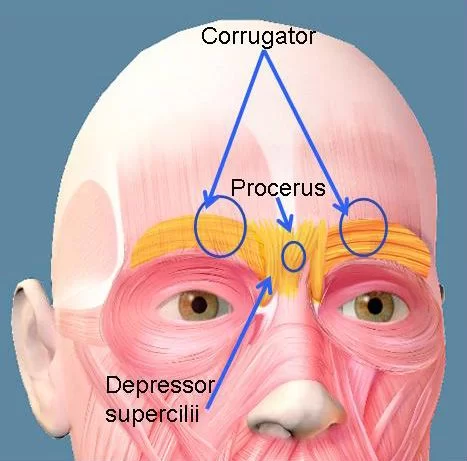
- The procerus muscle is a pyramidal-shaped muscle arising from the fascia of the superior nasal region, near the junction of the nasal bones, and the superolateral nasal cartilage.
- The procerus muscle fibers run superiorly and merge with the frontalis muscle. Muscle fibers insert into the skin between the eyebrows.
- The procerus muscle is located inferomedial to the frontalis muscles bilaterally.
- The corrugator supercilii, depressor supercilii, and orbicularis oculi muscles are in close proximity, located just lateral to the procerus muscle bilaterally.
- The nasalis muscle is inferior to the procerus muscle.
- The procerus muscle works with other muscles part of the glabellar complex.
- The glabellar complex includes bilateral fibers of the procerus, frontalis, corrugator supercilii, depressor supercilii, and orbicularis oculi muscles.
- These muscles depress the medial eyebrow, producing transverse cutaneous furrows, and also assist nostril flaring.
Procerus Muscle Exercise
Strengthening exercise
Place your index finger on the centre of your brows and extend them out while simultaneously inwardly squeezing them to strengthen the procerus.
Stretching exercise
The procerus responds well to this stretch. This stretch works to balance out the horizontal line that can be seen on the nose’s bridge.
Put both of your index fingers on the bridge of your nose while maintaining a neutral expression on your face.
Glide your fingers firmly upward, applying mild pressure. Stretch out fully and hold for 5 seconds.
then take a break. Increase the number of reps each week, starting with 5 reps per day and working your way up to 10.
Other Images of the Muscle:
FAQs
What does the procerus muscle do?
The medial portions of the eyebrows and the skin between them are depressed and wrinkled as the procerus muscle contracts. Procerus is a key component in the wide range of human facial emotions because it makes frowning possible.
What is the location of the procerus muscle?
Procerus muscle is located near the intersection of the nasal bones and the superolateral nasal cartilage, the procerus muscle emerges from the fascia of the superior nasal area. The procerus muscle’ superior fibres converge with those of the frontalis muscle. In the area of skin between the eyebrows, there are muscle fibres located.
What is the name of the procerus muscle?
musculus pyramidalis nasi
The procerus is a triangular-shaped facial expression muscle that is situated in the glabellar region between the forehead and the dorsum of the nose (Latin: musculus procerus, musculus pyramidalis nasi). It is categorized as the facial muscle of the nose.
How do you relax procerus?
Flick Between the Eyebrows
Next, flick your thumb repeatedly upward between your brows. The procerus muscle, which runs up between the eyebrows and extends out across the forehead, is relaxed by this motion. The procerus muscle is very tense in many people.