Upper Back Pain
What Is the Upper Back?
Upper back pain refers to discomfort or pain felt in the region between the base of the neck and the bottom of the rib cage. The upper back, also known as the thoracic spine, is composed of 12 vertebrae and is responsible for protecting the organs in the chest cavity, providing stability and support to the neck and shoulders, and facilitating the movements of the trunk.
Upper back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor posture, muscular strain or overuse, trauma, spinal abnormalities such as herniated discs or scoliosis, or medical conditions such as arthritis or osteoporosis. Symptoms of upper back pain may include aching, stiffness, burning, or sharp pain in the affected area, as well as difficulty moving or performing daily activities.
Treatment for upper back pain typically involves rest, physical therapy, pain management techniques such as hot or cold therapy, and in some cases, medication or surgery. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of the pain and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
- This upper back is the area that is situated next to the cervical spine – neck & above the low back(lumbar spine).
- Occasionally the upper back is also known as the thoracic spine & which is the stable region in the spine.
- The thoracic spine’s attachments to the ribs lead to the restricted range of motion of the upper back.
Some muscles attachments of the upper back:
- Trapezius muscle: It is situated near your shoulder blade which permits you to stand straight & throw.
- Latissimus dorsi: It is situated at the lower end of the scapula to the hip bone on your back which is help with arm movement & breathing.
- Rhomboids: It is Adjoining to the trapezius muscle which is provided support to your shoulder joint & helps you pull.
What are the Causes of Upper Back Pain?
This pain happens generally because of soft tissue(muscles and ligaments) injuries like sprains & strains.
This pain also happens because of muscle stress which is generated due to poor posture & looking downward for long periods.
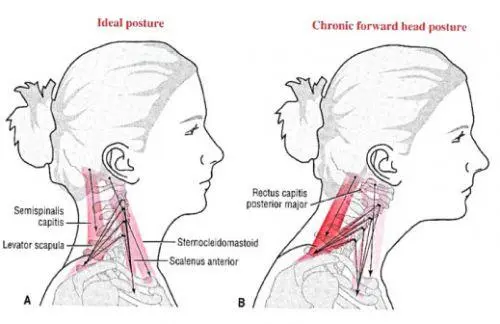
Text neck: Poor posture & text neck integrate to shatter your upper back which is caused muscle pain in the upper back.
Some everyday activities which provoke upper back pain contain:
- Twisting activities
- Poor posture
- Text neck
This pain is also provoked because of whiplash or another neck injury.
Upper back muscle pain occurs when you lift something improperly.
When you do the repetitious activities of the upper back while it’s painful.
Traumatic injury:
Some traumatic injuries for example:
- Slipping & falling
- Car accidents
- Lifting inaccurately
- Some work-related accidents
- When you do work out too hard
Some other reasons for muscle pain contain:
- Various forms of arthritis
- Herniated disc
- Osteoporosis
- Inflammatory conditions like ankylosing spondylitis
- Spinal stenosis
- Fracture of a vertebrae
- Sometimes Cancer that affects the spine
- Spinal deformity
- Problematic kyphosis
- Scoliosis
- Fibromyalgia
What are the Symptoms of Upper Back Pain?
When happening due to any injury in the upper back while daily activity, symptoms contain:
- In most injuries, you feel pain over the injury area.
- You also experience stiffness & tightness in the painful region area.
- You experience tenderness in the upper back.
- Sometimes you experience a headache.
- You experience weakness& numbness in your legs or hands.
- Sometimes you experience soreness in the upper back after a workout session.
- When the disc of the thoracic spine vertebrae is involved it is caused bowel or bladder leakage(Incontinence) occasionally.
- You also marked swellings & spasms in the painful region of the back.
How do you Diagnose Upper Back Pain?
When you consult a doctor for upper back pain, the doctor asks some questions related to the pain to try to know about the reasons behind the muscle pain.
Then asked to give the rank of their pain on the pain scale(NPRS or VAS) to get the severity of pain.
The doctor is also conducting a physical examination including palpating for swellings & muscle strength or ROM of the upper back.
Then the doctor is recommended some tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- MRI or CT scans & X-rays: These imaging tests are useful to your doctors to identify bone and soft tissue abnormalities or injuries. It is useful in the diagnosis of herniated vertebral disks & problems with muscles, nerves, ligaments & more.
- Blood tests: Blood tests assist doctors in finding infections & any abnormal diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis & cancer.
- Bone density test: It is also known as a DEXA test, which estimates your bone mineral density so that it assists to define the risk for osteoporosis.
- Nerve studies: Electromyography – EMG: It is a nerve study that calculates the activity of the nerve.
- It is useful to your doctor for the diagnosis of a herniated vertebral disc or spinal stenosis means the narrowing of your spinal canal.
Which are the Risk factors of Upper Back Pain?
When you don’t exercise it is a common factor that boosts your risk of upper back pain.
- Excess weight: Your spine reinforces the weight in your truck so that excess weight is applied to stress over your back.
- Psychological conditions: Sometimes this muscle pain is also provoked due to depression & anxiety.
- So in some cases, psychological disorders evolve to risk factors for upper back muscle pain.
- Belly fat: It is a particular issue that is conducted to the risk factor of upper back pain. When you hold a lot of weight in your core, it conducts stress on the soft tissues of your back.
What is the treatment for Upper Back Pain?
RICE protocol
When you experience pain in the upper back doctor is instructed on a RICE protocol as a home cure or primary management.
- R – rest: When you experience muscle pain doctor is recommended to take rest for sometimes including activities for release to muscle pain.
- I- ice: You are used to ice on the painful area for 10 minutes, It releases swellings & muscle pain but always used to the ice with the help of a towel between the skin & ice to control ice burn, you can also be used to ice pack & frozen peas for ice therapy.
- C- compression: You can also apply compression bandages to reduce swelling or edema.
- E- elevation: It is not viable for neck muscle or upper back because it boosts the pain but always use a gentle pillow while sleeping.
Pain medication
In many cases of pain, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory & muscle relaxant drugs.
When a doctor finds this muscle pain because of depression then the doctor is recommended an anti-depressant drug but doesn’t take it for the long term.
An opioid is suggested for unbearable pain but this drug is also not recommended for the long term, 7 to 10 days.
You can also use pain-alleviating gel & spray like move gel & spray on the area of muscle pain to reduce muscle pain & swelling.
Injections:
A trigger point injection is a blunt shot of strong pain medicine.
It assists you to alleviate muscle pain & swelling.
What is Physiotherapy Treatment for Upper Back Pain?
When the pain is not alleviated after the home management & pain medication then the doctor has recommended physiotherapy treatment to dismiss the muscle pain.
Physiotherapy treatment assists you to alleviate pain, swelling, spam & tightness of the upper back.
The physiotherapy treatment contains massage, electrotherapy treatment & exercise therapy.
Massage
- When the trigger & tender points are present in the painful area therapist is recommended to massage therapy reduce to muscle pain.
- Massage is involved after 2 – 3 days of obeying the RICE protocol when you experience reduced pain.
- Massage is applied with the use of oil or powder & applied for 5 -10 minutes.
- Massage is used 3 times/day at home.
Electrotherapy treatment
After the RICE protocol, pain medication, and massage if the pain is not reduced then used electrotherapy to reduce the upper back pain.
- To reduce the swellings, spasms & pain physiotherapist is recommended for electrotherapy treatment.
- Many options are available for electrotherapy treatment.
- When the tender points are present physiotherapists are recommended to use US(ultrasound) therapy the reduce the pain.
- This treatment is used with the help of ultrasonic gel & applies for 5 to 7 minutes on the area of pain.
- This therapy helps you remove pain & swelling and promote healing.
Other machines are also used to reduce pain for example SWD(short wave diathermy), IFT(Interferential Therapy), and TENS(Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) in the area of pain.
- SWD: Short Wave Diathermy is deep heat therapy to reduce spam in painful areas.
- IFT: Interferential Therapy & TENS: Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation is used with the help of ultrasonic gel & electrodes on the affected area.
This therapy is applied for 10-15 minutes.
Exercise therapy
After obeying the RICE protocol for 2- 3 days at home & primary management & the use of pain medication, you experience relief from the pain.
When you experience more comfort & free from your upper back pain then the physiotherapist is recommended exercise therapy for improving muscle strength and ROM.
The exercise therapy for upper back pain contains stretching & strengthening exercises.
Stretching exercise helps to reduce muscle tightness and strengthening exercise is beneficial you reduce muscle weakness.
Stretching exercise
After electrotherapy for 2-3 days to reduce muscle pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist is recommended to stretch to improve muscle flexibility.
- Child’s Pose
- Butterfly
- Upper trapezius stretch
- Levator scapulae stretch
- Trunk rotation
- Overhead arm reach
- Wall stretch
- Lat side stretch
1. Child’s Pose:

- Start this pose on the ground on all fours limb.
- With your big toes touching spread your knees as wide as your hips & sit on your heels.
- You are sitting straight up with your hands extended beyond your head.
- On the next expiration, hinge at the waist & drop your upper body forward between your legs.
- Try to let your forehead touch the ground & your shoulder joint stretch & your glute muscle down back.
- Maintain this position for 10-20 seconds.
- Conduct 3 times/set & 3 sets/day.
2. Butterfly pose:
- You put your hands on the same side shoulders & bring your elbow joints together to touch.
- Maintain this position for 20-30 seconds.
- Perform 3 times/set & 3 sets/day.
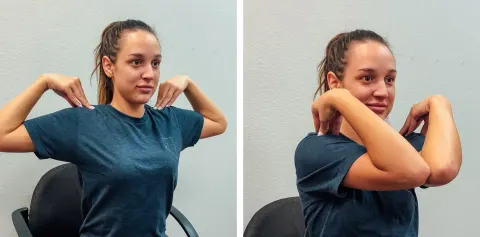
3. Upper trapezius stretch:
- This stretching is performed in both standing straight & sitting in a chair position.
- Take your right hand & put the hand on the left side of your head(above the left ear).
- Then try to bring your left hand & fold it toward the opposite side and backward.
- You are using your right palm & softly stretching your head toward your right shoulder.
- Maintain this stretching position for 20-30 seconds.
- Perform it 3 times/set & 3 sets/day.
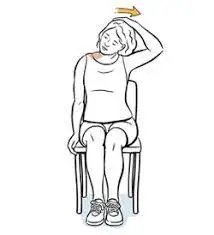
4. Levator scapulae stretch:
- This stretching is performed in both positions standing straight & sitting in a chair.
- For the right levator scapulae stretch turn your neck 45 degrees to the left side.
- Then flex your head forward and downward.
- You can use your left palm for a stronger stretch.
- Maintain this stretching position for 20-30 seconds.
- Perform it 3 times/set & 3 sets/day.
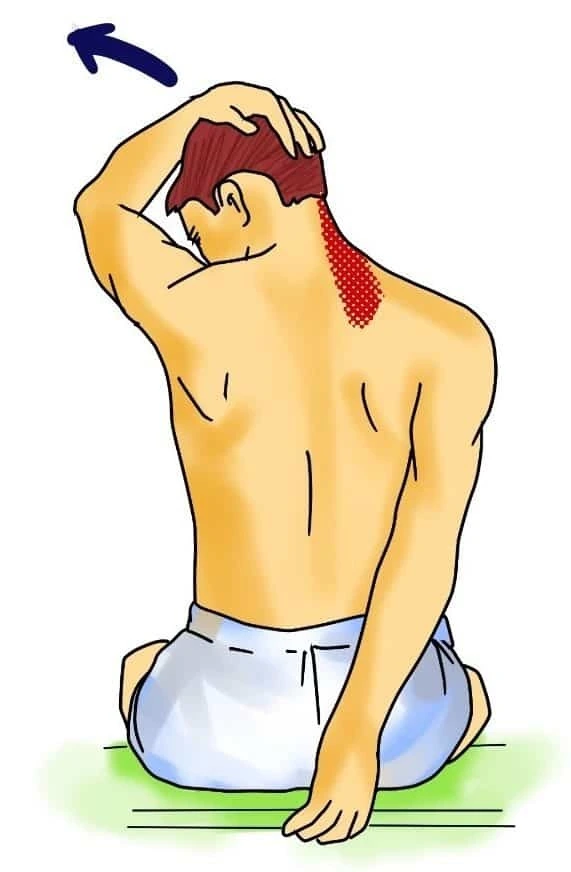
5. Trunk rotation:

- You lying on the back with the knee flexed & the feet flat on the ground.
- Must hold the knee flexed & softly rotate them to the right side.
- Maintain this stretching position for 10-20 seconds.
- Then return to the starting position and rotate it on the left side.
- Maintain this stretching position for 10-20 seconds.
- Perform it 3 times/set & 3 sets/day.
6. Overhead arm reach:
- This stretching is performed in both standing straight & sitting in a chair position.
- Take both arms over your head by the side of your body.
- Then bend towards the right side & must hold both arms stretched over your head.
- To stronger the stretch, use the right hand to softly pull the left arm to the right side.
- After that retrieval to the starting position.
- Perform 3 times/set & 3 sets/day.

7. Wall stretch:

- Begins with standing with the right side of the body facing a wall.
- Try to flex the right arm at the elbow joint & putting the forearm against the wall.
- The upper arm is fully straight so that the elbow joint forms a 90-degree angle.
- Softly take a step forward with the right foot & twisting to the left side.
- Then let the right shoulder and upper back stretch.
- Maintain this stretching position for 20-30 seconds & return to the starting position.
- Perform 3 times/set & 3 sets/day.
8. Lat side stretches:
- This stretching exercise is performed in a standing position & with both arms raised overhead.
- Carry the left wrist with the right hand.
- Then softly bend towards the right with a rainbow movement.
- This stretch is helped by softly pulling on the wrist.
- Maintain the stretching position for 20-30 seconds.
- Perform it 3 times/set & 3 sets/day.

Strengthening Exercises
After the obey of electrotherapy & massage for 2-3 days to release upper back pain by the physiotherapist then the therapist recommended to you do strengthening exercises for improving muscles strength.
This strengthening exercise is always instructed when you experience reduce pain & when you feel comfortable.
This strengthening exercise benefits you with muscle weakness & pain.
- Neck roll
- Shoulder roll
- Overhead arm reach
- Chair rotation
- Thoracic extension
- Row
- Face pulls
- Scapular squeeze
- Wall angel
- Reverse dumbbell fly
- Lat pulldown
- Shrugs
- W retract
1. Neck roll:
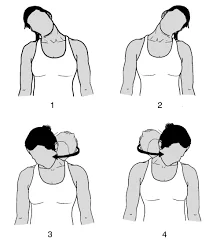
- You stand or sit facing forward for this exercise.
- Begins with tilting your neck to the right side.
- You experience the stretch via your neck to your trap upper back muscle.
- After a few repetitions gradually roll your head counterclockwise and clockwise.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times on one side then repeat this exercise on another side.
- Perform 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.
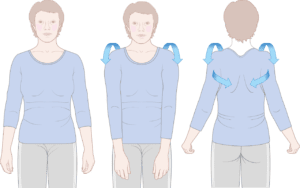
2. Shoulder roll:
- You stand with your arms down beside your body.
- Then roll your shoulders backward in a circular motion and do 10 rotations.
- After that do 10 rotations forward in a circular motion.
- Perform 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.
3. Chair seated rotation:
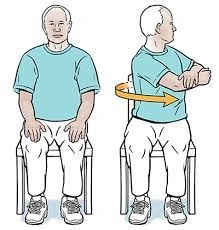
- You sit sideways in a chair.
- Tuck your arms and elbows just below shoulder height.
- Turn from the core with hips straight forward. Turn your head last. Don’t go through the pain.
- Keep for a count of 10-30 then return to starting position.
- Repeat 3 times on one side. Then change sides.
4. Thoracic extension:
- Do this exercise with the help of a foam roller or a chair.
- The foam roller, an am roller is put under your thoracic spine then letting your head and glute muscles fall on either side then Raise your arms beyond your head to stronger the stretch.
- With the chair, you sit facing forward and let your upper body fall on the back of the chair then raise your arms beyond your head for stronger stretch.
- Maintain in every position for 10-20 seconds, then relax.
- Perform it 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.

5. Row :
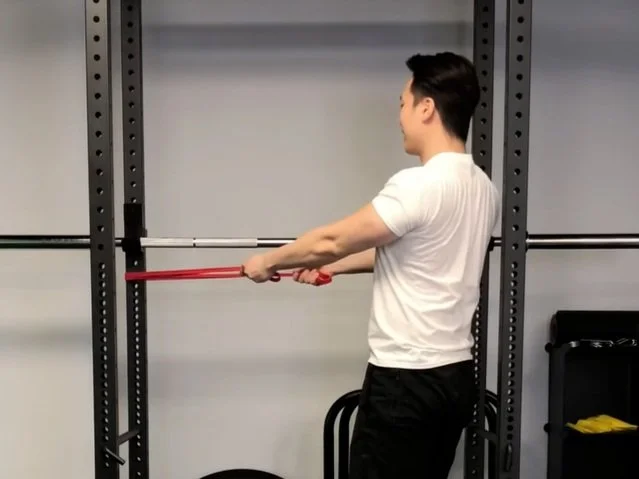

- For this exercise use a resistance band or light to moderate-weight dumbbell.
- First, connect the resistance band to a bar or another stable surface and grab each handle then extend your arms.
- Then pull the grips straight backward by flexing your elbow, which must be held handle close to your body.
- If you use a dumbbell for this exercise keep the dumbell in your right hand and brace your body on a wall using your left hand then extend the arm.
- Try to hinge at the core to a 45-degree angle and let the dumbbell swing down.
- Must hold your neck in the center and your knee soft then pull the dumbbell straight up with a flexed elbow.
- Perform 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.
6. Face pull:
- This exercise is done by using a resistance band.
- First, connect the band to a stable surface beyond eye level.
- Grasp each handle with an overhand hold.
- Then pull straight toward your face and flare your upper arms out to the sides and squeeze your shoulder together.
- Maintain this position for 5-10 seconds then return to the starting position.
- Perform 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.
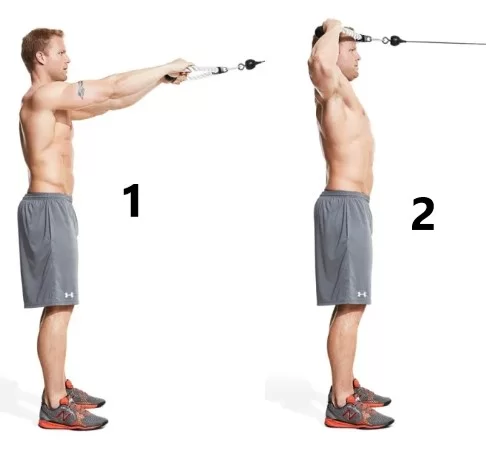
7. Scapular squeeze:
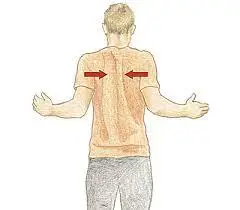
- You are in a standing position with your arms down beside your body.
- Then squeeze your shoulder and scapula together.
- Maintain this exercise for 5-10 seconds.
- Perform it 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.
8. Wall angel:
- You stand with your back flat on a wall.
- You must require to step your feet out just to let your back fully damp against the wall.
- Then extend your arms straight out and form a “T” shape against the wall and flex your elbow to make a 90-degree angle.
- Try to gradually move your arms straight up and down in a “snow angel” movement.
- Must be assured that you remain flat against the wall during the whole exercise.
- When your fingers connect above your head and return to the starting position.
- Perform 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.

9. Reverse dumbbell fly:
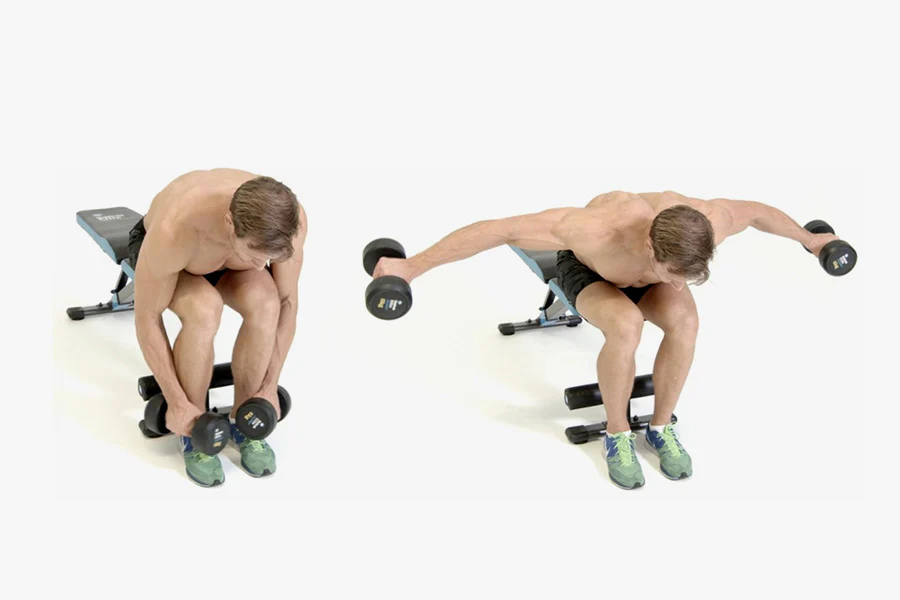

- Hold a light dumbbell in your hands.
- You are in a standing position than supports at the core at a 45-degree angle, with your arms swinging straight down.
- Your neck must be neutral and you look down.
- Start by raising your arms out to the sides and up.
- Squeeze your shoulder together at the end of the movement.
- Perform 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.
10. Lat pulldown:
- You Sit & stand beneath and a resistance band is connected to a stable surface beyond your head level.
- Try to pull down on the resistance band till your arms are parallel to the ground.
- Keep at the base and squeeze your lats and return to the starting position.
- Perform 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.
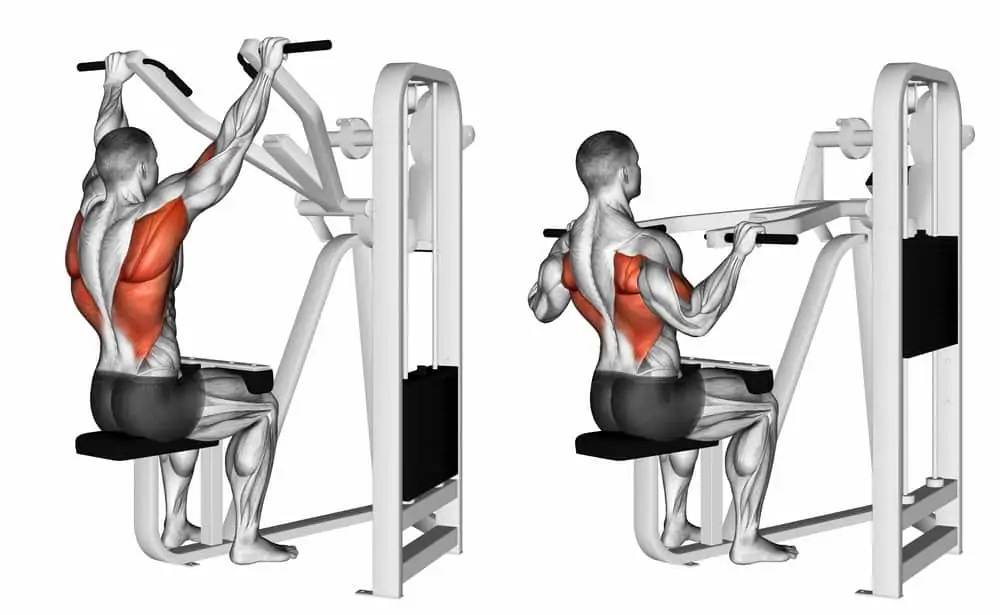
11. Shoulder shrugs:

- This shoulder shrugs exercise targets to improve the strength of trapezius muscles.
- This exercise is done either by keeping lightweight dumbbells or hand weights and also performing without any weight.
- Then kindly bring your shoulder straight to your ears.
- Maintain this exercise for 10 seconds and slowly relax.
- Perform 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.
12. W retract:
- This exercise begins with a standing position and raising arms up at an angle.
- Then pull your arms downward at a 90-degree angle and create a W shape with both hands by retracting them to the abdomen region.
- Try to Squeeze the shoulders and scapula and maintain for 10 seconds.
- Then relax and gradually move back to the starting position.
- Perform 10 times/set & 3 sets/day.

What is a surgical treatment for upper back pain?
If after the medical treatment and physiotherapy treatment pain is not reduced then the doctor is recommended surgical treatment.
Surgery for upper back pain is very irregular.
The surgery mainly includes thoracic spine injury.
Kyphoplasty or vertebroplasty:
- This surgery repairs contraction fractures because of osteoporosis.
- In this surgery, your doctor insinuates glue-like bone cement.
Spinal laminectomy or spinal decompression:
- When your muscle pain is because of spinal stenosis(narrowing of the spinal canal) your surgeon clears the bony walls of the vertebrae which are involved to relieve pressure on the nerves.
Microdiscectomy:
- When your pain causes vertebral disc bulging and compression on a nerve so the doctor recommended microdiscectomy indicates the minimally intrusive removal of a vertebral disc or portion of a vertebral disc.
- It is the gold standard procedure.
How to prevent Upper Back Pain?
It is not possible to prevent all causes of upper back pain, but some easy actions can prevent upper back pain, includes:
- Take to frequent breaks from prolonged sitting and lying down to stretch and move to different muscle groups in the back.
- Always take to periodic breaks when you are working at a desk to stretch, so the muscles evolve to remain relaxed and strong.
- Do regular stretching of the upper back muscles before any heavy activity.
- If you are lifting heavy things so must avoid twisting and raising with the back.
- Do regular massages which assist you to reduce the tension of the muscles.
- During pain avoid lifting heavy backpacks and purses.
- Always obey a good posture for example walking upright and sitting perfectly.
FAQs
Can upper back pain be heart-related?
The affinity between back pain and heart attack:
Heart attack pain can radiate to the back; because of that people experience both chest and back pain before heart attack episodes. Occasionally, the pain is exclusively present in the upper back. It’s also possible to experience pain in your neck, jaws, shoulders, or abdomen.
Can stress cause upper back pain?
When you’re worried, your breathing patterns change and cause stress and pressure in the mid-back region. Your shoulders scrunch up and generate pain throughout the upper and middle back region.
Can upper back pain be a tumor?
Even though primary cancer is usually analyzed before back issues originate, back pain can be the first sign of disease in people with metastatic vertebral tumors. Tumors that start in the bones of the spine (primary tumors) are less ordinary.
How can I sleep with upper back pain?
People with acute or chronic upper back pain can try to sleep on their back(supine lying), on their back in a slumped position, on the side with legs straightforward, on the side with legs flexed, and on the abdomen.
What are the symptoms of upper back tension?
You sense upper back pain as an aching, throbbing, or sharp pain in the thoracic region of your upper back or in your neck region with localized tightness of upper back muscles. It can be felt as branching pain in your arms to hands, tingling, numbness, weakness in your arms components, headache, or pain in your occipital area or jaw.



10 Comments