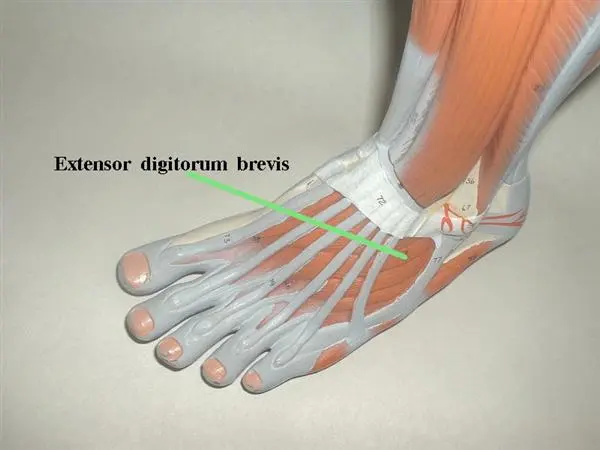
Extensor digitorum brevis muscle
What is the Extensor digitorum brevis muscle?
The extensor digitorum brevis muscle is a muscle located on the top of the foot. It is situated between the tendons of the extensor hallucis longus and the extensor digitorum longus muscles.
Functionally, the extensor digitorum brevis muscle helps with the extension of the toes, specifically the second, third, fourth, and fifth toes. It works in coordination with the other muscles of the foot to enable dorsiflexion (lifting the foot upward) and extension of the toes.
The extensor digitorum brevis muscle receives its nerve supply from the deep peroneal nerve, which is a branch of the sciatic nerve. This nerve innervates several muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg and foot, including the extensor digitorum brevis.
Extensor digitorum brevis crosses over the calcaneocuboid joint’s lateral portion and projects anteriorly toward the lateral malleolus. It goes on anteriorly and inserts on the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus of the second, third, and fourth toes. As an outcome, these muscles function in unison to extend the related digits of the foot.
Origin
One of the intrinsic muscles on the foot’s dorsum is the Extensor Digitorum Brevis muscle.
EDB Muscle originates from the
- the talocalcaneal ligament
- the floor of the tarsal sinus
- the upper and lateral surfaces of the calcaneus
- the stem of the inferior extensor retinaculum.
The muscle fibers of the extensor digitorum brevis then course forward and divide into four tendons, one for each of the second, third, fourth, and fifth toes. These tendons pass under the extensor retinaculum, a band of connective tissue that holds the tendons in place, and continue toward the toes to insert into the base of the proximal phalanges (the bones closest to the foot) of the respective toes.
Insertion
It inserts through tendons into the base of the proximal phalanx of the first toe and the middle phalanx of the three medial digits getting together with the extensor digitorum longus tendon (toes 2-4)
Relations
The belly of the muscle creates a small amount during dorsiflexion, which can be felt anterior to the lateral malleolus. As it courses over the dorsum of the foot, the muscle is partially surrounded by the tendons of the fibularis tertius and extensor digitorum longus muscles.
In extra, the most medial tendon of the extensor digitorum brevis crosses the dorsalis pedis artery over the calcaneocuboid joint and the lateral tarsal artery over the navicular bone. The lateral tarsal artery passes laterally beneath the extensor digitorum brevis and supplies it. The muscle also runs over the lateral terminal branch of the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve.
Innervation
The lateral terminal portion of the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve, which comes from the L5 and S1 spinal nerves, supplies the extensor digitorum brevis muscle.
Blood supply
Fibular artery and anterior tibial artery (dorsal pedis artery distally).
Function
The lack of direct bony attachments limits the extensor digitorum brevis to assist other muscles in doing their activities. Above all, it makes it more straightforward for the extensor digitorum longus to expand the second, third, and fourth toes at the proper distal interphalangeal joints. In addition, these two muscles work together to help the foot’s lumbrical muscles extend the same interphalangeal joints.
The great toe is extended at the metatarsophalangeal joint by the most medial tendon of the extensor digitorum brevis (extensor hallucis brevis). In addition, these two muscles work together to help the foot’s lumbrical muscles extend the same interphalangeal joints.
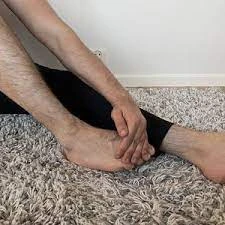
Extensor Digitorum Brevis muscle stretching
The best method to stretch the extensor digitorum brevis muscle is to put your ankle in a neutral position and then passively transfer your 2-4 toes downwards, conducting the flexion of the toes.
You can conduct passive action by holding your toes with your fingers and dragging your toes down. Maintain for the 30s.
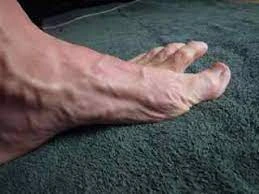
Extensor digitorum brevis muscle strengthening
4 Little Toes Lift
For this activity maintain the big toe driven down into the bottom while raising the further toes towards the roof. The key here is to keep up with the curve of the foot strong for this movement, dont permit the foot to move in while raising the little toes. This may offer you a false feeling of the elevation here.
FAQ
Why does my extensor digitorum brevis hurt?
Ache in the extensor digitorum brevis is frequently connected to poor footwear options or frequent walking and running on irregular surfaces that put an extreme workload on the foot muscles.
How do you manage extensor digitorum brevis pain?
Relax the involved foot for two to three days. Use them as little as possible to give the tendons time to rest. Ice your foot for 20 minutes every two or three hours while you relax it. Cover an elastic bandage near the injured site to ease inflammation, or use a brace.
What happens when the extensor digitorum is damaged?
An extensor tendon injury is a harm to the tissues on the back of the hand and fingers. It may make it difficult for you to open your hand, straighten your fingers, or extend your wrist. The incapability to complete these functions can hardly limit hand and upper extremity roles.
How long does it take for the extensor to heal?
The tendon may bring four to eight weeks, or longer in some persons, to heal fully. Extracting the splint early may result in the dropping of the fingertip, which may then need extra splinting.
What does the extensor digitorum brevis do?
The Extensor digitorum brevis expands the phalanges of the four toes into which it is inserted, however, the first toe works just on the first phalanx. The long Extensor’s oblique motion of the toes is balanced by its obliquity, so when both muscles are working, the toes are equally extended.


3 Comments