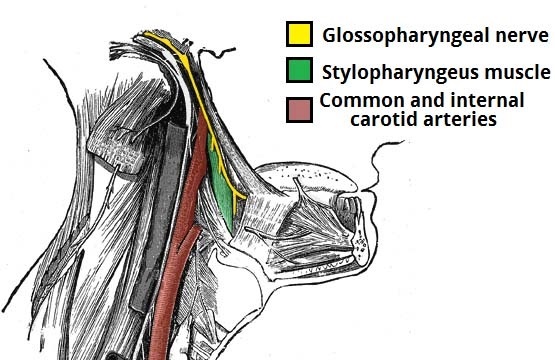
GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE
INTRODUCTION : The glossopharyngeal nerve, known as the ninth cranial nerve (CN IX), is a mixed nerve that carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. It exits the brainstem out from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. Sensory: Innervates the oropharynx, carotid body and sinus,…