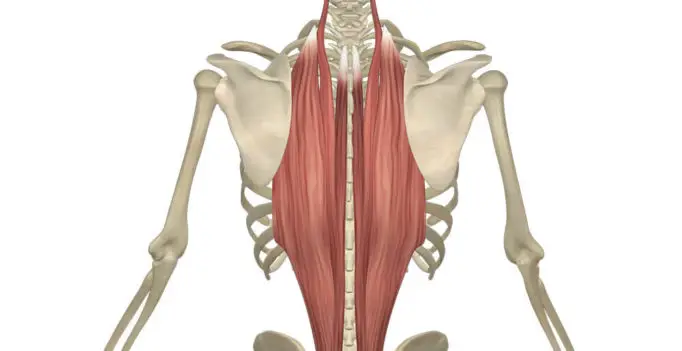
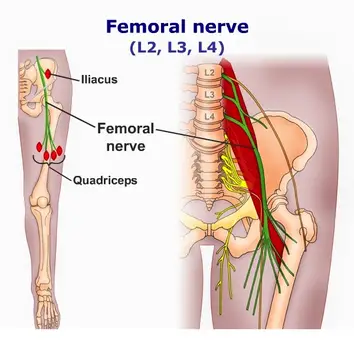
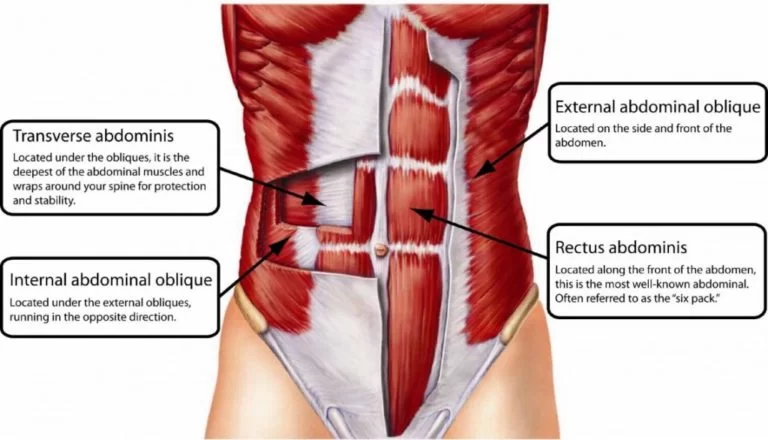
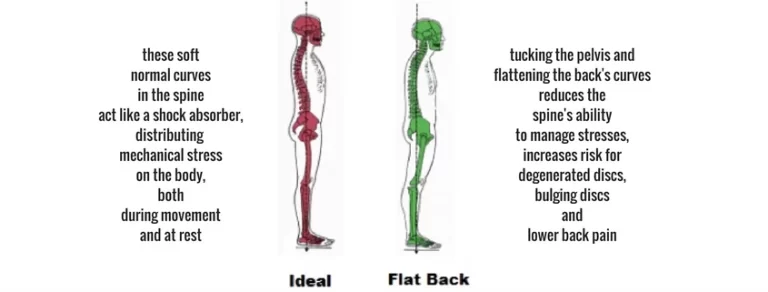
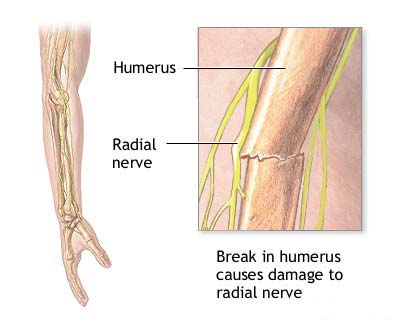
Vitamin B 12
What is a Vitamin B 12? Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is naturally present in some foods, added to others, and available as a dietary supplement and a prescription medication. Vitamin B12 exists in several forms and contains the mineral cobalt, so compounds with vitamin B12 activity are collectively called “cobalamins”. Methylcobalamin and…