35 Best Bicep Exercises for Mass and Strength
Introduction
Most men who are interested in bodybuilding want to grow as much muscular mass as they can. Many people who labor toward this objective frequently evaluate their efficacy and success on the vertical size, form, and ripped physique they can generate, whether it’s for show reasons or practical usage. The biceps are frequently the target muscle that receives the most concentration, that’s why there is an endless search for the best biceps workouts.
One of the body’s most well-known muscles is the biceps. Even when young, children raise their arms and flex them toward a mirror or toward one another to demonstrate who is more powerful and dominant. When someone asks you to flex, they’re not asking to see your detailed back they desire to see your biceps. Certain very particular routines can be done to generate maximal muscle in the biceps. It has been utilized to find out how much muscle a man has in his whole body.
Undoubtedly, these exercises are less effective when done alone. It is preferable to combine them with a comprehensive exercise program that covers the complete body. It’s crucial to keep in mind as you work that no skeletal muscle is more significant than another.
Concentrating on the biceps in the front and the triceps in the back can help you gain muscle in your arms. They require separate strength training routines because they are opposing functional muscle groups.
You must feel more sure if you have larger, stronger arms. Strongness and athleticism can also be expressed through muscular arms. But having stronger arms has some particular practical gain as well.
More muscular arms make it easier to perform any upper-body task, such as scooping up children or lifting large goods. Having additional muscle mass can: improve your everyday functional fitness. elevating your metabolism means torning more calories even when you should not exercise. minimize your risk of injury while raising muscle strength, endurance, and tone
How to Increase Bicep Size: attack from all directions
People often need to realize that the bicep is divided into more than one portion, which is one of the main reasons why their biceps don’t develop as quickly or as big as they would like.
Most guys primarily pay attention to their brachii. However, you must exercise every part of the bicep if you want your arms to appear thicker and more full.
Muscles Form the Biceps
The Latin word brachii, which means “two-headed muscle of the arm” and refers to both the short head and the long head, is used to refer to the biceps. The shoulder and the elbow are where the biceps are joined. Flexing the elbow and turning the wrist is its primary purpose.
In spite of their diminutive size, the biceps play a crucial role in the body. Every time you lift anything or press something overhead, your elbow and biceps are being partially flexed.
Biceps brachii: The two-headed biceps brachii muscle starts on your scapula and inserts into your forearm. Its two heads essentially do the same things, but you may change how it works by changing how you curl and where your upper arm is placed.
The brachialis: it is a large muscle that is located on the outside of the humerus and under the biceps. The brachialis is the main muscle for elbow flexion because it just spans the elbow joint and has no interaction with your shoulder.
Brachioradialis: This tiny muscle, which is regarded to be a component of your forearm, assists in bending the elbow, especially when you’re doing workouts with a pronated hand.
Guidelines for Increasing Bicep Size
Use this expert advice to make sure you get the most out of each rep and set in our list of the finest bicep exercises. After all, if you’re going to exercise your biceps, do it right.
Increase bicep size: Get Warm
Although it seems difficult, patience is a goodness, and it’s also vital. The muscle that has warmed up is more malleable. It will therefore function better. More red blood cells, and consequently more oxygen and nutrients, will be sent to the muscle while it is working, lowering the chance of incisions and tears. Furthermore, you’ll be able to lift more.
Bigger Biceps: Vary Your Workouts
Keep in mind that after roughly six sessions, your body will have fully acclimated and you won’t get the same benefits. Simply put, doing nothing but curling up there every week won’t do much. Variety is essential to existence.
Building Bigger Biceps: The Value of Breathing
Thought for breath-hold during the high lift weight is helping. In fact, not exhalation can cause the blood pressure to fasten and make you distracted. Structured, rhythmic breathing will help the person to concentrate, calm down, and hold the tempo more controlled. An oxygenated body will also lessen the risk of passing out and assist in transferring that sweet air to your muscles, granting them the to ‘breathe’ and work harder.
But there’s more to breathing accurately rather than a few gasps of air. adding the diaphragm, a process known as ‘bracing’ by powerlifters, is a major key to explosive performances.
Bracing: Imagine you’re about to get gut-punched. give thrust to the stomach into the belt as you breathe in, but also give thrust out to the sides and back. This is how you demand to brace when lifting.
When exercising, bear in mind that not all bicep exercises require this amount of regulated breathing, whereas every compound move must.
Rest More to Build Bigger Biceps
It’s frequently recommended that you take between-set breaks of 30 to 60 seconds. Really, this isn’t long enough for your muscles to properly recuperate. The muscles will have a chance to regain their full strength if you wait three to four minutes. Then, for your next set, you can lift additional weight for faster muscle growth.
Time is important, after all, so if you don’t want to wait around for four minutes, train a different set of muscles during the break. Pushdowns are a great way to work your triceps, and as your triceps recuperate, you may work your (rested) biceps.
This reciprocal exercise will accelerate muscular growth and cause tiredness.
Best mass exercises for biceps
Standing dumbbell curl

Why: This exercise must be included at the top of any list of bicep exercises; it’s a fan favorite for a reason. The curl is the best exercise for the biceps. However, it’s crucial to regulate your weight appropriately. Lifting the dumbbell by aggressively swinging and arching your back is inefficient and risky for injury. Maintain it controlled, calm, and concentrated on contracting your bicep as you raise.
How: Stand with your arms at your sides and a dumbbell in each of your hands.
Make sure your palms are pointing forward and your elbows are near to your body.
Exhale as you bend the weights up to shoulder level while squeezing your biceps and maintaining your arms motionless.
Hammer Curl

Why: specifically how you hold the dumbbell, makes a difference. The muscle that gives your arms their thicker appearance, the brachialis, receives more of the work by having the dumbbell converted on its side.
how to execute: With your palms towards your thighs, let a set of dumbbells hang at arm’s length close to the sides of your body.
Hold your arms motionless. Instead, band the elbows while bending the dumbbells as near as you should to the shoulders.
Before gradually lowering the weight back to the position from where it started, stop at the top and tighten.
Cable rope hammer curl
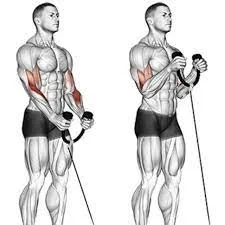
A common arm-focused workout that uses a rope handle linked by a cable to a weight stack is called a “cable rope hammer curl.” It utilizes a neutral position palms facing one another, which in addition to the biceps, targets the forearms and brachialis muscles. Due to the grip’s restriction, it is typically done for moderate to high repetitions, likewise 8 to 12 each set or more. target the brachialis, forearms, brachioradialis, and biceps. The neutral grip may relieve pressure on the elbows and wrists. The cable enables constant tension during each rep.
how to execute: Standing 12 inches away from the machine while facing it, tie a rope connector to a low pulley.
Holding the rope with a neutral palms-in)grip, stand up straight while maintaining the natural arch.
Place your elbows by your sides and hold them there motionlessly during the action. Remember to only move your forearms, do not push the upper arms. This will be where you begin.
As you expire, elevate your arms until your biceps contact your forearms by pulling up with your biceps. Remind yourself to maintain your upper arms still and your elbows tucked under.
Squeeze your biceps for one second, then begin to carefully lower the weight back to its starting position.
Continue for a tolerable amount of reps
Cable rope preacher hammer curl
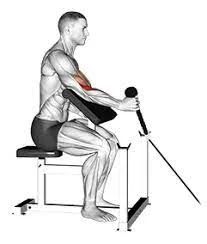
A preacher bench, a cable stack, and a rope grip are used in the single-joint arm workout known as the cable rope preacher hammer curl to increase biceps strength and growth. The “hammer” or neutral grip accelerates the activation of the brachialis and grip muscles, increasing arm thickness. The bench’s angle also successfully isolates the biceps by removing the shoulders from the exercise. At least 8–15 reps are usually performed for each set.
During the movement, especially at its maximal contraction, the cable maintains a consistent tension.
quick and simple weight changes for drop sets
work the brachialis, forearms, brachioradialis, and biceps.
Effective for increasing biceps thickness and assisting in boosting the “peak” of the biceps from low-level
how to execute: Set a preacher’s seat in front of a pulley machine approximately two feet.
A straight bar should be linked to the bottom pulley.
Have somebody give you the bar from the low pulley while you sit at the preacher’s bench with your elbow and upper arms firmly on top of the bench pad.
Take hold of the bar and raise your arms above the preacher’s bench pad. This will be where you begin.
As you begin to gather the weight up toward the shoulders, do a strong biceps contraction at the apex of the movement. As you carry out this action, breathe out. Maintain for a brief moment at the peak as well.
The weight should now be progressively lowered to its initial position.
Repeat for the 5 to 8 number of times.
Variations: To do one arm at a time, you can also utilize even a single-hand bar.
The Zottman Curl

Why: Because there aren’t many workouts that specifically target the biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis, the three main muscles that together make up the biceps. The zottman curl targets every part of the bicep by switching your grip midway through the exercise from an underhand to an overhand position.
How to execute: Rotate your arms so your palms are facing forward and hang your dumbbells by your sides.
Bend your elbows and bend the dumbbells towards your shoulder without moving your upper arms.
After pausing, rotate the dumbbells so that your hands are facing forward, and then gently revert to the initial position.
Barbell bent-Over Row

Why: when you drag, your biceps in particular are particularly active. You can use a lot greater weight than you would when curling while still keeping proper shape and function because the row uses a variety of muscles.
How to execute: Hinge over from the hips while keeping the knees slightly bent.
Keep your spine neutral and spread your hands shoulder-width apart.
Consider bringing your elbows in toward your body, maintain, and then bring the load back down.
Make sure the pull line enters the region of the belly button and not the sternum.
Chin-up

With just a pull-up bar, the chin-up is a bodyweight exercise that can significantly increase biceps (and back) muscular mass. To perform sets of chin-ups, all you want is a door-mounted pull-up bar in the house gym.
Your biceps have access to weights greater than you should lift with a barbell because you’re using your complete body weight to lift the weights. Engage your abdominal muscles and draw your shoulder blades back and down to ensure that you’re maintaining the focus on your biceps.
how to execute: Hang from a bar with your palms towards you and your hands slightly broader or shoulder-width apart.
From a downward hang, press your shoulder blades together.
As you raise your body, keep it from folding in on itself until your chin is at or above the bar.
Coach’s Advice: Visualize tucking your elbows a little bit into your back pockets.
Sets and Reps: Conduct three to five sets of as many reps as you can, utilizing a resistance band to help you if necessary.
Band-assisted chin-up

The band-assisted chin-up is a modification of the pull-up exercise that is done with a band wrapped around the feet or knees while the repetitions are done with the palms facing the body in a downward position. By doing this, weight and resistance are decreased at the bottom of the repetition and increased at the top.It strengthens and tones the upper back, biceps, and core, just like other pull-up variations, although it significantly emphasizes the biceps more than overhand band-assisted pull-ups. equipment-free, only need a bar and a band
muscle worked: Latissimus dorsi (latissimus), biceps, upper back, core, and grip muscles are strengthened.
Reps: can assist you in performing pull-ups with higher rep ranges, like 8 to 15 each set or more.
If a machine is not available, a simple substitute for reverse-grip lat pull-downs can be done.
Adding resistance bands to the feet from a low base will increase the level of difficulty. Release the band after 10 reps, then conduct another 10 reps. If you don’t have bands, perform a total of 20 reps solely using your body weight
L-sit and chin-up

An exercise for the back, biceps, core, and total upper-body strength is the L-sit chin-up. It is frequently conducted for relatively low reps, such as 5-8 reps per set or less, with an emphasis on strength and form because it is thought to be considerably more difficult than normal chin-ups.
Advantages: serious work with isometric cores
increases back, biceps and shoulder strength
translates to more difficult pull-up reps
how to execute: Hang from a pull-up bar using an underhand, shoulder-width grip, then raise the feet by bending at the hips so that the legs are now parallel to your chest. To maintain this posture, you should precisely tighten the abdominal muscles. This will be where you initiate. In a continuous action, tighten your biceps and lats to bring your chin over the bar. Then, let go to lower yourself to the limit of full arm extension. For each rep, repeat.5 to 8 reps
Regular EZ Bar Curl

Why: By using a bar instead of a curl, you may lift more weight while keeping proper technique and avoiding undue stress on your elbows and forearms.
How: The EZ bar should be held with an underhand, shoulder-width grip in front of the thighs.
Twist the bar until the handles are at your shoulders as you inhale.
Biceps contracted, slowly lower yourself.
Underhand Seated Row

Why: When you row while seated, your biceps are in the path of the pull, which makes them work harder on each repetition. Watch your back and biceps expand if you do it properly.
How to execute: Kneel down and grasp the bar with an underhand grip with your shoulders apart.
Tilt slightly while keeping your back straight, then drive the bar toward your belly button with your back muscles.
Put the bar back in its original place.
Reverse grip bent-over row

A combination exercise for developing the lower and upper back’s strength and growth is the reverse-grip bent-over row. The majority of the back muscles are targeted, but the lats, rhomboids, and lower back are given special attention. In comparison to overhand barbell rows, it is said to target the biceps and lats. It is a common movement in upper-body workouts that emphasize strength and building muscle since it may be loaded heavily.
strengthens the glutes, hamstrings, spinal erectors, and rhomboids
teaches effective ab bracing, and keeps the spine in its right alignment.
how to execute: Grasp a barbell with a supinated grip palms facing upward while standing straight.
Your body should be brought forward by bending at the waist and preserving your back straight till it is virtually equal to the floor. Your knees should be slightly bent.
Advice: check to ensure that maintain a straight head. Your arms should hang parallel to the floor and your torso while the barbell should be straight in front of you. Your starting point is here.
As you exhale, elevate the barbell while maintaining a still body, preserving the elbows close to the body and using only your forearms to hold the weights. Squeeze the back muscles when in the top constricted position, then maintain for a moment.
Repeat for the dedicated amount of repetitions.
Coach’s Advice: Utilize very heavy weights in this exercise. Load up the bar, but watch out for cheating by flinging your weight around between reps.
Conduct three to four sets of six to eight repetitions with a heavy weight.
Caution: For those with back issues, this exercise is not advised. For those who suffer from back problems, Low Pulley Row is a preferable option.
Additionally, if your back is good, be careful to maintain proper form and avoid slouching forward since this can harm your back, much like with the bent knee deadlift.
Utilize caution while choosing the weight; if in question, go with less weight rather than more.
Seated Cable Rows

The cable seated row is a well-liked exercise that uses a cable stack to prepare the upper back muscles, which include the lats (latissimus dorsi), traps, rhomboids, and rear deltoids. It somewhat targets the biceps as well. The cable row can be used well in a number of rep ranges, however, it is most frequently used in muscle-building exercises or as an add-on exercise for strength exercises.
Benefits: Maintaining tension throughout the whole movement, especially at the point of maximum contraction
Simple to simply change weights for drop sets or use lifting straps to lift more weight
may target various areas of the back with a range of handles and gripping widths.
How to execute: You require access to a low pulley row machine with a V-bar for seated cable row exercise. The V-bar will permit the person to have a neutral grip in which your hands and palms are facing each other. To begin, sit down on the machine and place your feet on either the front platform or the attached crossbar, being careful to keep your knees slightly bent but not locked.
Maintain your back straight as you lean over and grasp the V-bar handles.
Drawback with your arms outstretched until your body and legs form a 90-degree angle. Your chest should be sticking out and your back should be somewhat arched.
As you carry the bar in front of you, your lats preserve to feel nicely stretched. The exercise begins in this position.
Bring the handles back towards your body and maintain your arms close to it till you reach your abdominals while maintaining a still body. Exhale while you make that motion. You should rough to be tensing your back muscles at that time. After a brief period of holding the contraction, gradually get back to the starting posture while breathing in.
Repeat for the tolerable number of repetitions
Precaution: prevent hanging your body from side to side as this can harm your lower back.
Variations: Instead of a V-Bar, you can use a straight bar and execute the exercise with either pronated palms facing down-forward or supinated palms facing up-reverse grip.
Incline dumbbell curl
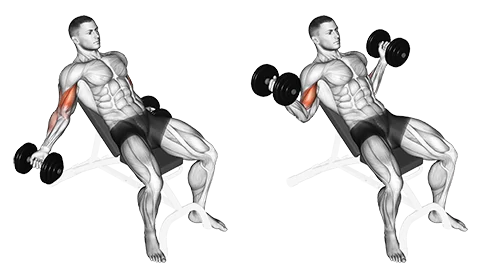
Why: Because you’re now starting from a lower position, inclining the bench puts additional strain on the lengthy head of your biceps brachii. In other words, you are beginning from a position where your leverage is lower than usual. Please take note that you must reduce your load because this exercise demands greater effort.
An upper-body workout that targets the latissimus dorsi, upper back, and biceps is the incline dumbbell row. It is easier to specifically target the lower lats when done on an inclined bench. In the upper body or back portion of a workout, dumbbell row variations are often performed for moderate to high reps, such as 8 to 12 reps per set or more.
Benefits: increase upper-back strength and size
The incline bench position requires exact technique and restricts movement.
Trains the posterior shoulders and biceps
How to execute: Lean into an inclined bench while maintaining a neutral grip.
Starting with straight arms, hold a dumbbell in per hand with a neutral grip. This will be where you initiate.
To row the dumbbells to your side, pull back your shoulder blades and flex your elbows.
come back to the initial position after a brief pause at the motion’s peak.
Palms-out incline biceps curl

A workout for the biceps is the palms-out, incline biceps curl. Although it resembles the incline dumbbell curl in many ways, the palms-out posture specifically targets the long head of the biceps, which is what gives the biceps their peak. Typically, 8 to 12 reps per set or more are used to do this curl variation as part of an upper-body or arm-concentrated preparations
how to execute: Lean back on an inclined bench while holding a dumbbell in each hand.
Your hands should be facing out and the dumbbells should hang at arm’s length from your sides. This will be where you begin.
Now, curl the weight upward and outward as you expiration, holding your forearms parallel to the side area of the deltoids. Curl the dumbbells until they are at shoulder level and parallel to your deltoids.
Advice: The action should end with a double-biceps pose-like appearance.
Start breathing in as you gradually lower the weights back to the beginning position utilizing the same motion you utilized to lift them up after a second contraction at the peak of the exercise.
Repeat the recommended number of times.
Incline hammer curl

Put a dumbbell in each hand and take a seat on an inclined bench. Your feet should be close together, pressing firmly against the back. Holding the dumbbells with a neutral grip, let them hang straight down by your side. This will be where you start.
Flex your elbow to begin the motion while trying to maintain your upper arm straight.
Reach the movement’s peak, pause, and then gently lower yourself down to the starting position.
Reverse Curl Straight Bar

Why: Because it exercises the brachialis, an arm muscle that is inconspicuous and necessary for developing larger biceps, it is sometimes disregarded. When the brachialis is properly trained, your bicep peak will rise higher, giving you more outstanding flex and larger-looking arms.
How to execute: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and take an overhand grip on a barbell.
Only utilizing your forearms, bend your elbows and rotate the barbell upward until it is parallel to your shoulders and your hands are facing outside.
Repeat while lowering it slowly back down.
Concentration Curl

The concentration curl targets the lateral head of the biceps for maximum performance while isolating the arm flexors.
How to execute a concentration curl: Put your legs out in a V shape and sit at the end of a flat bench.
bend gently forward and grasp a dumbbell in one hand.
Position the elbow against the inside of the thigh with your palm facing your center.
For support, place your other hand or elbow on the opposite thigh.
fold the weight rhythmically in the direction of the shoulder without moving the upper body.
Turn your wrist just a little bit as you raise to finish the curl with your palm towards your shoulder.
Permit yourself to feel the exertion in your bicep for a time, and then gradually lower the weight. should not rest the weight on the floor, till the last rep
conducts 12 to 15 times, then alter the arms
Seated close-grip Concentration barbell Curl

A barbell or E-Z Bar should be placed in front of you, between your legs, as you sit on a flat bench. With your knees bending and the soles of your feet flat on the ground, your legs should be extended wide.
Grab up the barbell with your arms, and then position your upper arms such that the backs of your inner thighs are about three and a half inches from the front of your knees. For this exercise, a supinated grip that is nearer than shoulder width is required. The barbell should be beyond the floor, and your arm should be fully extended. This will be where you begin.
Curl the weights forward while keeping the upper arms still and contract the biceps while exhaling. One should just use their forearms. Repeat the motion until the dumbbells are at shoulder height and your biceps are fully tensed. Tighten the biceps while maintaining the contracted position for a brief moment.
As you inhale, begin to gently bring the barbell to its initial position.
Advice: Prevent from swinging at all times.
Repeat for the suggested number of times.
Band standing concentration curl

The popular biceps-focused workout known as the band standing concentration curl uses a band in place of a dumbbell. It enables you to concentrate on just one bicep at a time and exert maximum effort during peak contractions. As part of an upper-body or arm-focused workout, band concentration curls are often performed for moderate to high reps, such as 8 to 12 reps per set or more.
Benefits: increase biceps strength and size.
restricts motion to focus only on the biceps and avoid help from other muscle groups
Excellent for developing a great biceps peak.
Each rep is progressively nervous by the band.
how to execute: Lean forward while holding a dumbbell in your working hand. Permit the elbow of your working arm to point out and swing parallel to the ground. This will be where you begin.
To curl the weight, bend the elbow while maintaining the upper arm still. Be sure to flex your biceps and pause at the end of each repeat.
Return the dumbbell to its initial position by lowering it.
Do the required number of repetitions of the movement.
You must exert extra effort to prevent upper arm movement because the back of your arm is not supported by your legs. This form of exercise is more difficult and is not suggested for those who have lower back problems. As a result, you will be kneeling, and the barbell’s weight will aid in keeping you balanced.
Dumbbell Twist Curl

Why: Although your forearms will be used, this workout won’t stress your biceps as hard as other arm exercises. Over a meal, squeezing begins; this motion will hit more of your arm in a shorter amount of time.
How to execute: Dumbbells should be held at your sides, palms facing one another.
Alternately raise the dumbbells to your shoulders using your biceps, turning your palms to face your chest as you do so.
do this again after rhythmically lowering the dumbbells back to your side.
Prone dumbbell Spider Curl

Why: Lying against the bench teaches you how to curl properly. It is cheating if your chest lifts off. Keep it flat during every rep, and you will have completed a second set in the search for bigger biceps
How to execute: Take a dumbbell in each hand and let it hang below your shoulders as you lay on an inclined bench.
fold the dumbbells in the direction of the shoulders by utilizing the biceps. come back gently to your initiate position and then repeat.
leaned forward EZ Bar Curl

Why: The forward tilt means utilizing the hips to hang up the final reps is a no-no. This demands full strength and ideal form for perfect improvements.
How to execute: The EZ bar should be held with an underhand, shoulder-width grip in front of your thighs.
Lean slightly forward until your body is at a 30-degree angle with your hips. Bend the bar until the hands are at the shoulders as you inhale.
Tighten your biceps, then slowly and carefully allow go.
Inverted row

Why: The inverted row, a calisthenics alternative to a bent-over row, mandates a straight back and strong core stability to maintain proper form. Along with getting a good six-pack, you may also adjust your grip to target different muscle groups during your workout. utilize an overhand hold to target your back and deltoids, and an underhand grip to maximize your biceps. a core and arm burner that is underappreciated.
If you utilize a supinated, underhand grip, an inverted row is a two-for-one exercise: If you’re not quite ready to complete a chin-up, you can work toward developing the back strength necessary.
how to execute: In a frame or cage, place a barbell at a height of approximately hip height.
Reach up and grasp it with an underhand grip while lying below it on the floor.
Bend your elbows and squeeze your biceps to lift your body off the ground.
Flip the motion after pausing at the top when your body is only inches away from the bar.
Coach’s Advice: Spend some time determining the precise grip breadth that best activates your biceps.
Bodyweight exercises like the inverted row make great workout finishers. Finish your biceps workout with two sets that you can’t complete.
Meadows Row

Why: a “barbell” must refer to two hands. By adding extra weight and tackling an unfamiliar technique, you may challenge yourself with this challenging rowing variant. When you do this T-bar style row to one side rather than between the legs, your entire body has to work extra hard to maintain balance. One of the quickest routes to larger arms is this maneuver. Just keep it a secret or everyone will start doing it.
How to execute: Elevate the other end of a barbell with one hand while stabilizing the other end with a big weight. Maintain your knees a little bent and your arm outstretched.
Drag the barbell up to your side using your shoulder muscle while flexing your elbow. then come back down and repeat
Barbell Curl

Why: It doesn’t get any more fundamental than barbell curl. With barbells, you may evenly and concurrently work both arms. You may exercise various muscle groups by adjusting the grip position.
How to execute: With a shoulder-width grip, take hold of a barbell and hang it in front of your thighs.
Brace your abdominal muscles as you roll the bar up to your chest, keeping your upper arms motionless. come back to the starting location under control.
Decline the dumbbell curl

Why: Lying down on the bench helps you isolate your biceps by relieving stress in your legs and core.
How to execute: Lay on the bench with your chest against it and incline it 45 degrees.
Curl the dumbbell as close to your shoulders as you can without moving your arms.
Take a moment, then gradually lower the weight to the initiate position
Overhead Press

Why: Although this exercise is primarily used to develop the shoulders, its overhead nature also helps to develop larger biceps.
How to execute: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and lift the dumbbell or barbell to your shoulders with your palms facing forward.
Rapidly raise the barbell or dumbbell above your head until your arms are completely extended, then slowly reduce the weight.
Towel grip pull-up

Why: Attempt this bicep-burning pull-up variant while improving your grip strength to get a bigger set of biceps. Get your workout towel.
How to execute: Hang a towel over a pull-up bar while keeping your arms straight. Hold the towel firmly in both palms.
By bending the elbows and pushing the shoulder blades together, you should elevate yourself. your chin touches your wrist’s fist, stop before coming back to your original position. Repeat, switching which side of your head moves your body is on each time.
Banded bicep curls

Why: All you need is a resistance band to develop biceps that bulge. To get an arm pump that stretches your T-shirt, increase the rep ranges if your band is light.
How to execute: grasp the resistance band in an underhand grip while standing tall and with your arms straight. Loop the band beneath your feet.
Your thumbs should be touching your collarbones as you curl your arms upward with your elbows locked tight to your waist.
Reverse the motion gradually to make the band go back to its beginning position.
Single-arm dumbbell preacher curl

The biceps, and more specifically the bicep peak, are the key points of the single-dumbbell preacher curl workout. Most people will execute this exercise lightly, with moderate to high repetitions as part of an upper body or arm workout. increases biceps peak size
The precise form required by the preacher’s bench makes the biceps work harder.
One side cannot make up for the other when training one arm at a time.
how to execute: With your right arm, grab a dumbbell and rest your upper arm on the preacher bench or the incline bench. Holding the dumbbell at shoulder height is proper. This will be where you start.
Gradually drop the weight as you inhale until your upper arm is extended and your biceps are fully stretched.
Utilize your biceps to curl the weight up as you exhale, until they are fully clenched and the dumbbell is at shoulder level. Again, keep in mind that you must raise that small finger above the thumb to guarantee complete contraction.
Repeat for the prescribed number of repetitions after giving the biceps a strong second of contraction.
The motion is repeated while switching arms.
Variations: Instead of using a dumbbell, you might conduct this exercise with a low pulley. You must place the seat in front of the pulley in this situation.
Incline dumbbell preacher curl

The biceps, and more specifically the bicep peak, are the target of the dumbbell preacher curl workout. All you need is a preacher bench and a couple of dumbbells. It is typically done as part of an upper-body or arms-focused workout for a range of moderate to high repetitions.
How to execute: Put the upper arms on top of the preacher’s bench or the incline bench while holding a dumbbell in each hand. Holding the dumbbell at shoulder height is proper. This will be where you begin.
Carefully drop the weights as you inhale until your upper arm is extended and your biceps are fully stretched.
Use your biceps to curl the dumbbells up as you exhale until your biceps are fully tightened and the weights are at shoulder level.
Repeat for the prescribed number of repetitions after giving the biceps a strong second of contraction.
Face-down incline dumbbell biceps curl

A workout that targets the biceps is the face-down incline dumbbell biceps curl, which is carried out on an inclined bench. By establishing a vertical arm angle, you can isolate your biceps while minimizing the use of your shoulder muscles. As part of upper-body or arm-focused training, this curl variation is typically done for moderate to high reps, like 8-12 reps per set or more.
how to execute: Lay face down on an incline bench with your shoulders close to the top of the inclination. Hold a dumbbell in each hand. You have a choice between crossing your legs to the sides or putting your knees on the seat.
Allow your arms to naturally stretch and hang in front of you so that they are parallel to the ground.
Maintain your elbows at your sides while turning your palms forward. This will be where you begin.
Biceps contraction is required to raise the dumbbells until your arms are fully extended. During this part of the exercise, exhale while making sure that only your forearms are moving. At all times, the upper arms should be kept still.
until your arms are fully stretched, lower the dumbbells.
Repeat as many times as necessary.
EZ bar spider curl

Face down on either an incline bench or the flat side of a preacher bench, the EZ-bar spider curl is a biceps-targeting exercise. A more comfortable wrist posture is made possible with the EZ-bar, and the angle works to isolate the biceps while minimizing the use of the shoulder muscles. conduct Ez bar spider curl 8 to 10 reps
how to execute: On the portion of the preacher bench that you would typically sit on, place the bar first. To ensure that the barbell is balanced and won’t fall off, make sure to line it correctly.
Your body and stomach should be forced against the front side of the preacher’s bench, which is where the preacher’s arms often rest. Move to this side of the preacher’s bench.
Place your upper arms on top of the pad on the inside of the preacher bench, making sure your feet significantly toes are firmly planted on the floor.
in your palms facing up and your arms around shoulder width apart or just a little closer to one another, grasp the barbell in a supinated grip.
Exhale as you slowly start to move the barbell upward. Squeeze the biceps while maintaining the contracted position for a brief moment.
Eventually, start bringing the barbell back to the initiate position as you inhale
conduct ez bar spider curl exercise for 8 to 10 reps
Dumbbells are another option for executing this workout. Just be sure the portion of the preacher bench where you would normally sit is where you set the dumbbells properly
TRX suspension curl
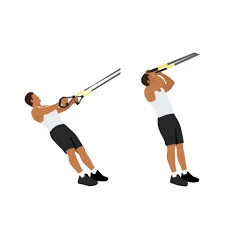
Anyone with limited access to free weights, cables, and machines will benefit from this curl variation. The exercise’s difficulty can also be readily changed, just like with other suspension-based exercises, by modifying the body’s position; the more upright you are, the simpler the exercise will be.
Since you are merely utilizing your body weight as resistance, changing the repetition rhythm can lengthen the period of time your biceps are under tension.
How to execute: Attach a TRX suspension to the support above.
Take hold of the handles and advance a short distance toward the anchor point
Lean back while maintaining a neutral spine and straight hips and shoulders.
curl the body weight up
Coach’s Tip: Change the body position to make the exercise more challenging. The more body weight you oppose throughout the exercise, the further back you tilt. You can put the body in a more upright position to make the workout simpler.
Execute three to four sets of reps until failure, changing your foot posture as necessary.
Benefits of best mass biceps Training
the biceps are a beautiful muscle type, at least in the mind. The usefulness of strengthening your biceps may seem clear if you’re aiming for round, peaked biceps. However, even if you aren’t driven by a specific aesthetic, having strong biceps should aid the person in lifting heavy things
Support Compound Lifts: Strong, muscular biceps are a pre needed for building a strong, powerful back. the person mandates biceps strength to support all that weight whenever he/she rowing in any manner.
During powerful rows, the back should be conducting the majority of the work. However, if the biceps should not capable enough to support the person, the back improvements will stop before they even initiate.
It’s mandatory to grow your biceps in addition to supporting those back-builders. However, they are crucial for powerful pushing motions as well. If the person likes to do bench pressing, people will properly pay close concentration to the triceps. generate the biceps to preserve equilibrium in the arms. This equilibrium is vital for preventing harm.
Fitness That Is Useful: Not all big biceps involve removing the shirt sleeves. The capability to lift the children and pressure the grocery bags into the trunk of the car is made possible by having strong upper arms. Exercise for the biceps is also beneficial to the wrists and forearms. These muscles are necessary for maintaining your grip throughout lengthy training sessions that focus on practical motions like farmer’s carry.
Physical Conditioning: Training the biceps will aid you in achieving the large physique objectives in addition to aiding your big lifts. Work your attempts if you want thicker arms, but working your biceps will just go so far in permitting the shirt sleeves to enlarge to a certain extent.
Pre workout Drink
There is no doubt that a pre-workout pill helps motivate you to hit the gym. However, there are drawbacks and dangers that might exist.
Many pre-workout drinks are little more than a few cheap stimulants with some powder thrown in in order to create an attractive label and convincing ad text. They are sometimes loaded full of worthless substances and/or microscopic quantities of otherwise desirable ingredients.
Many others are total failures who don’t even have any stimulants working in their favor.
Caffeine: Beyond just boosting energy, caffeine has other benefits. Additionally, it makes muscles stronger and more resilient.
Beta-Alanine: A naturally occurring amino acid called beta-alanine can speed up muscle growth and lessen the effects of exercise-induced weariness.
Malate of citrulline: An amino acid called citrulline reduces muscular soreness, increases aerobic capacity, and enhances muscle endurance.
Betaine: Betaine, a substance present in plants like beets, boosts the production of human growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 in response to acute exercise, as well as improving muscle endurance and strength.
Ornithine: Ornithine is an amino acid that is abundant in dairy products and beef. It helps to increase lipid oxidation, which is the process of burning fat for energy rather than carbohydrates or glycogen.
Theanine: The amino acid theanine, which is predominantly present in tea, improves mood, boosts nitric oxide synthesis, promotes blood flow, and lessens the effects of physical and mental stress.
A word regarding dietary intake
For wider, powerful arms, the proper exercises are necessary, but you are also mandated to concentrate on the nutritional requirements. You also need to concentrate on choosing the correct nutrients to encourage muscular building.
Your body may be limited if you don’t provide it with the fuel it requires results of the arm workout
When aiming for larger arms have the following in mind
Increase your intake of protein. Protein helps muscles strengthen and accelerates healing time in between workouts. Eggs, salmon, chicken breast, tuna, lean beef, turkey breast, Greek yogurt, beans, and chickpeas are examples of foods high in protein that the person must want to have in the diet. From the perspective of building muscle, a daily protein consumption of 1.4 to 1.8 grams per pound of body weight is necessary.
Consume more complex carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates just like protein, are important for growing muscle. These carbohydrates give the body a power source and nourishment. Oatmeal, quinoa, brown rice, potatoes, sweetcorn, and green peas should be categorized along with whole-grain bread and pasta.
Concentrate on good fats.
Your body may begin utilizing protein for energy instead of fat if you don’t get enough fat in your diet. peanut butter, avocado, olive oil, and salmon are all skillful sources of healthful fats.
Do not cut calories. preserve in mind that should not consume enough calories each day. You probably won’t see effects from your arm-building exercises if your calorie intake is too low. attempt to meet caloric needs by taking fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and carbohydrates from healthy sources.
Exercise Mistakes to Avoid for Biceps
Prevent drop; it’s just as crucial to raise during the eccentric phase as it is to lower during the eccentric phase. Keep the action regulated, keeping tension throughout the entire movement, and don’t forget to squeeze at the top.
Avoid swinging: a little momentum near the end of your set is accessible and possibly acceptable, but we won’t tolerate raising a dumbbell with a heavy enough weight that you have to use your body weight to raise it. You guys are acting it out. Keep your body still and upright.
you concentrate on slowly overloading by gradually increasing the weight or reps to develop bigger biceps. Your muscles will be pushed to their limits and encouraged to expand if you alternate sets of higher reps with lighter weight and lower reps with heavier weight.
Conclusion
To develop larger arms, you must perform exercises that concentrate on your biceps and triceps. Work these muscles at least twice or three times per week, and as your strength increases, try to perform more repetitions and sets of each exercise.
Be sure that you incorporate exercises that build your shoulders, back, chest, core, and legs as well for a well-rounded workout.
Along with doing focused exercises, it’s crucial to maintain a diet that is high in complex carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats and has enough calories to power your workouts.
FAQs
Should you train the biceps muscles every day?
Even though it could be appealing to incorporate these exercises into your everyday regimen, Shirdan cautions, You should not train your biceps every day.”
Muscle fibers are damaged during exercise, and they need time to repair themselves in order to grow stronger. Without adequate mending, repeatedly breaking down muscles can hinder growth, gains, and general health.
How frequently should you exercise your biceps if you want to bulk up?
As long as you allow 24-36 hours between each session of bicep-focused training, there is nothing preventing you from incorporating it into your schedule.
Train hard, train wisely, and change up your bicep exercises.
Since the triceps make up over 70% of the upper arm, don’t be scared to perform a little triceps work on days when you aren’t exercising the biceps.
How Much Repetition to Develop Biceps?
The number of reps you should perform to build your biceps depends on your skill level and the weights you have accessible. targeting 6–12 repetitions should be sufficient for hypertrophy (muscle growth). However, you might find programming for isolation exercises like bicep curls with 10 to 15 repetitions. This is due to the fact that working at greater rep ranges will produce more of a pump, which is what we strive for when training the biceps. As a general rule, 3-4 sets of your preferred rep range can lead to muscle growth.
How can I grow my biceps by 1 inch in a week?
Strategy: Perform this every other day.
Pull-ups: 20–30 total reps across the max.
Preacher curls with an E-Z bar: 3 sets X 6–8 reps, 2 sets X 8–10 reps, and 1 set X 20 reps.
Hammer curls: 4 sets of 8, 10, 12, and 15 repetitions.
cable curl: 7 sets of 7 reps, with 30-second rests in between sets
21 repetitions total in 3 sets of barbell curls.
Zottman Curls: 30 reps in one set.
How can I bulk up my biceps in a month?
If you exercise while following these 5 easy steps, you should initiate noticing noticeable benefits in just 30 days:
begin arm exercises with the heaviest sets. First, convert your arm workout into a push-pull routine to boost your training volume. Increase your training frequency, change your rep ranges, and train until you reach failure.
Are two bicep workouts sufficient?
In general, you don’t need as much volume to break down the muscle fibers for growth if you are fresh to training. All you require is 2 to 3 to get your muscles to adapt and grow. If you’re an experienced lifter, you might need four to five exercises for each muscle group and follow a four to five-day split.
should an individual obtain biceps in two weeks?
You can’t definitely pick up massive arms fast because it takes time and effort to build muscle, but with regular coaching that gradually increases load and intensity, you should initiate a change in your arm strength and size after around four weeks.
Which biceps curl is the best?
Increase bicep size by performing bicep curls. But for overall bigger arms, we advise focusing on bicep curl varieties like hammer curls and EZ bar curls. Keep in mind that it may take a month or two before you see improvements in your arms.
Are 2 finger gap biceps nicely?
How to tell if your biceps are short or long.
Then, between the end of the muscle and the forearm, measure the length of your biceps tendon with your finger. It’s as simple as that: if it measures more than two fingers, your biceps are short, and if it measures fewer than two fingers, your biceps are long. Both varieties of biceps have benefits and drawbacks.
Do heavy lifts help you develop your biceps?
You don’t always need to lift really heavy weights to develop great biceps, strength, and conditioning coach if your bicep-building exercises involve you flinging around 75-pound or more dumbbells. He created the biceps exercise with simply a resistance band and two light weights.
Do hammer curls work well?
Hammer curls are excellent for strengthening your forearms, wrists, and some of your biceps. The bicep curl, on the other hand, is more effective at working your complete bicep. There is a reason why so many people use this workout to develop their arms.
Do biceps increase with weight or repetitions?
As a result, high repeats with lightweight tend to develop muscle endurance while low reps with heavy weight tend to increase muscle mass. This does not bind you to use just one technique. For long-term success, alternating forward and backward between the two may be the ideal strategy.
When do biceps stop developing?
Strength and muscular mass typically increase gradually starting at birth and peak between ages 30 and 35. From that, muscle strength and performance begin to diminish gradually and linearly, but from age 65 for women and 70 for males, the decline becomes more pronounced.
References
- 10 Best Biceps Workout Exercises for Building Muscle. (2021, May 13). Bodybuilding.com. https://www.bodybuilding.com/content/10-best-muscle-building-biceps-exercises.html
- Hicks, R. (2023, September 26). 22 Best Bicep Exercises to Build Muscle. Men’s Health. https://www.menshealth.com/uk/building-muscle/a758801/best-bicep-exercises-for-building-muscle/
- Dewar, M. (2023, August 30). The 20 Best Biceps Exercises & Workouts, Chosen By Experts. BarBend. https://barbend.com/best-biceps-exercises/
- Stewart, A. (2021, March 18). The Top 5 Exercises For Increasing Bicep Mass. Muscle & Strength. https://www.muscleandstrength.com/articles/top-5-exercises-increasing-bicep-mass.html
- Roland, J. (2019, November 25). 8 Best Exercises for Bigger, Stronger Arms. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/exercise-fitness/how-to-get-bigger-arms#bottom-line
- McGuire, J., & Shirdan, P. (2022, May 1). Best bicep exercises: 7 of the best bicep exercises for building your arms. Tom’s Guide. https://www.tomsguide.com/news/best-bicep-exercises
- Michael,Matthews(2015,november 27). The Absolute Best Biceps Workout: Biceps 5 Exercises That Build Big Guns.Legion Athletics.https://legionathletics.com/best-biceps-workout/