Quadriceps Muscle
Quadriceps femoris muscle Anatomy
The quadriceps Muscle also called simply the quadricep Femoris or Knee extensor is a large muscle group that Covers the Front Of the Thigh And the four muscles Group That Makes One Strongest Muscle Of The Lower Limb ( on the front of the thigh).
It is the super extensor muscle of the knee, forming a Bulky fleshy mass That Comes to the front and sides of the femur.
Quadriceps are subdivided into four Muscle portions or Muscle ‘heads’:
The Quadriceps Muscle Origin:
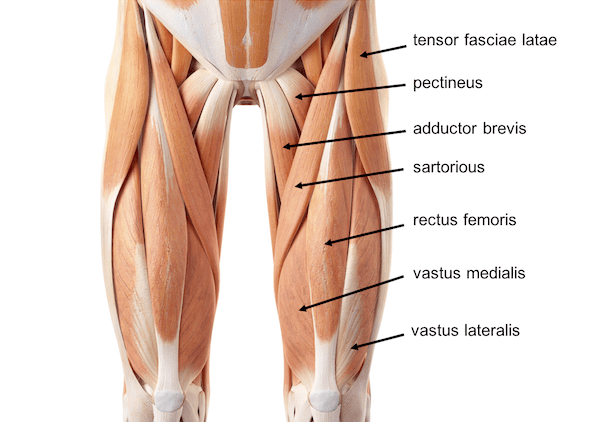
Rectus femoris: This Muscle is Located At The Centre Of The Thigh And Covers All the Other Three Muscles. The origin Of The Rectus Femoris is On The Ilium.
the middle of the thigh, covering most of the other three quadriceps muscles. It originated on the ilium. It is named after its straight course.
All three lie deep to the rectus femoris and origination is from the body of the femur, which they cover from the trochanters to the condyles:
Vastus lateralis: on the lateral side of the femur
Vastus medialis: on the medial side of the femur
Vastus intermedius: lies between vastus lateralis and vastus medialis on the front of the femur and Deep To Rectus Femoris. Palpation Of This Muscle Action Is Difficult.
Muscle Insertion:
All four parts of the quadriceps muscle insert into the tuberosity of the tibia, Through the patella, where the quadriceps tendon becomes the patellar ligament, which then attaches to the tibia.
There is a fifth muscle of the quadriceps complex that is often forgotten called articularis genu.
Rarely Seen Muscle The Tensor Vastus intermedius is the sixth Muscle Seen In the Quadriceps Group.
Nerve Supply: Femoral Nerve
Quadriceps muscle innervated by Femoral nerve (L2,3, 4).
The femoral nerve originates from L2 to L4, innervating the contractile portions of the thigh anteriorly (quadriceps muscle, sartorius muscle), of the hip (comb), and the skin in the anteromedial portion of the thigh, knee, leg, and the back of the foot. Additionally, L1 fibers are present. The major psoas muscle’s thickness is where the roots converge downward and sideways, merging in a single trunk close to the L5 transverse process. The created nerve descends and leaves the psoas muscle caudally, continuing its caudal journey through the center of the psoas/iliac muscle complex.
Blood Supply
The lateral femoral circumflex artery.
The quadriceps muscle gets its blood by the femoral artery. It is the external iliac artery’s continuation (after the inguinal ligament). It becomes a popliteal artery as it descends via the anteromedial region of the thigh to the ring of the adductor channel. The femoral artery can be visualized as a straight line that joins the posterior region of the femur’s medial condyle to the inguinal canal’s center. Both the superficial and deep femoral arteries are considered to be among its most significant branches for the quadriceps muscle.
Lymphatic Drainage
The popliteal vein continues as the femoral vein, which then becomes the external iliac vein by traveling along the femoral artery’s course up to the inguinal ligament.
The right and left lumbar trunks include the lumbar aortic lymph nodes, which are reached by the lower limb lymphatic arteries; outflow from these nodes ends in the cisterna chyli.
Quadriceps Muscle Action (Work of the muscle)
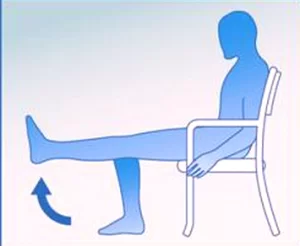
All four quadriceps are powerful extensors of the knee joint. They are crucial in day-to-day activities like walking, running, jumping, and squatting.
Rectus Femoris is also a Hip Flexor With Other Hip Flexor Assistance. This action is also crucial to walking or running as it swings the leg forward into the ensuing step.
The vastus medialis stabilizes the patella and the knee joint during gait.
This Muscle is of Prime Importance, Because Of Our Daily Activity, Mostly And Highly used in day-to-day activity. Quadriceps, physiotherapists, and Orthopedics give Prime Importance To Their Rehabilitation Program to train and develop Quadriceps as early as possible.
This Muscle requires regular attention to do regular Exercise and lengthen properly – To Walk, Stand Properly, and Live a Healthy Life.
How To Strengthen & Stretch the Quadriceps Muscles?
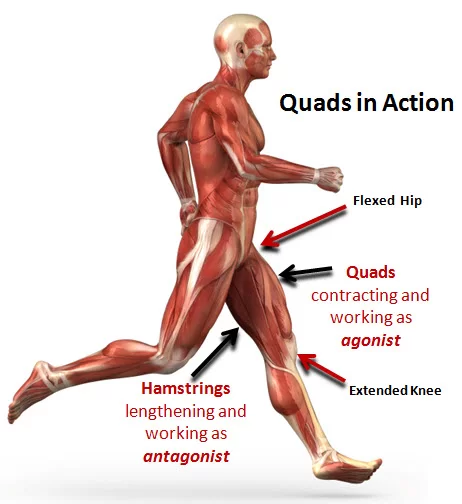
Quadriceps Muscles Strengthening Exercise:
In strengthening training, the muscles are trained by Too Many Way of exercises. Effective exercises include squatting and leg presses.
Isotonic Exercise For the Quadriceps is the leg extension exercise With a Weight Cuff.
Stretching Of Muscle is in a Prone Position With Knee Fully Flexed And With Hip Extension Required.
Running and squatting Are Famous forms of Exercise In Which the Quadriceps are Highly Used.
In Bodybuilding communities, the Quadriceps muscle is referred to as the “leg triceps”.

Quadriceps muscles Stretching Exercise:
In Sports Persons, Specially Footballers, Gymnastics, and Hockey players Other Forms Of Competitive Outdoor Games Require Bulky And Lengthening Quadriceps And That’s Why They Doing Regular Stretching And Strengthening Exercises.
Regular Strengthening And Stretching Exercise Avoid Too Many Lower limb Diseases Like OA Knee And Ligament Injury.
Muscle Fibres
As the femoral quadriceps muscle descends in-depth, more aerobic fibers will replace the superficial anaerobic fibers. The white fibers will activate following the activation of the red fibers; the initial fibers are less vascularized than the oxidative fibers. During a contraction, there will be delayed deoxygenation of the underlying fibers.
Men exhibit higher percentages of contractile strength and speed than women, most likely due to hormone levels and greater muscle mass in men. Testosterone increases the electrical impulse speed of the motor unit, increases the amount and rate of calcium released into the fibers (faster contraction), and speeds up the healing process and the hypertrophic response. The proportion of white fibers is higher in men.
Clinical Importance
Quadriceps Muscle Strain
A quadriceps muscle strain is an acute tearing injury of the quadriceps. This injury is usually due to an acute stretch of the muscle, often at the same time as a forceful contraction or repetitive functional overloading. to know more about Quadriceps strain click here.
The muscle component most affected by indirect lesions is the rectus femoris, and in 60% of cases, the trauma affects the most proximal location. The distal portion of the rectus femoris will be damaged in 10% of instances, with a lesion level of the third degree.
A whole rupture of the quadriceps muscle is uncommon in athletes; older individuals, those on steroids, and those suffering from systemic illnesses are more likely to have this kind of lesion. A whole rupture of a vastus might happen in an asymptomatic manner, simulating another issue. Such as the presence of back pain with anterior irradiation of the leg. Complete rupture of one or more vastii may be the consequence of deteriorating hypertrophy brought on by an underlying illness, such as multiple sclerosis, an orthopedic condition, or a neurological condition.
Quadriceps Muscle Examination
The Nachlas sign is a manual diagnostic used to assess the femoral nerve. The patient is prone as the operator grips the ankle, bending the knee with the thigh resting on the bed and pushing the heel closer to the buttock. The femoral nerve may be compressed or irritated if radial discomfort in the thigh is felt anteriorly; if additional symptoms develop in the buttock or at the articular sacroiliac level, the source of the issue needs to be found elsewhere.
The patient can be placed to the side for another assessment. The operator grasps the non-supporting side’s thigh from behind and pulls the limb towards the extension, first extending the knee and then repeating the action with the knee flexed. Traction of the femoral nerve is caused by flexion of the knee and extension of the hip; pain radiating down the anterior part of the thigh indicates a specific problem at the root of L3, whereas symptomatology in the medial tibial region indicates problems with L4. Potential symptoms on the other side throughout the test would suggest that a contralateral root irritation or constriction occurred.
Multiple Sclerosis
The quadriceps muscle loses strength and bulk as a result of multiple sclerosis, with an increase in anaerobic fibers and a decrease in oxidative fibers. White fibers become more numerous, but they also experience greater atrophy. Increase intramuscular fat and fibrosis processes.
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
The lack of the dystrophin protein, which is necessary for the regeneration of muscle fibers, is a characteristic of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). The muscle cell manifests with necrotic fibers, increased intramuscular fat, and fibrosis. The quadriceps muscle becomes less functional and sculptural, and its volume and regenerative ability decrease.
Aging
The structure and function of the quadriceps change as we age due to muscular adaptation. The musculature tends to lose bulk, and volume (sarcopenia) weakens the muscles’ ability to coordinate and exert force. Denervation processes result in the loss of motor units while the proportion of red fibers rises. Fibrosis processes and intramuscular fat increase as a result.
Fibromyalgia
Less phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are found in muscle cells, which also have a reduced capacity for contraction. DNA fragmentation, decreased capillarization with thickening of the endothelium, marked hypotrophy of white fibers and mitochondrial suffering of red fibers, and elevations in intramuscular fat are all seen.
Summary
Quadriceps muscles play an essential role in performing day-to-day activities like walking, running, jumping, and kicking. Quadriceps muscle injuries, such as strains can prevent you from doing day-to-day activities such as straightening your knee or bearing weight on your leg.
Mostly mild-to-moderate quadriceps pain gets better with medical treatments. A severe injury, such as a quadriceps muscle tear may require surgery to repair.
FAQ
What is the 5th quad muscle?
5th muscle of Quad. the muscle group is tensor vastus intermedius (TVI) newly found in the latest research located in the anterolateral thigh and counted as the fifth muscle.
Is the quadriceps a muscle or tendon?
Quadriceps is a group of four muscles that join together just above the patella to form the quadriceps tendon. This tendon attaches attached to the shinbone (tibia) by the patellar tendon.
Which is the biggest quad muscle?
Vastus lateralis
Vastus lateralis connects your femur bone to your patella. It travels along the lateral side of your thigh. It’s the biggest and strongest of the five quadriceps muscles.
What is the weakest quad muscle?
Vastus medialis is the weakest & smallest of the quad. muscles and is mostly weak mainly in women and runners.
What are thigh muscles called?
The thigh has attaches 3 sites strong groups of muscles:
1 – The hamstring muscles in the back of the thigh.
2- The quadriceps muscles in the front of the thigh.
3 – The adductor muscles on the inside of the thigh.

95 Comments