Rotator Cuff Injuries: Physiotherapy Treatment, Exercise
A Rotator cuff injuries is a tear of one or more of the tendons of the four rotator cuff muscles of the shoulder. A rotator cuff ‘injury’ can include any type of irritation or overuse of those muscles or tendons and is among the most common conditions affecting the shoulder.
Anatomy of Rotator cuff lesion
The tendons of the rotator cuff Muscle Group, not the muscles, are most commonly involved, and of the four Muscle Tendon Are Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Minor And Subscapularis, the supraspinatus is most frequently affected, as it passes below the acromion. The role of the supraspinatus is to resist downward motion. The supraspinatus resists downward motion while the shoulder is relaxed as well as when carrying weight.
Such a tear usually occurs at its point of insertion onto the humeral head at the greater tubercle. Even though the supraspinatus is the most commonly injured muscle of the four muscles in the rotator cuff, the other three muscles that comprise the rotator cuff, the infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis, may also be injured.
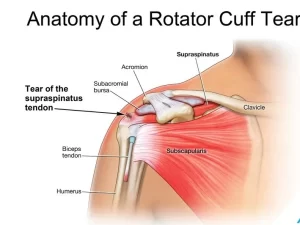
The Rotator cuff is responsible for stabilizing the glenohumeral joint, abducting, externally rotating, and internally rotating the humerus. When shoulder trauma occurs, these functions can be compromised. Because individuals are highly dependent on the shoulder for many activities, overuse of the muscles can lead to tears, the vast majority again occurring in the supraspinatus tendon.
Signs and symptoms :
Signs :
It has been suggested that no single physical examination test distinguishes reliably between bursitis, partial-thickness, and full-thickness tears. On the contrary, a combination of tests seems to provide the most accurate diagnosis. For impingement, these tests include the Hawkins-Kennedy impingement sign in which the examiner medially rotates the patient’s flexed arm, forcing the supraspinatus tendon against the coracoacromial ligament and so producing pain if the test is positive a positive painful arc sign, and weakness in external rotation with the arm at the side.
For the diagnosis of full-thickness rotator cuff tear, the best combination appears to include once more the painful arc and weakness in external rotation, and in addition, the drop arm sign. This test is also known as Codman’s test. The arm is raised to the side to 90° by the examiner. The patient then attempts to look to lower the arm back to neutral, palm down. If the arm drops suddenly or pain is experienced, the test is considered positive.
Symptoms of Rotator cuff Injuries:
Symptoms may occur immediately after trauma Which is acute Injury or develop over time Gradually Which is chronic Pain.
Acute injury is less frequent than chronic disease, but may follow bouts of forcefully raising the arm against resistance, as occurs in weightlifting, for example. In addition, falling forcefully on the shoulder can cause acute symptoms. These traumatic tears predominantly affect the supraspinatus tendon or the rotator interval and symptoms include severe pain that radiates through the arm, and limited range of motion, specifically during abduction of the shoulder. Chronic tears occur among individuals who constantly participate in overhead activities, such as pitching or swimming, but can also develop from shoulder tendinitis or rotator cuff disease. Symptoms arising from chronic tears include sporadic worsening of pain, debilitation, and atrophy of the muscles, noticeable pain during rest, crackling sensations (crepitus) when moving the shoulder, and inability to move or lift the arm sufficiently, especially during abduction and flexion motions.
Pain in the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder is not specific to the shoulder and may arise from, and be referred from, the neck, heart or gut.
Patient history will often include pain or ache over the front and outer aspect of the shoulder, pain aggravated by leaning on the elbow and pushing upwards on the shoulder (such as leaning on the armrest of a reclining chair), intolerance of overhead activity, pain at night when lying directly on the affected shoulder, pain when reaching forward (e.g. unable to lift a gallon of milk from the refrigerator). Weakness may be reported, but is often masked by pain and is usually found only through examination. With longer-standing pain, the shoulder is favored and gradual loss of motion and weakness may develop, which, due to pain and guarding, are often unrecognized by the patient and only brought to attention during the examination.
Primary shoulder problems may cause pain over the deltoid muscle intensified by abduction against resistance – the impingement sign. This signifies pain arising from the rotator cuff, but cannot distinguish between inflammation, strain, or tear. Patients may report that they are unable to reach upwards to brush their hair or to lift a food can from an overhead shelf.
Many rotator cuff tears are asymptomatic. They are known to increase in frequency with age and the most common cause is age-related degeneration and, less frequently, sports injuries or trauma. Both partial and full-thickness tears have been found in post-mortem and MRI studies in those without any history of shoulder pain or symptoms. However, the most common presentation is shoulder pain or discomfort. This may occur with activity, particularly shoulder activity above the horizontal position, but may also be present at rest in bed. Pain-restricted movement above the horizontal position may be present, as well as weakness with shoulder flexion and abduction.
Risk factors :
Risk factors of Rotator cuff tears
Some risk factors of experiencing a rotator cuff tear cannot be changed: age, body mass index, and height. Recurrent lifting and overhead motions are at risk for rotator cuff tears. People who have jobs that involve overhead work, such as carpenters, painters, custodians, and servers are at risk of also experiencing a rotator cuff tear. People who play sports that involve overhead motions, such as swimming, volleyball, baseball, tennis, and American football quarterbacks, are at a greater risk of experiencing a rotator cuff tear. Generally, the incidence of rotator cuff tears or injuries increases with age while corticosteroid injection for pain relief increases the risk of the tendon tear and delays tendon healing.
Mechanisms of injury :
The two main causes are injury (acute) and degeneration (chronic and cumulative), and the mechanisms involved can be either extrinsic or intrinsic or, probably most commonly, a combination of both.
Acute tears :
The amount of stress needed to tear a rotator cuff tendon acutely will depend on the underlying condition of the tendon prior to the stress. In the case of a healthy tendon, the stress needed will be high, such as a fall on the outstretched arm. This stress may occur coincidentally with other injuries such as a dislocation of the shoulder, or separation of the acromioclavicular joint. In the case of a tendon with pre-existing degeneration, the force may be surprisingly modest, such as a sudden lift, particularly with the arm above the horizontal position. This is a common occurrence with rear-seated passengers in a motor vehicle collision, regardless of speed.
Chronic tears :
Chronic tears are indicative of extended use in conjunction with other factors such as poor biomechanics or muscular imbalance. Ultimately, most are the result of wear that occurs slowly over time as a natural part of aging. They are more common in the dominant arm, but a tear in one shoulder signals an increased risk of a tear in the opposing shoulder. Several factors contribute to degenerative, or chronic, rotator cuff tears of which repetitive stress is the most significant. This stress consists of repeating the same shoulder motions frequently, such as overhead throwing, rowing, and weightlifting. Many jobs that require frequent shoulder movements such as lifting and overhead movements also contribute.
Another factor in older populations is impairment of blood supply. With age, circulation to the rotator cuff tendons decreases, impairing the natural ability to repair, ultimately leading to, or contributing to, tears.
The final common factor is impingement syndrome, the most common non-sports related injury and which occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles become irritated and inflamed while passing through the subacromial space beneath the acromion. This relatively small space becomes even smaller when the arm is raised in a forward or upward position. Repetitive impingement can inflame the tendons and bursa, resulting in the syndrome.
Extrinsic factors :
Well-documented anatomical factors include the morphologic characteristics of the acromion. Hooked, curved, and laterally sloping acromia are strongly associated with cuff tears and may cause tractional damage to the tendon. Conversely, flat acromia may have an insignificant involvement in cuff disease and consequently may be best treated conservatively. The development of these different acromial shapes is likely both genetic and acquired. In the latter case, only age has been positively correlated with progression from flat to curved or hooked. The nature of mechanical activities, such as sports involving the shoulder, along with the frequency and intensity of such sports, may be responsible for the adverse development. Sports such as bowling in cricket, swimming, tennis, baseball, and kayaking, are most frequently implicated. However, a progression to a hooked acromion may simply be an adaptation to an already damaged, poorly balanced rotator cuff that is creating increasing stress on the coracoacromial arch. Other anatomical factors that may have significance include os acromiale and acromial spurs. Environmental factors implicated include increasing age, shoulder overuse, smoking, and any medical condition that affects circulation or impairs the inflammatory and healing response, such as diabetes mellitus.
Intrinsic factors :
Intrinsic factors refer to injury mechanisms that occur within the rotator cuff itself. The principal is a degenerative-microtrauma model, which supposes that age-related tendon damage compounded by chronic microtrauma results in partial tendon tears that then develop into full rotator cuff tears.As a result of repetitive microtrauma in the setting of a degenerative rotator cuff tendon, inflammatory mediators alter the local environment, and oxidative stress induces tenocyte apoptosis causing further rotator cuff tendon degeneration. A neural theory also exists that suggests neural overstimulation leads to the recruitment of inflammatory cells and may also contribute to tendon degeneration.
Pathophysiology :
The shoulder joint is made up of three bones: the shoulder blade (scapula), the collarbone (clavicle) and the upper arm bone (humerus).
Further information: Shoulder
The shoulder is a complex mechanism involving bones, ligaments, joints, muscles, and tendons.
MRI of normal shoulder intratendinous signal :
MRI of rotator cuff full-thickness tear
Tears of the rotator cuff tendon are described as partial or full thickness and full thickness with complete detachment of the tendons from bone.
Partial-thickness tears often appear as fraying of an intact tendon.
Full-thickness tears are “through-and-through”. These tears can be small pinpoint, larger buttonhole, or involve the majority of the tendon where it still remains substantially attached to the humeral head and thus maintains function.
Full-thickness tears may also involve complete detachment of the tendon(s) from the humeral head and may result in significantly impaired shoulder motion and function.
Shoulder pain is variable and may not be proportional to the size of the tear.

However, for simplicity, tears are sometimes classified based on the trauma that caused the injury:
Acute, as a result of a sudden, powerful movement which might include falling onto an outstretched hand at speed, making a sudden thrust with a paddle in kayaking, or following a powerful pitch/throw
Subacute, arising in similar situations but occurring in one of the five layers of the shoulder anatomy
Chronic, developing over time, and usually occurring at or near the tendon (as a result of the tendon rubbing against the overlying bone), and usually associated with an impingement syndrome
Diagnosis :
A complete tear of the supraspinatus resulted in a shift upwards of the head of the humerus
Diagnosis is based on physical assessment and history, including a description of previous activities and acute or chronic symptoms. A systematic, physical examination of the shoulder comprises inspection, palpation, range of motion, provocative tests to reproduce the symptoms, neurological examination, and strength testing. The shoulder should also be examined for tenderness and deformity. Since pain arising from the neck is frequently ‘referred’ to the shoulder, the examination should include an assessment of the cervical spine looking for evidence suggestive of a pinched nerve, osteoarthritis, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Diagnostic modalities, dependent on circumstances, include X-ray, MRI, MR arthrography, double-contrast arthrography, and ultrasound. Although MR arthrography is currently considered the gold standard, ultrasound may be the most cost-effective. Usually, a tear will be undetected by X-ray, although bone spurs, which can impinge upon the rotator cuff tendons, may be visible. Such spurs suggest chronic severe rotator cuff disease. Double-contrast arthrography involves injecting contrast dye into the shoulder joint to detect leakage out of the injured rotator cuff and its value is influenced by the experience of the operator. The most common diagnostic tool is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which can sometimes indicate the size of the tear, as well as its location within the tendon. Furthermore, MRI enables the detection or exclusion of complete rotator cuff tears with reasonable accuracy and is also suitable to diagnose other pathologies of the shoulder joint.
The logical use of diagnostic tests is an important component of effective clinical practice.
Clinical judgment, rather than overreliance on MRI or any other modality, is strongly advised in determining the cause of shoulder pain or planning its treatment since rotator cuff tears are also found in some without pain or symptoms. The role of X-ray, MRI, and ultrasound, is adjunctive to clinical assessment and serves to confirm a diagnosis provisionally made by a thorough history and physical examination. Over-reliance on imaging may potentially lead to overtreatment or distraction from the true underlying problem.
MRI :
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound are comparable in efficacy and helpful in diagnosis although both have a false positive rate of 15 – 20%. MRI can reliably detect most full-thickness tears although very small pinpoint tears may be missed. In such situations, an MRI combined with an injection of contrast material, an MR-arthrogram, may help to confirm the diagnosis. It should be realized that a normal MRI cannot fully rule out a small tear (a false negative) while partial-thickness tears are not as reliably detected. While MRI is sensitive in identifying tendon degeneration (tendinopathy), it may not reliably distinguish between a degenerative tendon and a partially torn tendon. Again, magnetic resonance arthrography can improve the differentiation. An overall sensitivity of 91% (9% false negative rate) has been reported indicating that magnetic resonance arthrography is reliable in the detection of partial-thickness rotator cuff tears. However, its routine use is not advised, since it involves entering the joint with a needle with potential risk of infection. Consequently, the test is reserved for cases in which the diagnosis remains unclear.
Ultrasound :
Musculoskeletal ultrasound has been advocated by experienced practitioners, avoiding the radiation of X-ray and the expense of MRI while demonstrating comparable accuracy to MRI for identifying and measuring the size of full-thickness and partial-thickness rotator cuff tears. This modality can also reveal the presence of other conditions that may mimic rotator cuff tear at clinical examination, including tendinosis, calcific tendinitis, subacromial subdeltoid bursitis, greater tuberosity fracture, and adhesive capsulitis. However, MRI provides more information about adjacent structures in the shoulder such as the capsule, glenoid labrum muscles and bone and these factors should be considered in each case when selecting the appropriate study.
Projectional radiography :
Projectional radiograph of normal glenohumeral position.
High-riding humeral head in a rotator cuff tear.
X-ray projectional radiography cannot directly reveal tears of the rotator cuff, a ‘soft tissue’, and consequently, normal X-rays cannot exclude a damaged cuff. However, indirect evidence of pathology may be seen in instances where one or more of the tendons have undergone degenerative calcification (calcific tendinitis). The humeral head may migrate upwards (high-riding humeral head) secondary to tears of the infraspinatus, or combined tears of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus.The migration can be measured by the distance between:
A line crossing the center of a line between the superior and inferior rims of the glenoid articular surface
The center of a “best-fit” circle positioned over the humeral articular surface
Normally, the former is positioned inferiorly to the latter, and a reversal is therefore indicating a rotator cuff tear. Prolonged contact between a high-riding humeral head and the acromion above it, may lead to X-rays findings of wear on the humeral head and acromion and secondary degenerative arthritis of the glenohumeral joint (the ball and socket joint of the shoulder), called cuff arthropathy, may follow.
Incidental X-ray findings of bone spurs at the adjacent acromioclavicular joint may show a bone spur growing from the outer edge of the clavicle downwards towards the rotator cuff. Spurs may also be seen on the underside of the acromion, once thought to cause direct fraying of the rotator cuff from contact friction, a concept currently regarded as controversial.
If pain is relieved, the test is considered positive for rotator-cuff impingement, of which tendinitis and bursitis are major causes. However, partial rotator-cuff tears may also demonstrate good pain relief, so a positive response cannot rule out a partial rotator-cuff tear. However, with a demonstration of good, pain-free function, treatment will not change, so the test is useful in helping to avoid overtesting or unnecessary surgery.
Prevention of Rotator Cuff Injuries:
Avoid Long-term overuse of the shoulder joint is generally thought to limit the range of motion and productivity due to daily wear and tear of the muscles, are the best option for preventive advice.
The following recommendations usually include:
- regular shoulder exercises to maintain strength and flexibility
- using proper form when lifting or moving heavy weights
- resting the shoulder when experiencing pain
- application of cold packs and hot pads to a painful, inflamed shoulder joint
- strengthening program to include the back and shoulder girdle muscles as well as the chest, shoulder, and upper arm
- adequate rest periods in occupations that require repetitive lifting and reaching
Size
According to a study that measured tendon length against the size of the injured rotator cuff, researchers learned that as rotator cuff tendons decrease in length, the average rotator cuff tear severity is proportionally decreased, as well This shows that larger individuals are more likely to suffer from a severe rotator cuff tear if they do not tighten the shoulder muscles around the joint.
Position :
Another study observed 12 different positions of movements and their relative correlation with injuries that occurred during those movements. The evidence shows that putting the arm in a neutral position relieves tension on all ligaments and tendons.
Stretching Exercise :
One article observed the influence of stretching techniques on preventative methods of shoulder injuries. Increased velocity of exercise increases injury, but beginning a fast-movement exercise with a slow stretch may cause muscle/tendon attachment to become more resistant to tearing.
Muscle groups :
When exercising, exercising the shoulder as a whole and not one or two muscle groups is also found to be imperative. When the shoulder muscle is exercised in all directions, such as external rotation, flexion, extension, or vertical abduction, it is less likely to suffer from a tear of the tendon.
Physiotherapy Treatment :
Physiotherapy treatments are pain relieving Electrotherapy modalities such as Interferential Therapy (IFT), TENS, and Ultrasound Therapy are used to relieve pain, and spasms of muscles.
Initially, isometric shoulder exercise and gradual Range of motion exercises are started as your pain and symptoms are relieved.
The pendulum swing is a good exercise to start with.
- Overhead stretch
- Posterior stretching
- Up-the-back stretch
- Wall climbing to the side
- Wall climbing to the front
Strengthening exercises
Start these exercises only after your doctor says it’s okay. Usually, these exercises are started slowly, as soon as you can do the stretching without pain. But most people wait 6 to 8 weeks after surgery to do these exercises and others like them.
For any strengthening exercises where your arms start at or stretch from your sides, the motion should be on a diagonal. That means the motion should be about 30 degrees to the front of where your arms would be if you raised them straight out to the side.
The list below links to strengthening exercises with pictures and instructions.
- Arm raises to the side
- External rotator
- Internal rotator
- Shoulder flexor and extensor
Scapular strengthening exercises :
- The shoulder blade (scapula) is one of the main bones of the shoulder joint. It helps to keep the shoulder stable and move well. If the scapula doesn’t move well, it puts a lot of pressure on the rotator cuff and related muscles, which can cause strain. Also, if the scapula is not moving well, you have a higher chance that one of the tendons will be squeezed and rubbed against the bone. This is called impingement.
These exercises can help you keep or improve strength around the shoulder blade. They also can help your rotator cuff work as it should.
The list below links to scapular strengthening exercises with pictures and instructions.
- Scapula protraction with arm reach
- Scapula protraction with wall push-ups
- Scapula retraction
Weightlifting physical therapy exercise :
Those suspected of having a rotator cuff tear are potential candidates for either operative or non-operative treatment. However, any individual may move from one group to the other based on clinical response and findings on repeated examination.
No evidence of benefit is seen from early rather than delayed surgery, and many with partial tears and some with complete tears will respond to nonoperative management. Consequently, many recommend initial, nonsurgical management. However, early surgical treatment may be considered insignificant (>1 cm-1.5 cm) acute tears or in young patients with full-thickness tears who have a significant risk for the development of irreparable rotator cuff changes.
Finally, a review of more than 150 published papers in 2010 concluded that no solid evidence indicated rotator-cuff surgery benefited patients more than nonoperative management, adding to management and treatment controversies.
Non-operative treatment :
Ice pack :
Those with pain but reasonably maintained function are suitable for nonoperative management. This includes oral medications that provide pain relief such as anti-inflammatory agents, topical pain relievers such as cold packs, and if warranted, subacromial corticosteroid/local anesthetic injection.
An alternative to injection is iontophoresis, a battery-powered patch that “drives” the medication to the target tissue. A sling may be offered for short-term comfort, with the understanding that undesirable shoulder stiffness can develop with prolonged immobilization. Early physical therapy may afford pain relief with modalities (e.g. iontophoresis) and help to maintain motion. Ultrasound treatment is not efficacious. As pain decreases, strength deficiencies and biomechanical errors can be corrected.
A conservative physical therapy program begins with preliminary rest and restriction from engaging in activities that gave rise to symptoms. Normally, inflammation can usually be controlled within one to two weeks, using a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and subacromial steroid injections to decrease inflammation, to the point that pain has been significantly decreased to make stretching tolerable. After this short period, rapid stiffening and an increase in pain can result if sufficient stretching has not been implemented.
A gentle, passive range-of-motion program should be started to help prevent stiffness and maintain range of motion during this resting period. Exercises, for the anterior, inferior, and posterior shoulder, should be part of this program.
Codman exercises (giant, pudding-stirring), to “permit the patient to abduct the arm by gravity, the supraspinatus remains relaxed, and no fulcrum is required” are widely used.
The use of NSAIDs, hot and cold packs, and physical therapy modalities, such as ultrasound, phonophoresis, or iontophoresis, can be instituted during this stretching period, if effective.
Corticosteroid injections are recommended two to three months apart with a maximum of three injections. Multiple injections (four or more) have been shown to compromise the results of rotator cuff surgery which result in weakening of the tendon. However, before any rotator cuff strengthening can be started, the shoulder must have a full range of motion.
After a full, painless range of motion is achieved, the patient may advance to a gentle strengthening program. Rockwood coined the term orthotherapy to describe this program which is aimed at creating an exercise regimen that initially gently improves motion, then gradually improves strength in the shoulder girdle. Each patient is given a home therapy kit, which includes elastic bands of six different colors and strengths, a pulley set, and a three-piece, one-meter-long stick. The program is customized, fitting the needs of the individual, and altering when necessary. Participants are asked to use their exercise program whether at home, work, or traveling.
Several instances occur in which nonoperative treatment would not be suggested:
20 to 30-year-old active patient with an acute tear and severe functional deficit from a specific event
30 to 50-year-old patient with an acute rotator cuff tear secondary to a specific event
a highly competitive athlete who is primarily involved in overhead or throwing sports
These patients may need to be treated operatively because rotator cuff repair is necessary for the restoration of the normal strength required to return to the preoperative, competitive level of function. Finally, those who do not respond to, or are unsatisfied with, conservative treatment should seek a surgical opinion.
Surgery :
The three general surgical approaches are arthroscopic, mini-open, and open-surgical repair. In the recent past, small tears were treated arthroscopically, while larger tears would usually require an open procedure. Advances in arthroscopy now allow arthroscopic repair of even the largest tears, and arthroscopic techniques are now required to mobilize many retracted tears. The results match open surgical techniques, while permitting a more thorough evaluation of the shoulder at the time of surgery, increasing the diagnostic value of the procedure, as other conditions may simultaneously cause shoulder pain. Arthroscopic surgery also allows for shorter recovery time although significant differences in postoperative pain or pain medication use apparently are not seen between arthroscopic- and open-surgical patients.
Even for full-thickness rotator cuff tears, conservative care (i.e., nonsurgical treatment) outcomes are usually reasonably good. However, many patients still suffer disability and pain despite nonsurgical therapies. For massive tears of the rotator cuff, surgery has shown durable outcomes on 10-year follow-ups. However, the same study demonstrated ongoing and progressive fatty atrophy and repeat tears of the rotator cuff. MRI evidence of fatty atrophy in the rotator cuff prior to surgery is predictive of a poor surgical outcome. If the rotator cuff is completely torn, surgery is usually required to reattach the tendon to the bone.
If a significant bone spur is present, any of the approaches may include an acromioplasty, or a subacromial decompression, as part of the procedure. Subacromial decompression, the removal of a small portion of the acromion that overlies the rotator cuff, aims to relieve pressure on the rotator cuff in certain conditions and promote healing and recovery. Although subacromial decompression may be beneficial in the management of partial and full-thickness tear repair, it does not repair the tear itself and arthroscopic decompression has more recently been combined with “mini-open” repair of the rotator cuff, allowing for the repair of the cuff without disruption of the deltoid origin. The results of decompression alone tend to degrade with time, but the combination of repair and decompression appears to be more enduring.
Repair of a complete, full-thickness tear involves tissue suture. The method currently in favor is to place an anchor in the bone at the natural attachment site, with a resuture of the torn tendon to the anchor. If the tissue quality is poor, mesh (collagen, Artelon, or other degradable material) may be used to reinforce the repair. The repair can be performed through an open incision, again requiring detachment of a portion of the deltoid, while a mini-open technique approaches the tear through a deltoid-splitting approach. The latter may cause less injury to muscles and produce better results. Contemporary techniques now use an all-arthroscopic approach. Recovery can take as long as three–six months, with a sling being worn for the first one–six weeks.
In a small minority of cases where extensive arthritis has developed, an option is shoulder joint replacement (arthroplasty).
Rehabilitation :
Rehabilitation after surgery consists of three stages. First, the arm is immobilized so that the muscle can heal. Second, when appropriate, a therapist assists with passive exercises to regain range of motion. Third, the arm is gradually exercised actively, with the goal of regaining and enhancing strength.
Yoshitsugu Takeda and his team have recently studied rotator cuff injuries and rehab exercises that target the supraspinatus. As mentioned earlier, the supraspinatus muscle is the muscle and tendon within the rotator cuff that is most often injured. In order to rehab the supraspinatus and combat future injuries in the rotator cuff, Takeda’s team has concluded that the empty can and full can exercises are most effective at isolating and strengthening the supraspinatus.
Following arthroscopic rotator-cuff repair surgery, patients undergo rehabilitation to regain shoulder function. Orthopaedic surgeons stress that physical therapy is crucial to healing. Exercises decrease shoulder pain, strengthen the joint, and improves the arm’s range of motion. Therapists, in conjunction with the surgeon, design workout regimens in accordance with individuals’ needs and risk factors.
Traditionally, patients have been advised to immobilize their shoulders for six weeks before doing rehabilitation. However, the appropriate timing and intensity of therapy are subject to debate. Regardless, most surgeons advocate to remain in the sling for at least six weeks. Some authorities advocate early, aggressive rehab. They favor the use of passive motion, which allows a patient to move the shoulder without physical effort. Alternatively, some authorities argue that therapy should be started later and carried out more cautiously. Theoretically, that gives tissues time to heal; though there is conflicting data regarding the benefits of early immobilization. A study of rats suggested that it improved the strength of surgical repairs, while research on rabbits produced contrary evidence. Patients, especially those recovering from large rotator cuff tears, are prone to developing new tears. Rehabbing too soon or too strenuously might increase the risk of retear or failure to heal. However, no research has proven a link between early therapy and the incidence of re-tears. In some studies, patients who received earlier and more aggressive therapy reported reduced shoulder pain, less stiffness, and better range of motion.[56] Other research has shown that accelerated rehab results in better shoulder function. Ross et al. note that, despite the findings, “no definitive consensus exists supporting a clinical difference” between the two methods of rehab.
There is consensus amongst orthopaedic surgeons and physical therapists regarding rotator cuff repair rehabilitation protocols. The timing and duration of treatments and exercises are based on biologic and biomedical factors involving the rotator cuff. For approximately two to three weeks following surgery, a patient experiences shoulder pain and swelling; no major therapeutic measures are instituted in this window other than oral pain medicine and ice. All in all, those patients at risk of failure, should undergo a more conservative approach to rehabilitation.
That is followed by the “proliferative” and “maturation and remodeling” phases of healing, which ensues for the following six to ten weeks. The effect of active or passive motion during any of the phases is unclear, due to conflicting information and a shortage of clinical evidence. Gentle physical therapy-guided motion is instituted at this phase, only to prevent stiffness of the shoulder; the rotator cuff remains fragile. At three months after surgery, physical therapy intervention changes substantially to focus on scapular mobilization and stretching of the glenohumeral joint. Once full passive motion is regained (at usually about four to four and a half months after surgery) strengthening exercises are the focus. The strengthening focuses on the rotator cuff and the upper back/scapular stabilizers. Typically at about six months after surgery, most patients have made a majority of the gains.
The objective of repairing a rotator cuff is to enable the patient to regain full function. Surgeons and therapists analyze outcomes in several ways. Based on their examinations of patients, they compile scores on tests; some examples are those created by the University of California at Los Angeles and the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons. Other outcome measures include the Constant score; the Simple Shoulder Test; and the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand score. The tests assess a patient’s range of motion and the degree of shoulder function.
Due to the conflicting information about the relative benefits of rehab conducted early or later, an individualized approach is necessary. The timing and nature of therapeutic activities are adjusted according to patients’ ages, the tissue integrity of their rotator cuff repairs, and other factors. Special considerations are appropriate for those who have suffered multiple tears.
Prognosis :
While people with rotator cuff tears may not have any noticeable symptoms, studies have shown that over time 40% will have enlargement of the tear over a five-year period. Of those whose tears enlarge, 20% have no symptoms while 80% eventually develop symptoms.
There is no irrefutable evidence that rotator cuff surgery benefits patients more than non-surgical management and a percentage of patients never regain full range of motion after surgery.
Epidemiological studies strongly support a relationship between age and cuff tear prevalence. In a recent study, the frequency of such tears increased from 13% in the youngest group (aged 50–59 y) to 20% (aged 60–69 y), 31% (aged 70–79 y), and 51% in the oldest group (aged 80–89 y). This high rate of tear prevalence in asymptomatic individuals suggests that rotator cuff tears could be considered a “normal” process of aging rather than a result of an apparent pathological process.
Complications :
Patients usually regain function in their shoulders, and experience less pain, following surgery. For some, however, the joint continues to hurt. Weakness and a limited range of motion also may persist. Those who report such symptoms frequently are diagnosed with failed rotator cuff syndrome.




11 Comments