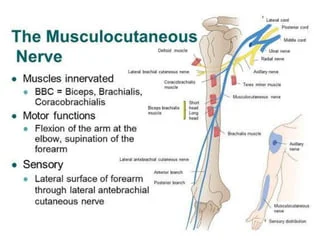
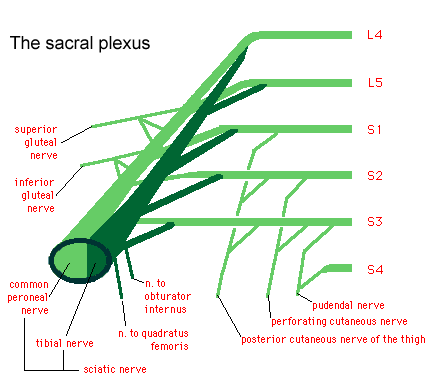
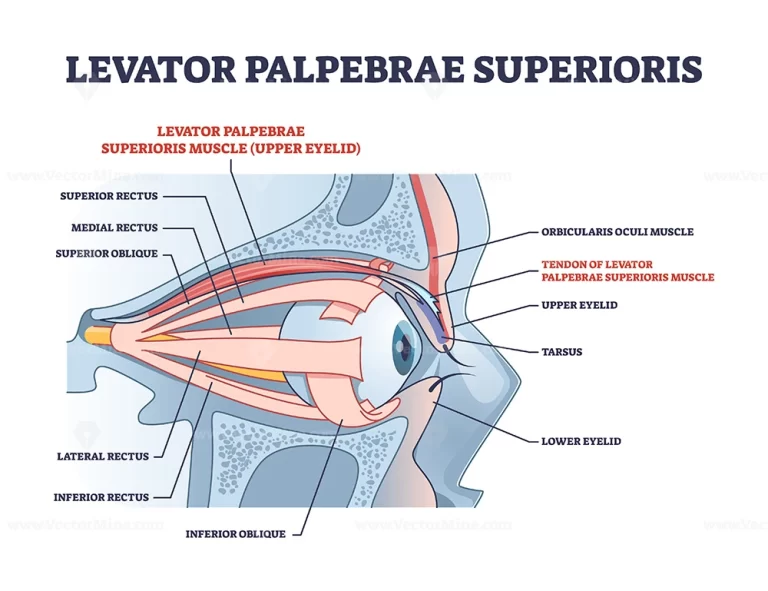
Manual Physical Therapist
Description Manual therapy, or manipulative therapy, is a physical treatment primarily used by physical therapists, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists to treat musculoskeletal pain and disability; it mostly includes kneading and manipulation of muscles, joint mobilization, and joint manipulation. It could also be used by Rolfers, massage therapists, athletic trainers, osteopaths, and physicians. Manual therapy has…